A recent archaeological discovery near Jerusalem has challenged long-held beliefs about ascetic practices in the Byzantine era, revealing the remains of a woman in a burial typically associated with male ascetics, thus prompting a reevaluation of women’s roles in extreme religious traditions of the 5th-century AD.
The remains initially believed to belong to an ascetic monk, bound in “chains,” were subjected to scientific analysis by researchers who examined the proteins in the tooth enamel. Their findings suggest that the tomb, dating to the 5th century AD, likely contained a woman who engaged in self-torment through the use of iron chains. This significant discovery, published in the Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, raises important questions regarding the role of women in extreme ascetic practices during the Byzantine era.
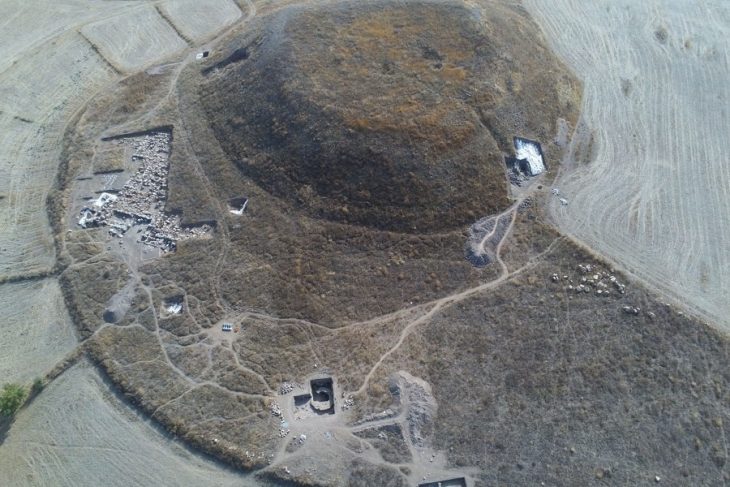
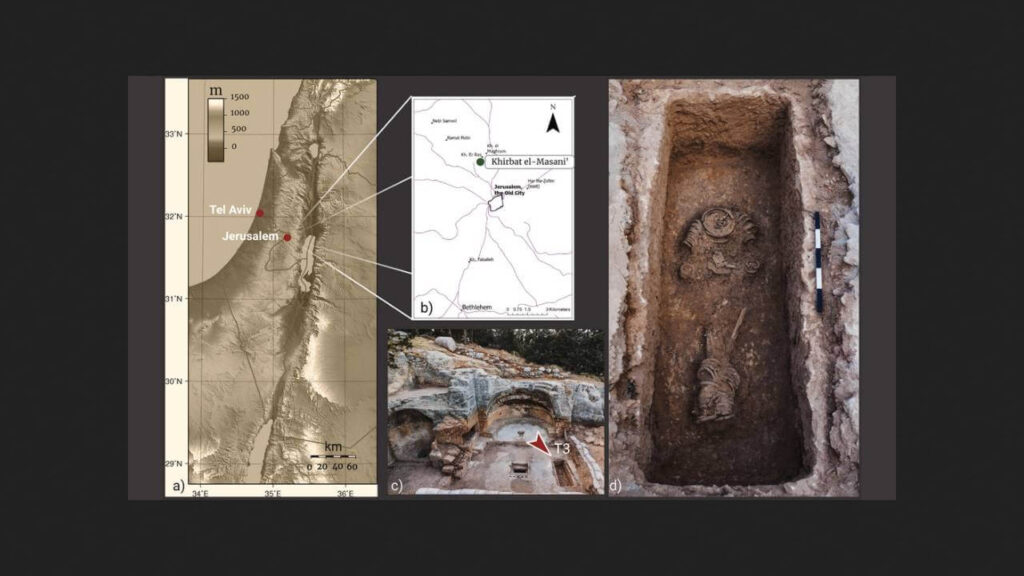
In East Jerusalem, just a few kilometers from the Old City, archaeologists have made a significant discovery at the site of Khirbat el-Masani, where the remains of a Byzantine monastery dating from 350 to 650 CE have been uncovered.
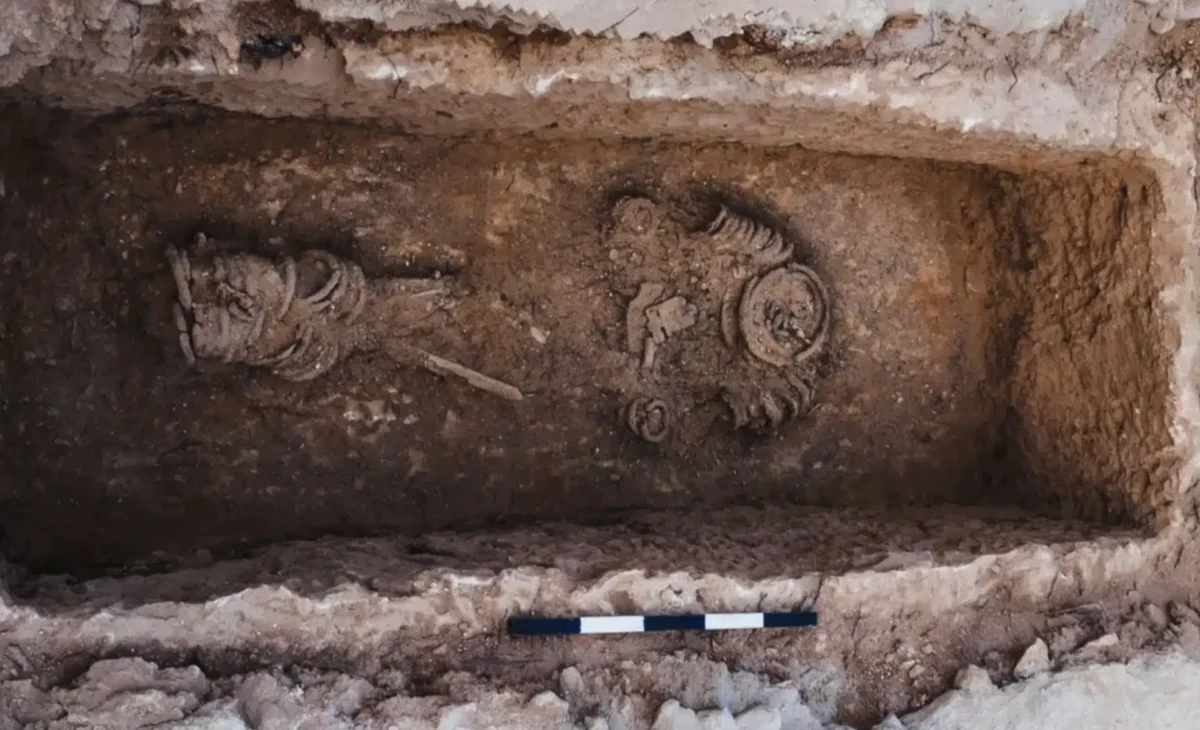
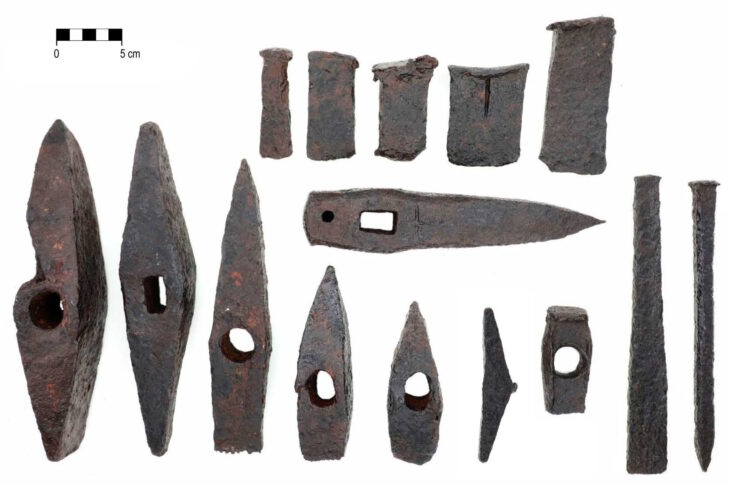
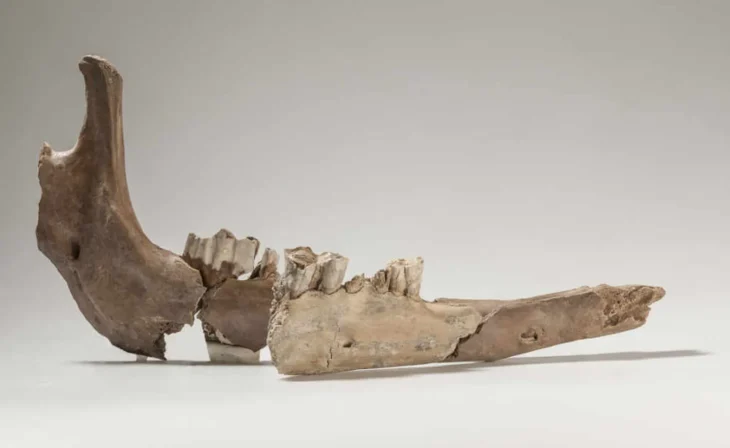
Recent excavations revealed several burials believed to date back to the 5th century CE. Among these, researchers found the poorly preserved remains of a man buried in chains—heavy iron objects typically worn by ascetic monks to restrain the flesh. Notably, instead of a traditional burial, scientists discovered numerous large metal rings in place of the man’s neck, arms, and legs, with diameters reaching approximately ten centimeters and a total weight of several dozen kilograms.
The skeleton of the ascetic monk has survived in a highly fragmentary state, with the few preserved bones crumbling upon contact. Despite this, Paula Kotli from the Weizmann Institute of Science, along with her Israeli colleagues, conducted a thorough study of the remains. Their analysis of three preserved cervical vertebrae and one tooth allowed them to determine that the burial belonged to an adult, likely aged between 30 and 60 years at the time of death.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
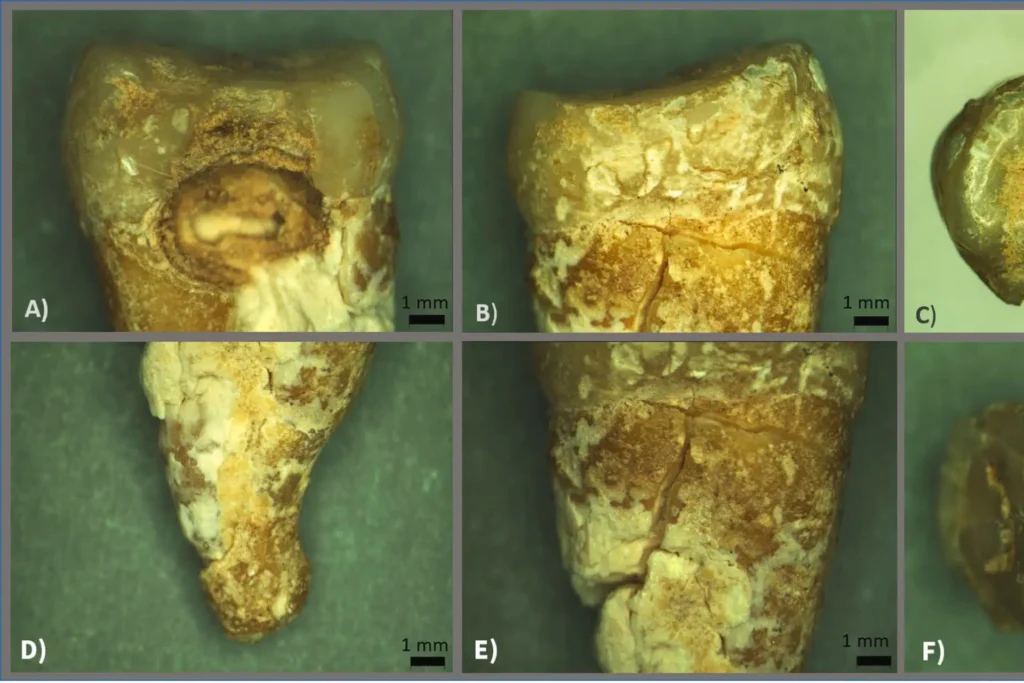
To determine the sex of the individual, scientists employed peptide analysis on the enamel of the only remaining tooth, specifically the second premolar of the upper jaw. Their findings revealed an absence of peptides associated with the AMELY protein, which is encoded by a gene located on the Y chromosome. In contrast, they identified a significant presence of peptides corresponding to the AMELX protein, linked to a gene on the X chromosome.
This compelling evidence led researchers to conclude that the tomb from the late antique period likely contained the remains of a woman, challenging previous assumptions about the burial’s association with male asceticism. This discovery not only sheds light on the individual’s identity but also raises important questions about the roles of women in ascetic practices during the Byzantine era, suggesting that women may have engaged in similar extreme religious behaviors as their male counterparts.
According to the researchers, historical records indicate that women in the Roman Empire began practicing asceticism as early as the 4th century AD. Notable figures, such as Melania the Elder, a Christian saint from a wealthy noble family, and her granddaughter, Melania the Roman, exemplified this trend by embracing self-restraint to achieve spiritual goals.
However, the burial under investigation in the scientists’ new article is particularly significant, as it represents the first archaeological evidence that women, alongside men, engaged in self-torture through the use of heavy chains in Byzantine society during that period. This finding not only highlights the presence of female ascetics but also challenges traditional narratives surrounding ascetic practices, emphasizing the active role women played in these extreme religious behaviors.
The monastery where the tomb was discovered was strategically positioned along the Christian pilgrimage route to Jerusalem, a city that blossomed into a major religious hub during the Byzantine period, drawing worshipers from all corners of the Roman Empire. These monasteries were not merely spiritual sanctuaries; they also provided refuge for weary pilgrims seeking solace and guidance. In this vibrant context, the presence of a female ascetic challenges conventional perceptions and suggests that women may have played a far more active and rigorous role in these communities than previously acknowledged.
Paula Kotli, David Morgenstern, Yossi Nagaret, Corine Katina, Zubair ’Adawi, Kfir Arbiv, Elisabetta Boaretto, Sexing remains of a Byzantine ascetic burial using enamel proteomics. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, Volume 62, April 2025, 104972. doi.org/10.1016/j.jasrep.2025.104972
Cover Image Credit: Paula Kotli / Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports