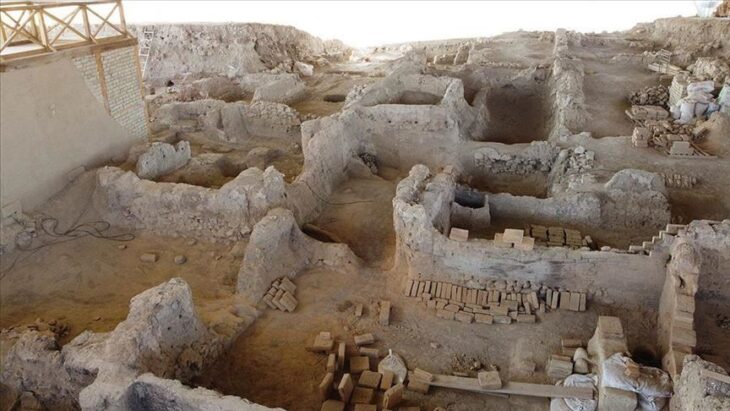
During excavations at the Roman fortress of Apsaros in Georgia, archaeologists discovered a unique gold votive plaque presented to Jupiter Dolichensky.
In the second century AD, the mystery cult of Jupiter Dolichenus, a Roman god and so-called “Oriental deity,” peaked under the Severi in the early third century AD, and then quickly faded. Scholars occasionally refer to Jupiter Dolichenus as the “Baal of Doliche” or the “Dolichenian Baal.” With this discovery, the researchers confirmed the cult of this deity, popular among Roman soldiers.
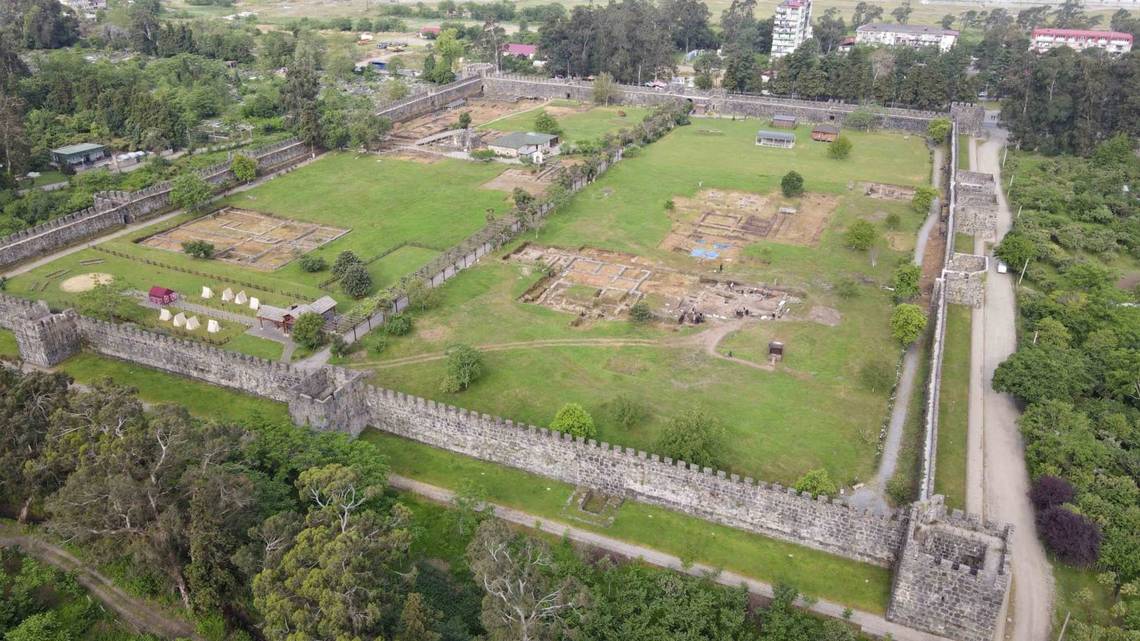
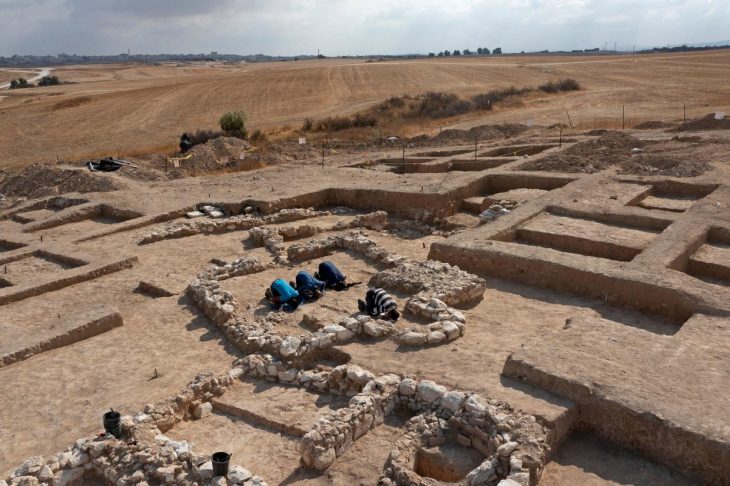
Gonio Fortress, also known as the Fortress or Castle of Apsaros, is a well-preserved 1st-century AD Roman fort located in western Georgia, just before the modern Turkish border. Apsaros Fort (this was the name by which the fortress was known among the ancients) was built around 2,000 years ago on the border of the Roman province of Cappadocia.
According to the Greek historian Procopius of Caesarea, Absyrtos, son of King Aietes (Kingdom of Colchis), is buried on the site of the fortress and that is why it was called Apsaros.
A Polish-Georgian archaeological expedition has been working there since 2014. Another excavation season has been completed by a team led by Dr. Radosław Karasiewicz-Szczypiorski, Professor at the University of Warsaw (Centre for Mediterranean Archaeology, University of Warsaw), and Dr Lasha Aslanishvili (Agency for the Protection of Adjara Cultural Heritage).
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
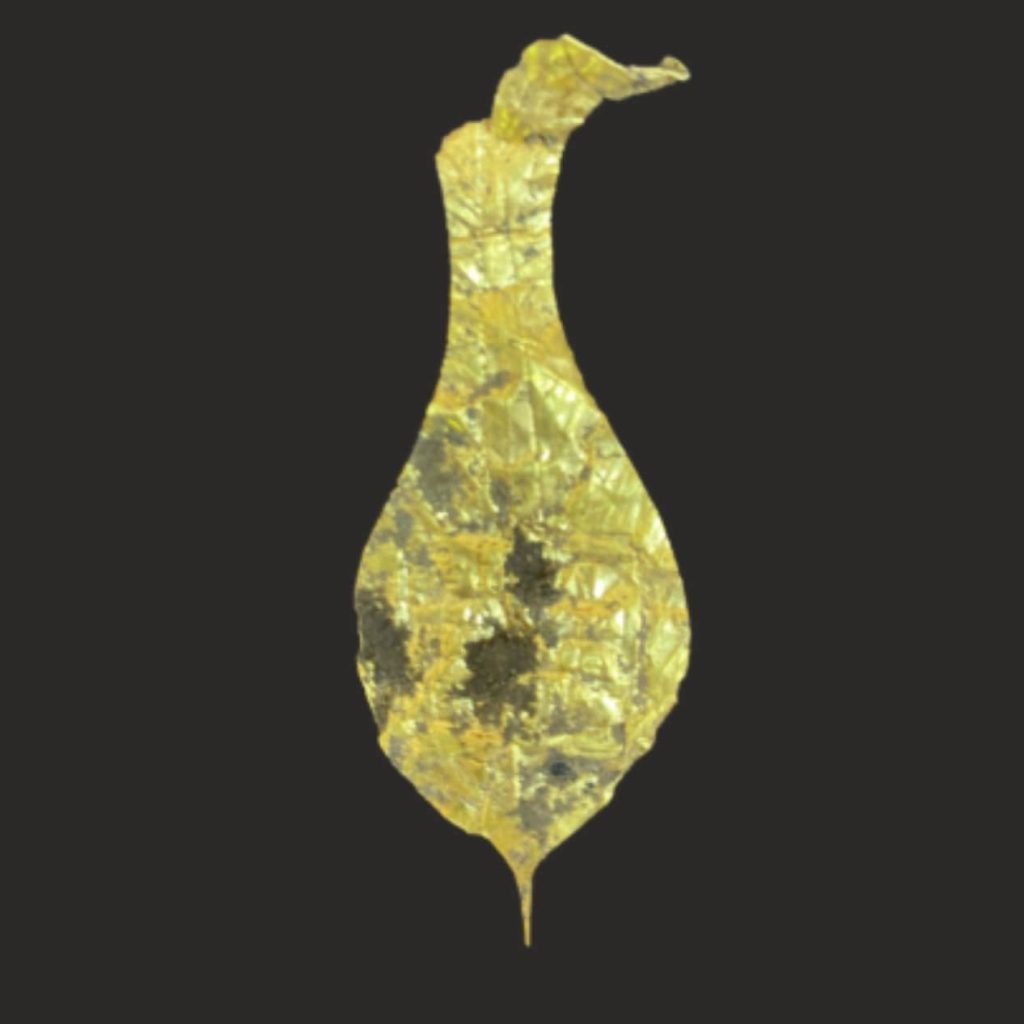

This year, for the first time, archaeologists discovered a gold votive plate. It is a small, thin plate, fitting in the palm of the hand, with embossed decorations and an inscription in Greek. The plate found was a gift to Jupiter of Doliches, a deity popular with Roman soldiers.
‘It confirms the functioning near the find, a place of worship, a temple dedicated to Jupiter Capitolinus. This deity is distinct from Jupiter Capitolinus, the official Roman deity. The roots of the cult of Jupiter of Dolicheń can be traced back to the east, the borderlands of modern Syria and Turkey. It was a local deity that, for reasons not fully explained, became popular in Roman military circles,’ – Dr Radosław Karasiewicz-Szczypiorski described to Science in Poland.
He stressed that finding a virtually intact gold object from ancient times is a unique event. ‘Also in our position it is rare. This may be because the military community did not wear gold, a rare occurrence in everyday use. This does not mean that the garrison or the officers did not have financial reserves in gold,’ – said the archaeologist.
He recalled that Gonio is known for the treasure of gold objects found in the 1970s. It is indirectly linked to the garrison, proving that officers or people in charge of the garrison’s financial resources, may have buried chests of gold, under special circumstances.
In addition to the gold plaque, the researchers collected other items that point to the incomplete explanation of the cult of Jupiter Dolichensky. These are mainly small bronze figurines, which, depict a bull and an eagle, symbolizing Jupiter.
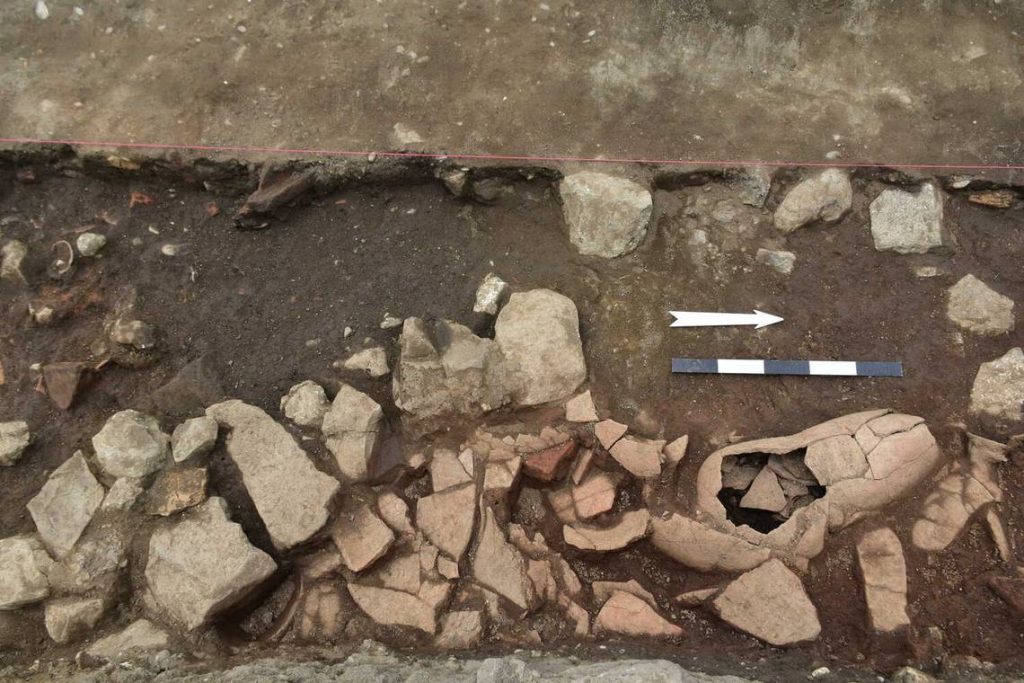

‘The votive plaque left at the place of worship brings us closer to finding the temple. Maybe we will find its remains in the coming years,” said researchers.
Archaeologists also unearthed a set of ancient Roman pottery kilns “used for firing amphorae, vessels typically used to store wine.”
Near the kilns, the team found a wine press, “suggesting that local wine may have been exported in these amphorae, likely for use by the Roman military,” the archaeologists said.
Based on these findings, Karasiewicz-Szczypiorski said the team believes large-scale pottery manufacturing and wine production took place at the ancient Roman fort, something atypical for the military. The craftsmen likely worked at the fort when soldiers were not around and were removed when the military returned.
Cover Image Credit: Polish Centre of Mediterranean Archaeology at the University of Warsaw