Archaeologists from Oregon State University have discovered projectile points in Idaho that are thousands of years older than any that have previously been discovered in the Americas.
This discovery has helped to fill in the history of how early humans made and used stone weapons.
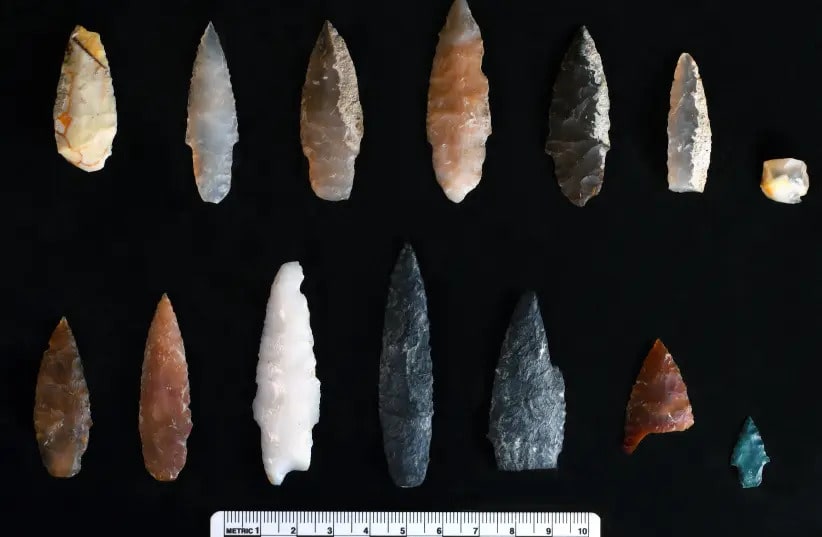
At the Cooper’s Ferry site along the Salmon River in present-day Idaho, the researchers discovered 13 complete and numerous fragmentary projectile points. They are 3,000 years older than the Clovis fluted points found across North America and 2,300 years older than the points previously discovered at the same location.
The 13 full and fragmentary projectile points, razor-sharp and ranging from about half an inch to 2 inches long, are from roughly 15,700 years ago, according to carbon-14 dating.
The findings were published in the journal Science Advances.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

“From a scientific point of view, these discoveries add very important details about what the archaeological record of the earliest peoples of the Americas looks like,” said Loren Davis, an anthropology professor at OSU and head of the group that found the points. “It’s one thing to say, ‘We think that people were here in the Americas 16,000 years ago;’ it’s another thing to measure it by finding well-made artifacts they left behind.”
The points are revelatory not just in their age, but in their similarity to projectile points found in Hokkaido, Japan, dating to 16,000-20,000 years ago. Their presence in Idaho adds more detail to the hypothesis that there are early genetic and cultural connections between the ice age peoples of Northeast Asia and North America.
Davis said: “The earliest peoples of North America possessed cultural knowledge that they used to survive and thrive over time. Some of this knowledge can be seen in the way people made stone tools, such as the projectile points found at the Cooper’s Ferry site.”

“By comparing these points with other sites of the same age and older, we can infer the spatial extents of social networks where this technological knowledge was shared between peoples,” added Davis.
These slender projectile points are characterized by two distinct ends, one sharpened and one stemmed, as well as a symmetrical beveled shape if looked at head-on. They were likely attached to darts, rather than arrows or spears, and despite the small size, they were deadly weapons, Davis said.
“There’s an assumption that early projectile points had to be big to kill large game; however, smaller projectile points mounted on darts will penetrate deeply and cause tremendous internal damage,” he said. “You can hunt any animal we know about with weapons like these.”
These discoveries add to the emerging picture of early human life in the Pacific Northwest, Davis said. “Finding a site where people made pits and stored complete and broken projectile points nearly 16,000 years ago gives us valuable details about the lives of our region’s earliest inhabitants.”
The Salmon River site where the points were found is on traditional Nez Perce land, known to the tribe as the ancient village of Nipéhe. The land is currently held in public ownership by the federal Bureau of Land Management.
The recently discovered pits are a part of the larger Cooper’s Ferry record, which also includes a fire pit that dates back 14,200 years and a food-processing area with the remains of an extinct horse, both of which were previously reported by Davis and colleagues. In total, they found and mapped more than 65,000 items, recording their locations to the millimeter for precise documentation.