In ancient times, the dead were buried with their living and non-living things. The offerings placed as dead gifts varied according to cultures.
Dead presents were put in certain cultures to assist the deceased in his next life, while in others, they were placed so that he would wake up with the things he loved when he was reborn so that he would not feel lonely.
When the dead gifts were examined, they showed differences according to the gender of the deceased, the job he did, and the social and economic status of the person.
Mostly, the dead gifts consisted of jewelry such as necklaces, bracelets, rings, earrings, idols, items used in life, weapons and hunting equipment, and precious metal parts, albeit a little.
The tomb of the Urartu revealed the firsts
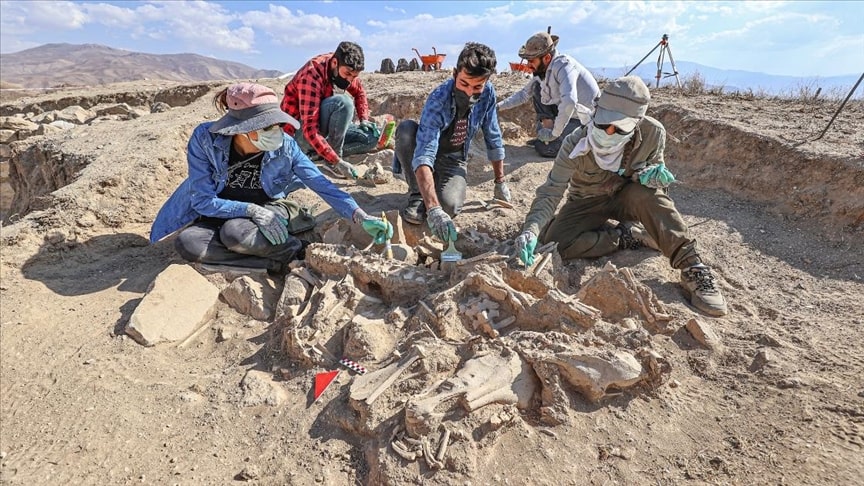
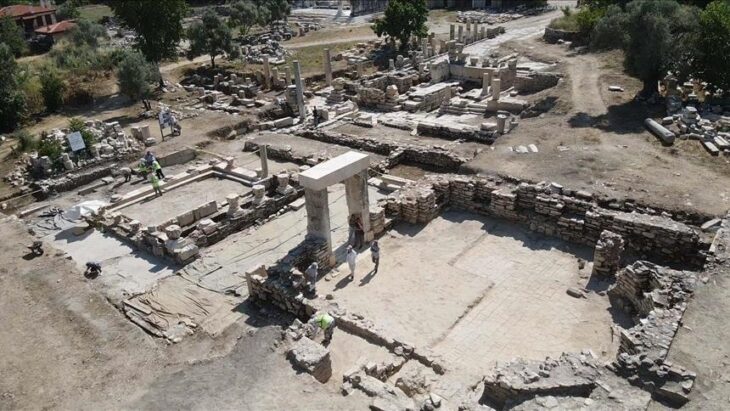
Interesting dead gifts were found in the tomb of the Urartians, which were unearthed during the excavations in the Çavuştepe Castle in the Gürpınar district of Van and the necropolis in the northern part.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
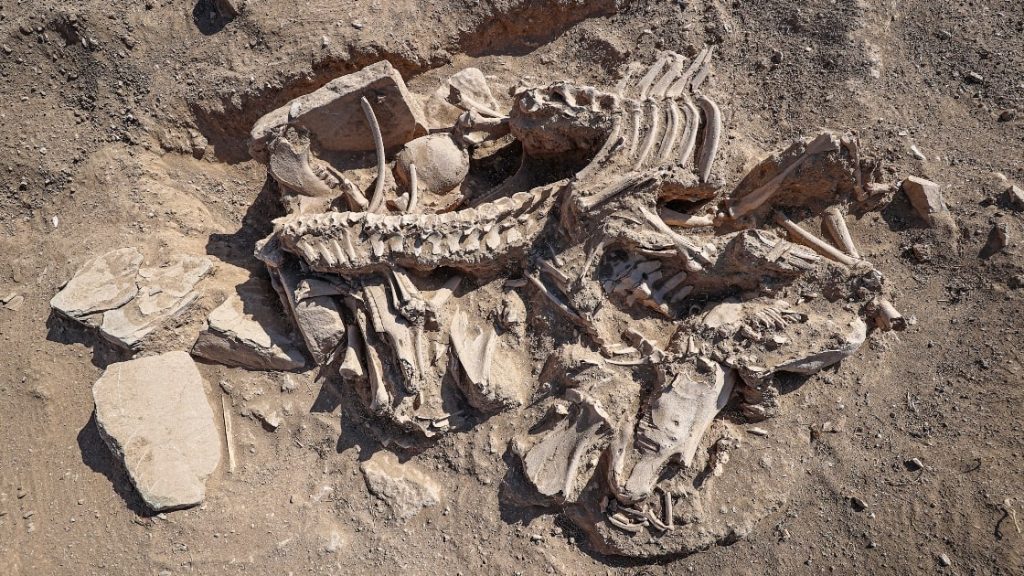
It was observed that 4 horses, cattle, and small ruminants were buried in the tomb discovered in the Çavuştepe Castle and the necropolis area in the northern part, which provides information about burial and offering materials from the Urartian period.

Professor Rafet Çavuşoğlu, Head of the Archeology Department at Yüzüncü Yıl University, who was the head of the excavation, told Anadolu Agency (AA) correspondent Mesut Varol about the find.
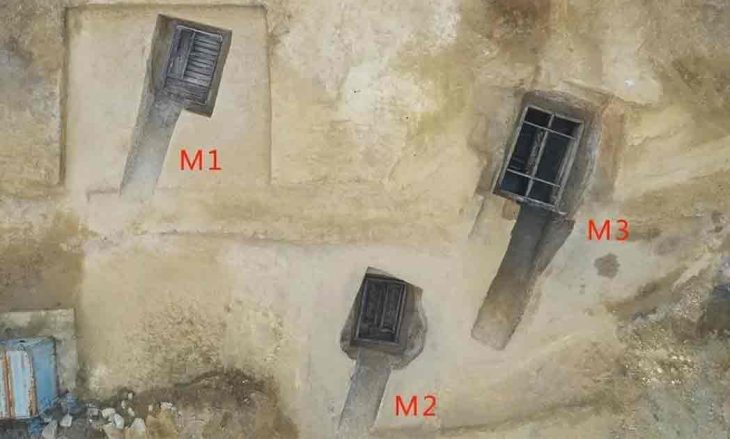
“This place has always brought firsts about the Urartian burial tradition. Today, we are faced with one of those firsts. In the studies we carried out with our expert team, we encountered an in-situ (as it was first placed) tomb. We saw a human being buried with 4 horses, cattle, and small cattle. Pieces of pottery were found right next to it. Here we encountered an oil lamp with chamber that we have never seen before. It also gives important clues about lighting.” he said.
Stating that the newly found area excited the excavation team, Çavuşoğlu said, “The burial and in-situ condition of a human being with his horses is a situation we encounter for the first time. Our work continues. We will reveal the extent of his nobility in the coming days. It shows that the person buried with his four horses was someone important. We think he’s a ruling-class or military high-ranking person who has a relationship with horses.” made its assessment.
An unprecedented find in the Urartian burial tradition
Associate Professor Hakan Yılmaz, Faculty Member of the Department of Archeology, said, “We came across an interesting find this year. It’s interesting that the person was buried with his horses. There are 4 horses. The skulls of the two horses are intact. The other both have lower jaws. There are human skulls and bones right next to the tomb. Next to them are cattle bones. We understand that the individual is buried with his animals. It is the first find I have ever come across in the Urartian burial tradition. This tomb belongs to an important person. It’s something that surprises us. We will analyze the bones in the laboratory.” said.

High-quality pottery fragments found in the tomb
Associate Professor of Archeology. Dr. Hanifi Biber, on the other hand, stated that they are faced with a different burial custom here and gave the following information:
“It is the pottery shards next to the tomb that caught my attention. High quality. There are very high-quality ceramics in the Van Museum, this is similar to them. It is very small and looks like a trefoil jug. The tomb has not been fully opened yet, other finds may come. Therefore, it shows that he is not an ordinary person, both with his horses and with the quality of the ceramics, and that he has a high probability of becoming an executive.”
Archaeologists excavating at Çavuştepe Castle in 2019 discovered a cemetery belonging to Urartian royals from the 9th century. The burial site, which measures 50 square meters (538 square feet), is believed to be the final resting place of the Urartian aristocracy.
Van, considered the pearl of Anatolia, has been home to various civilizations for millennia due to its position. In the 9th century B.C., the Urartians, who are thought to have originated in Central Asia, controlled the region for 247 years.
The Urartian kingdom mysteriously disappeared in the 6th century B.C. but was rediscovered as a distinct ancient culture by excavations, carried out in the 19th century.