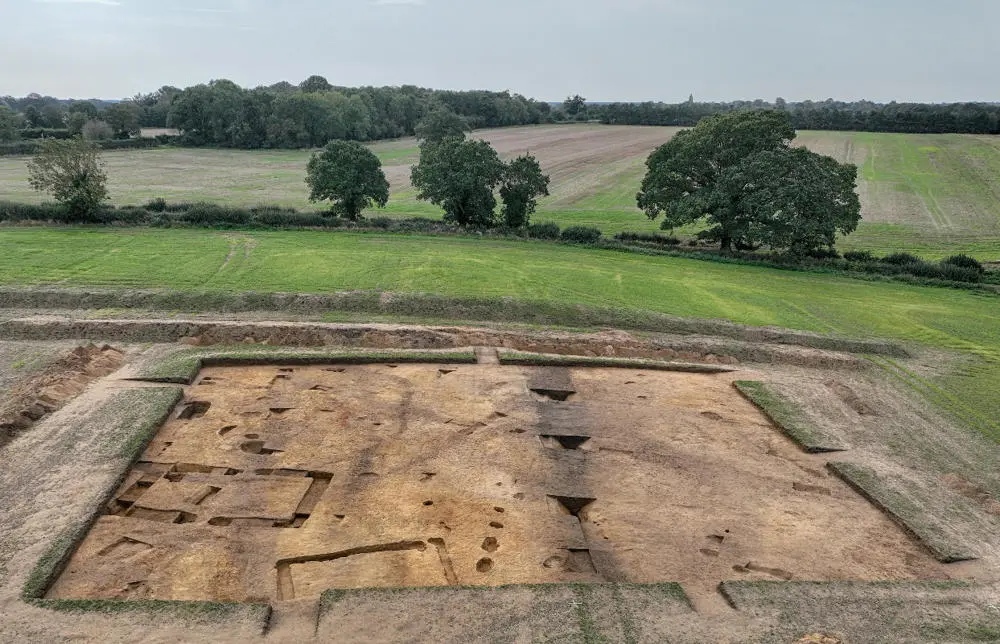
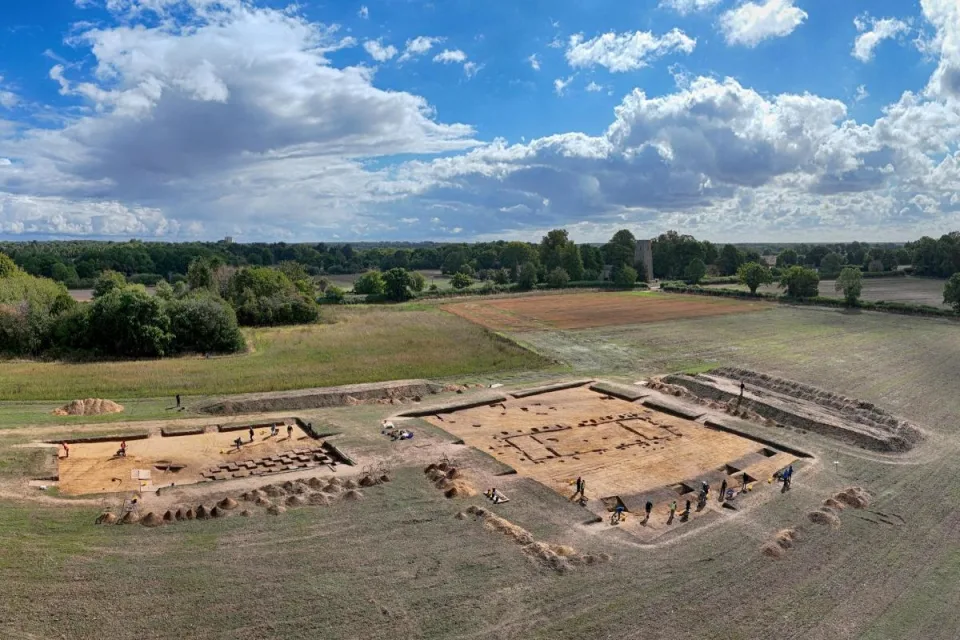
Archaeologists have uncovered a possibly pre-Christian temple from the time of the East Anglian Kings at Rendlesham, near Sutton Hoo in Suffolk, England.
The discovery was made this summer by Suffolk County Council’s Rendlesham Revealed community archaeology project, which is funded by The National Lottery Heritage Fund.
Last year the project uncovered the remains of a large timber Royal Hall, confirming the location as a royal settlement of the East Anglian Kings.
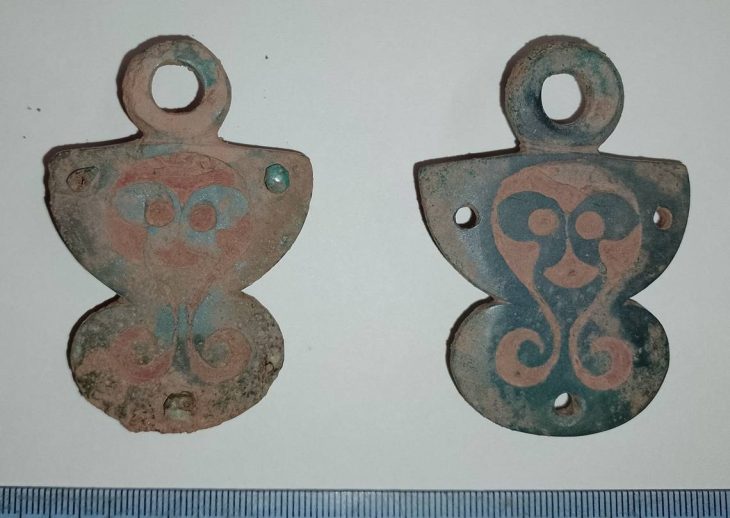
This year’s excavations also uncovered evidence of metalworking associated with royal occupation, including a mould used for casting decorative horse harnesses similar to that known from the burial ground at Sutton Hoo.
The royal compound was found to have been more than twice the size than previously thought at around 15 hectares, which is equivalent to the size of 20 football pitches. The compound was part of a wider settlement complex covering around 50 hectares which is unique to the archaeology of fifth to eighth-century England.

Professor Christopher Scull of Cardiff University and University College London was the project’s principal academic advisor.
Professor Scull said: “The results of excavations at Rendlesham speak vividly of the power and wealth of the East Anglian kings, and the sophistication of the society they ruled. The possible temple, or cult house, provides rare and remarkable evidence for the practice at a royal site of the pre-Christian beliefs that underpinned early English society.
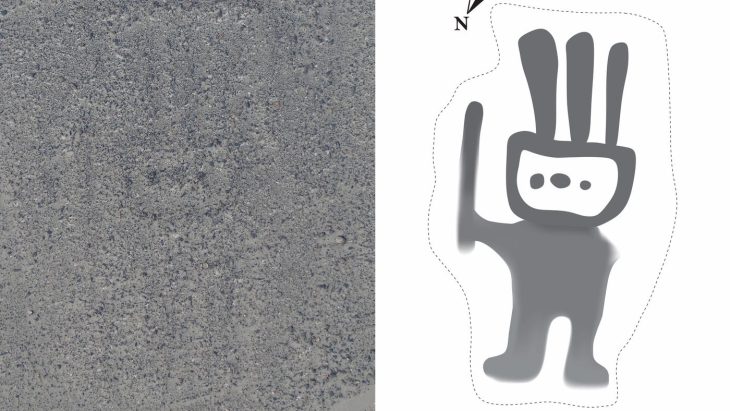
“Its distinctive and substantial foundations indicate that one of the buildings, 10 metres long and 5 metres wide, was unusually high and robustly built for its size, so perhaps it was constructed for a special purpose. It is most similar to buildings elsewhere in England that are seen as temples or cult houses, therefore it may have been used for pre-Christian worship by the early Kings of the East Angles.”
The Venerable Bede identifies Rendlesham as an East Anglian royal center in his Ecclesiastical History of the English People. Bede records that King Redwald, who died around AD 625 and whose grave is thought to be the Sutton Hoo ship burial, kept a temple with altars to pre-Christian Gods alongside an altar to Christ – though he does not specify where this was.
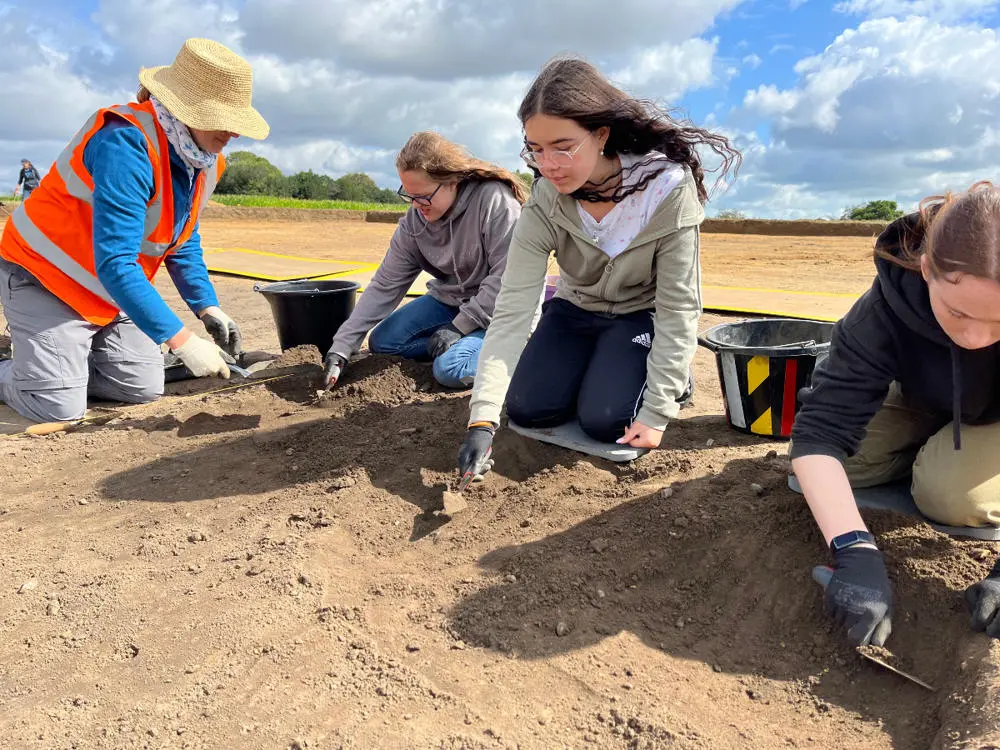

This year’s breakthrough comes after three years of excavation that has transformed the understanding of the period.
This year’s excavations also discovered enclosures and evidence of earlier settlements and activities from the Neolithic (4th millennium BC), Bronze Age, Iron Age and Roman periods.
These archaeological discoveries show that Rendlesham has been a favored location for human settlement and activity for 6,000 years from the fourth millennium BC to the present day, but that it was most important when a royal center during the 6th to 8th centuries AD.
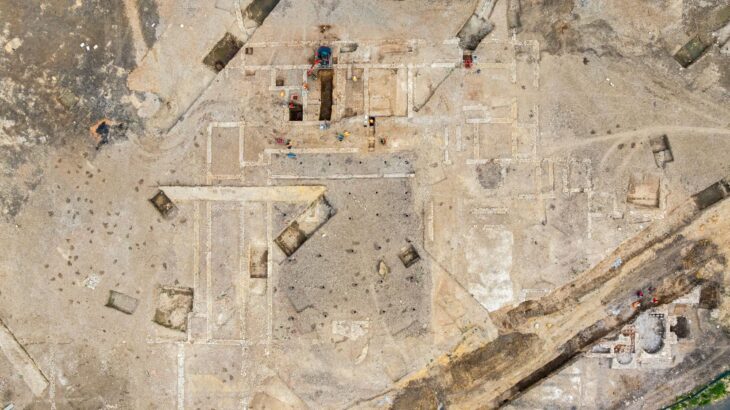
Cover Photo: Rendlesham Revelead: showing the archaeological remains including the probable temple or cult house (left hand side) and boundary ditch (center). Photo: by Jim Pullen