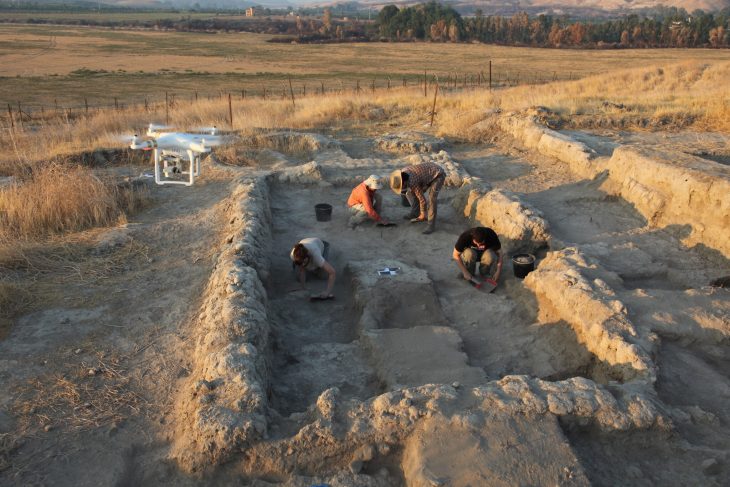
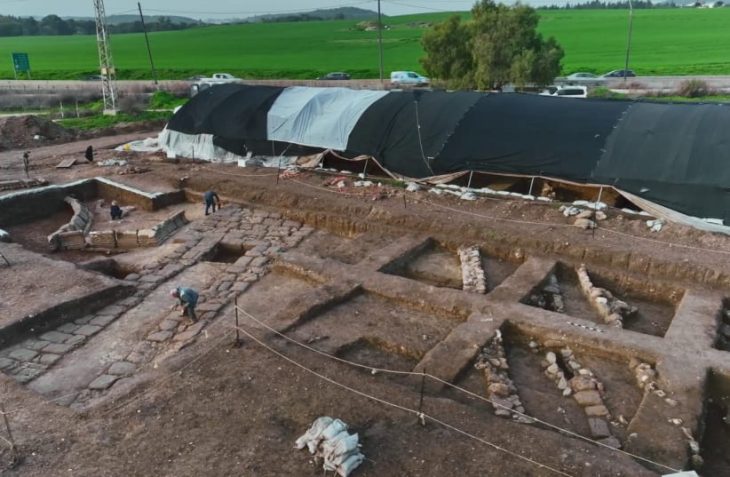
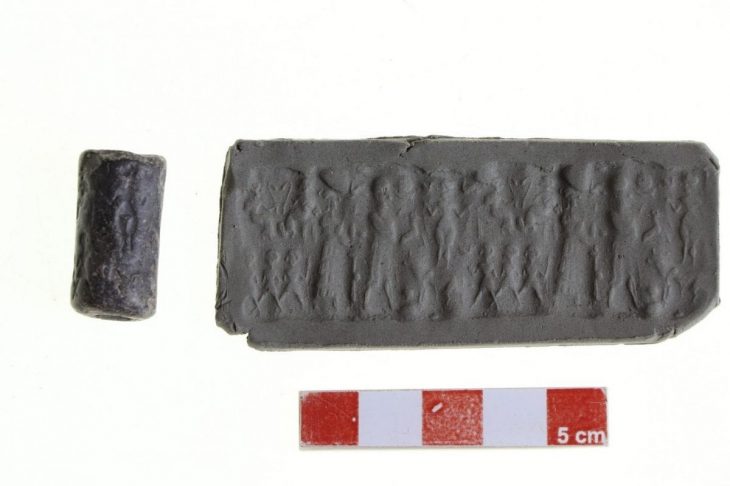
In the 2022 excavations of Tepebag Mound, located around Taşköprü, the center of Adana province in Turkey’s Mediterranean Region, a 3800-year-old cylinder seal was found.
It is thought that the mound was located in the same place as “Uru Adaniya”, one of the most important cities of the Cilicia region, mentioned in Hittite written sources.
The first find of the 2022 excavation season of the Tepebağ Mound excavations, which started in 2013 under the scientific consultancy of Osmaniye Korkut Ata University Associate Professor İrfan Tuğcu, under the presidency of Adana Museum Directorate, was a 3800-year-old cylinder seal.
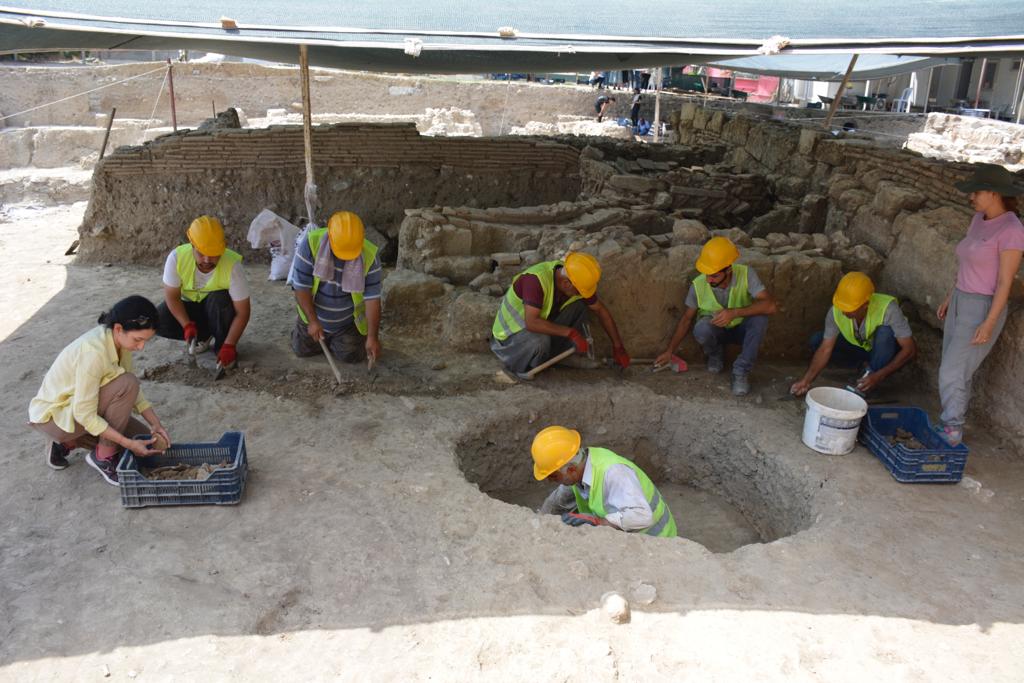

The news of the discovery of the seal was posted on the social media account of the Department of Excavations and Research: “The early period city history of Adana (Adania) is lighting up. A 3800-year-old cylinder seal from the 2022 excavations at Tepebag Mound,” announced as.
In previous excavations at Tepebağ Mound, which was on important trade routes in ancient times, the remains of an Assyrian palace dating back to the 7th century BC were reached. In addition, an Egyptian Seal belonging to the 7th century BC was found in the same layer.
Excavations in Adana, one of Turkey’s most important cities, shed light on Adana’s past.
What is the Cylinder seal?
A cylinder seal is a small pierced object, like a long round bead, with written characters or figurative scenes or both, carved in reverse (intaglio) and hung on strings of fiber or leather. A cylinder seal is a small round cylinder, typically about one inch (2 to 3 cm) in length.
According to some sources, cylinder seals were invented around 3500 BC in the Near East. Other sources, however, date the earliest cylinder seals to a much earlier time, to the Late Neolithic period (7600-6000 BC), hundreds of years before the invention of writing
Cylinder seals were ubiquitous in the Ancient Near East and remain a unique record of individuals from this era. Each seal was owned by one person and was used and held by them in particularly intimate ways, such as strung on a necklace or bracelet.
Cuneiform was used for official accounting, governmental and theological pronouncements, and a wide range of correspondence. Nearly all of these documents required a formal “signature,” the impression of a cylinder seal.
When a signature was required, the seal was removed and rolled over the flexible clay document, leaving the engraved reverse pictures behind in a positive imprint.