Stunning new reconstructions have revealed how Scotland’s largest known Pictish fort may have looked over one thousand years ago.
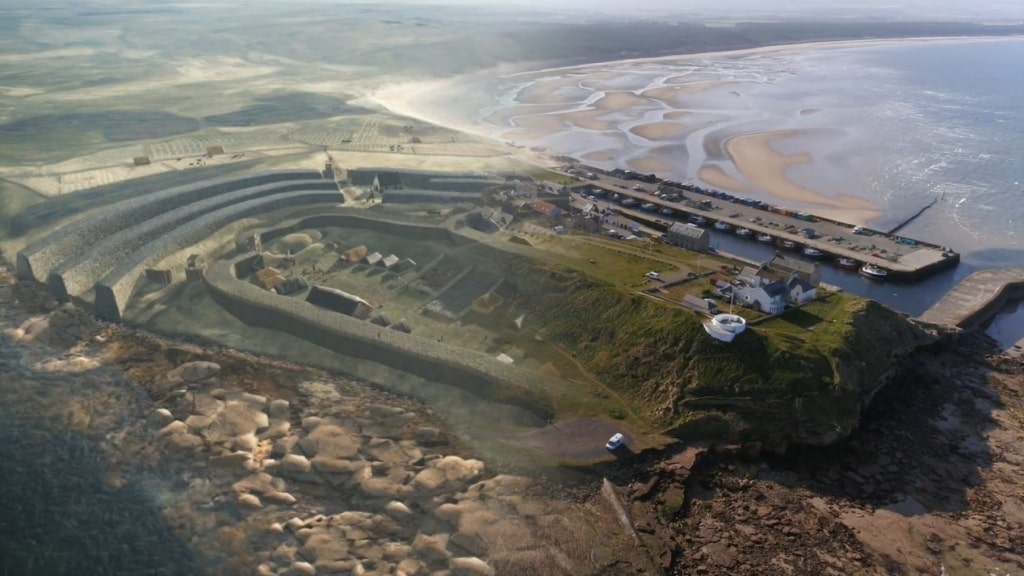
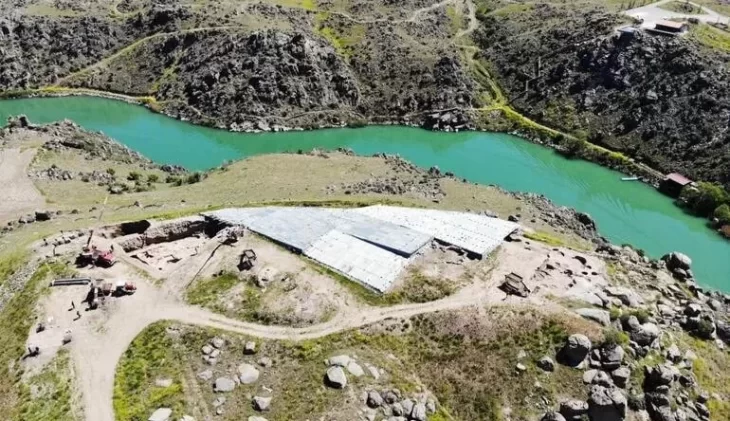
Three-dimensional images of Burghead in Moray have been created based on archaeological excavations by the University of Aberdeen.
Funded by Historic Environment Scotland as part of a wider video project to enable the public to learn more about Scotland’s Pictish past, the images showcase the enormous defensive ramparts, which were once thought to be eight metres thick and six metres high, as well as dwellings within the fort.
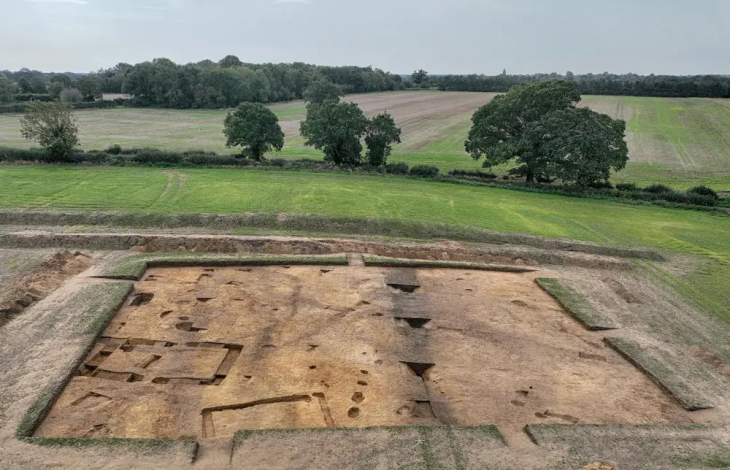
It has long been known that Burghead was home to a Pictish settlement but it was thought that the 19th-century development of the modern town had eroded most traces of this important period of its history.
The landward ramparts were levelled and part of the seaward defences was destroyed in order to build the modern harbour.
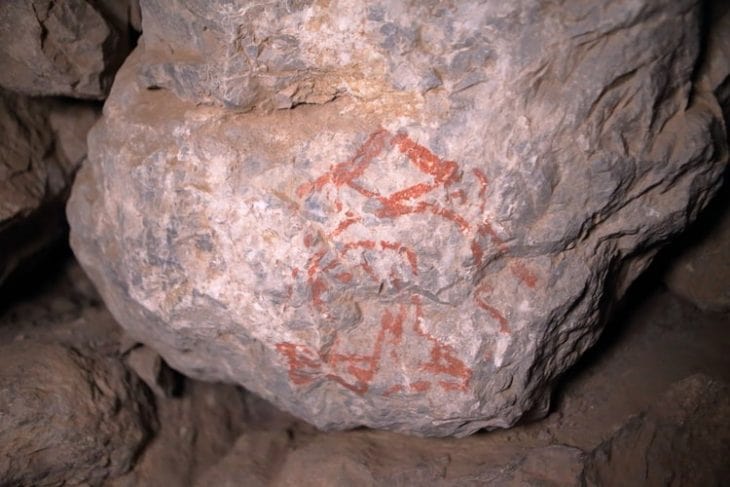
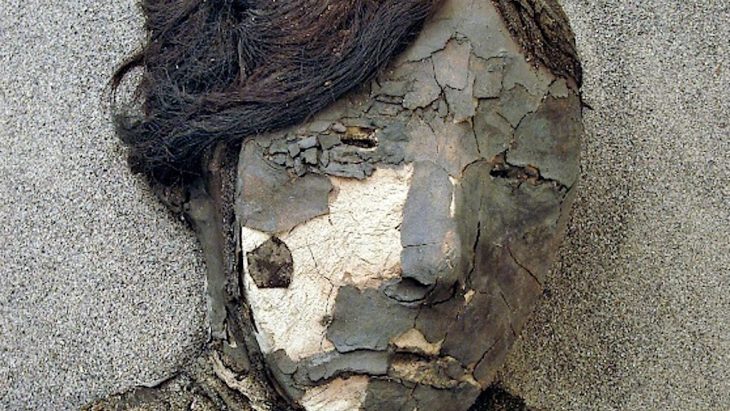
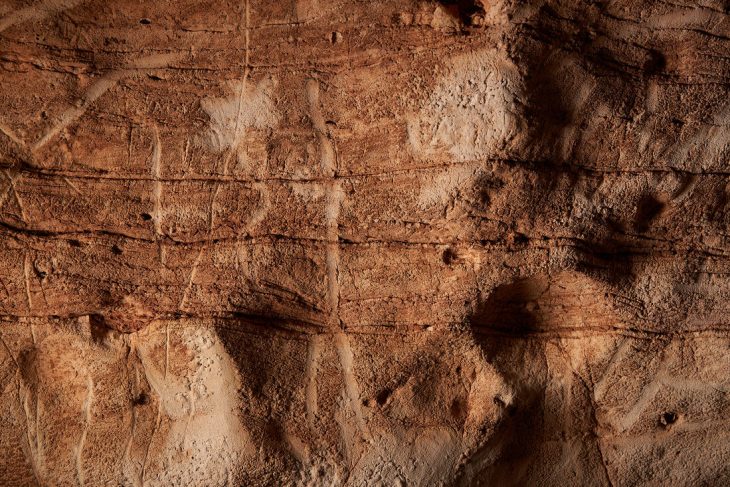
More than 30 Pictish carved stones were discovered during this destruction of the fort but just six carved bulls have survived along with a number of fragments of early Christian sculpture. When University of Aberdeen archaeologists first began excavations there in 2015, they expected little to have survived such extensive building work close by.
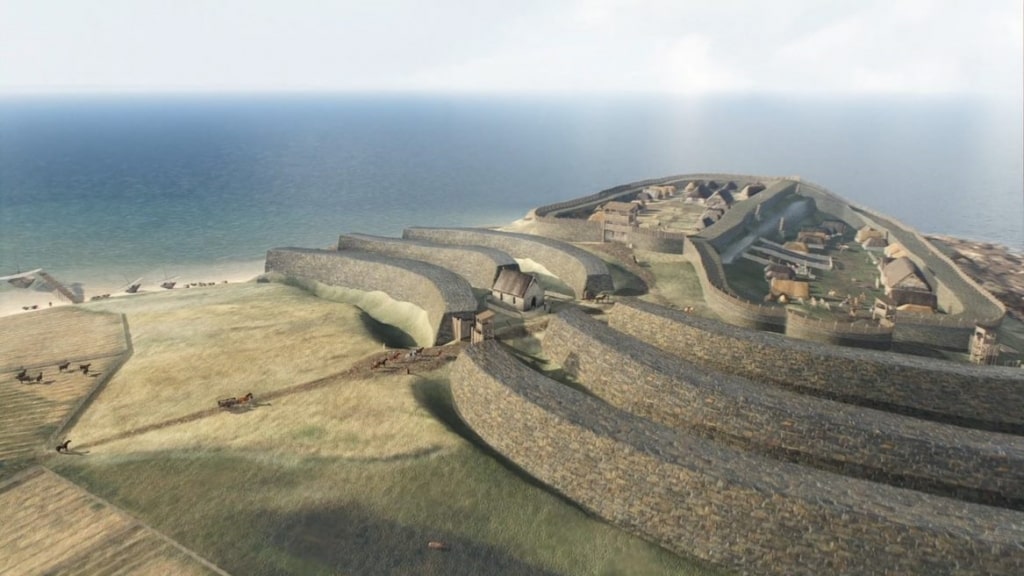

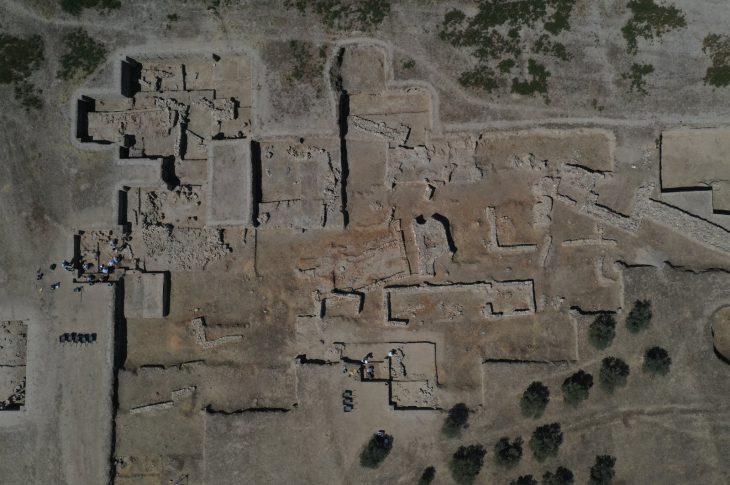
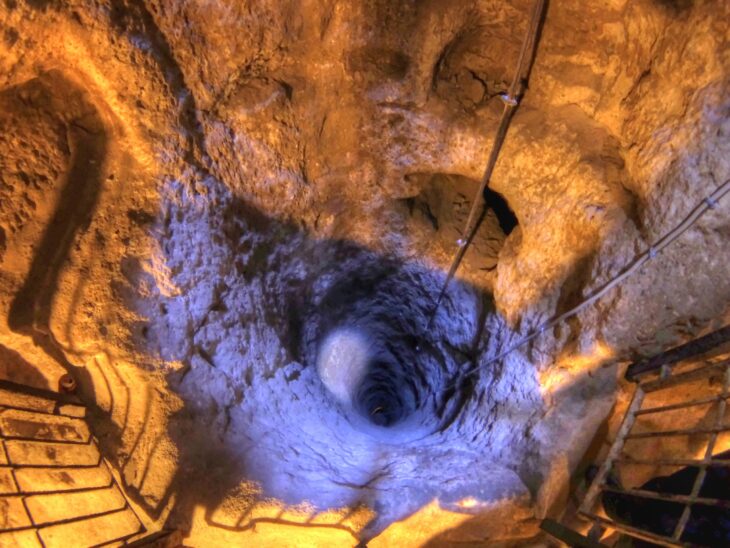
But over the last five years, a very different picture has emerged and the digs, led by the University’s Professor Gordon Noble, and funded by both Historic Environment Scotland and the Leverhulme Trust, have yielded some of the most significant Pictish items and building remains ever uncovered.
It is this work that has enabled such a detailed reconstruction of how the site may have looked.
Stunning new reconstructions have revealed how Scotland’s largest known Pictish fort may have looked over one thousand years ago.
Three-dimensional images of Burghead in Moray have been created based on archaeological excavations by the University of Aberdeen.
Funded by Historic Environment Scotland as part of a wider video project to enable the public to learn more about Scotland’s Pictish past, the images showcase the enormous defensive ramparts, which were once thought to be eight metres thick and six metres high, as well as dwellings within the fort.
It has long been known that Burghead was home to a Pictish settlement but it was thought that the 19th century development of the modern town had eroded most traces of this important period of its history.
The landward ramparts were levelled and part of the seaward defences was destroyed in order to build the modern harbour.
More than 30 Pictish carved stones were discovered during this destruction of the fort but just six carved bulls have survived along with a number of fragments of early Christian sculpture. When University of Aberdeen archaeologists first began excavations there in 2015, they expected little to have survived such extensive building work close by.
But over the last five years, a very different picture has emerged and the digs, led by the University’s Professor Gordon Noble, and funded by both Historic Environment Scotland and the Leverhulme Trust, have yielded some of the most significant Pictish items and building remains ever uncovered.
It is this work which has enabled such a detailed reconstruction of how the site may have looked.