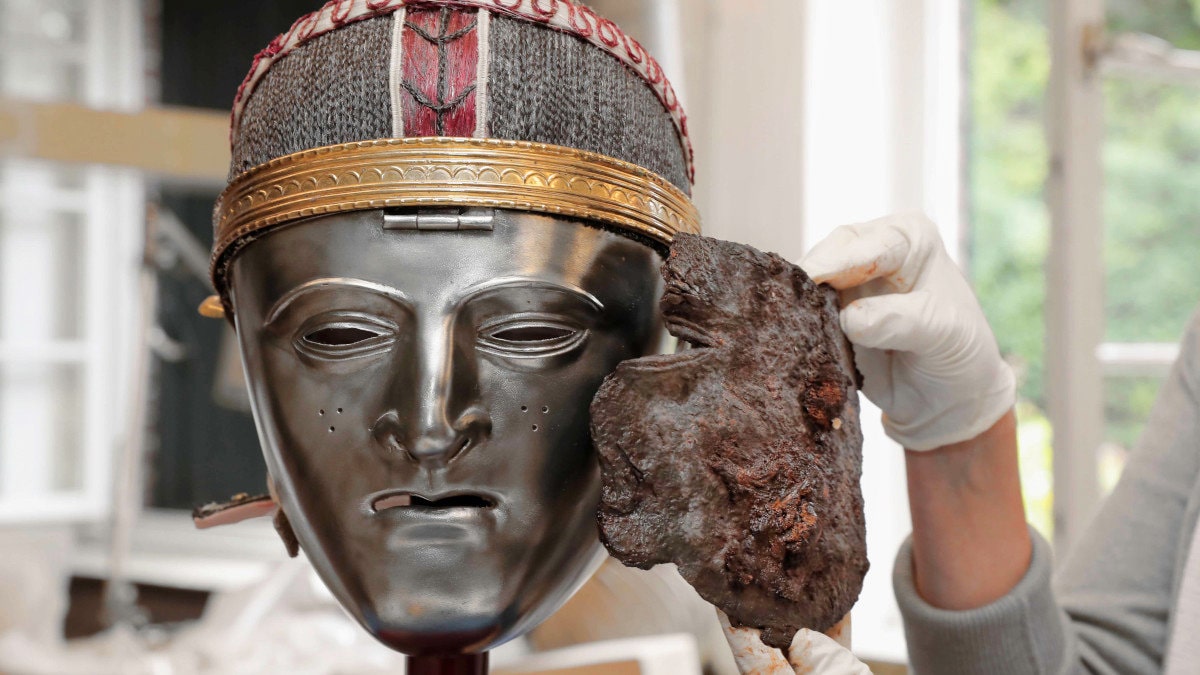
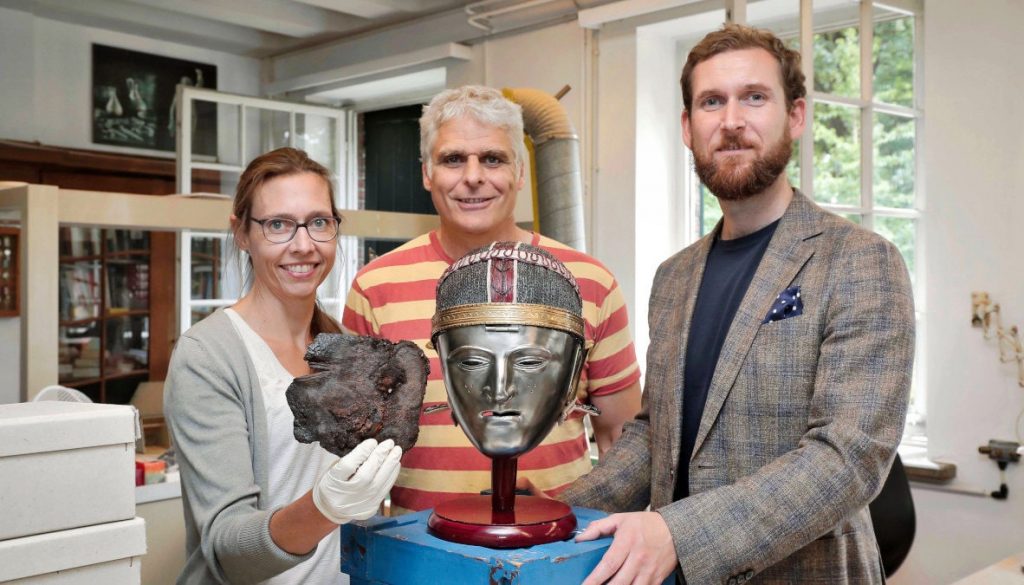
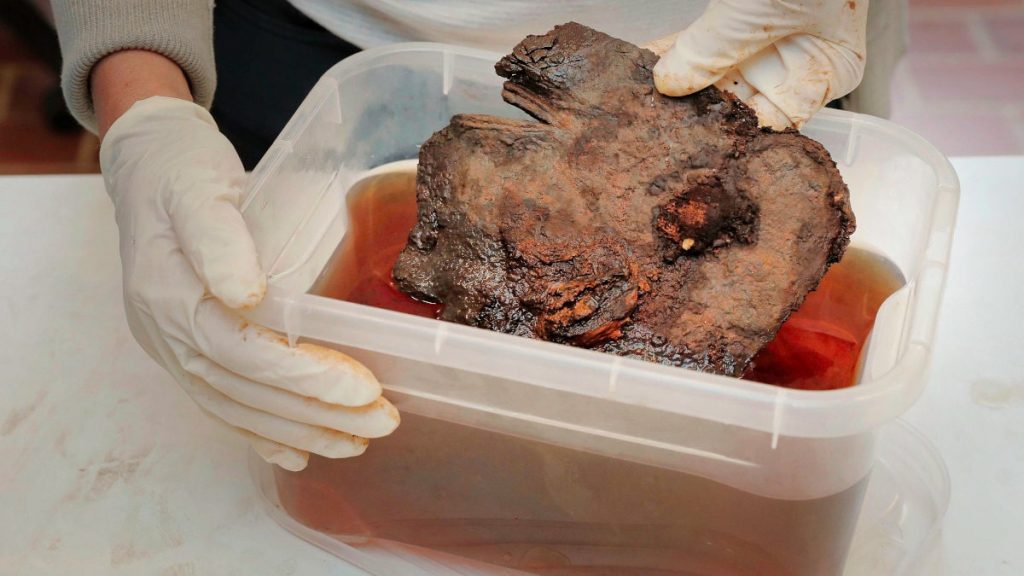
Archaeologists have discovered that a rusty corroded plate they found 4 years ago at an old battlefield in the city of Krefeld, in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia, is a large fragment of a rare Batavian Cavalry Mask dating back to the 1st century.
Archaeologists think the mask is probably part of a face mask worn by a Batavi horseman in the Batavi War in 69.
Only 15 masks of the Nijmegen-Kops type have been discovered so far. All of the masks found were found on the Nijmegen-Kops plateau. Most are in the Batavi region, now the Netherlands, between the Meuse and the Rhine. So the type is closely associated with Batavi horseman. It was attached to the headband of the helmet with a hinge. The emotionless silvered visage was meant to be intimidating for opponents on the battlefield and in hand-to-hand combat.
The Batavi were an ancient Germanic tribe living -around the Rhine delta of modern Netherlands- in an area, the Romans called Batavia. (1st century BC, 3rd century AD). Tacitus (De Origine et situ Germanorum XXIX), a Roman Historian and Politician, described the Batavi as the bravest of the tribes of the region.

The Batavi were so famed for their prowess in combat that Rome granted them a special tax and tribute exemption in return for their service in Roman auxiliary infantry, cavalry, and in the Augustan-era imperial bodyguards. In the first century, out of a population of less than 40,000 Batavi, 5,500 served as elite warriors in the Roman legions. That means that half of all Batavi men enlisted after they turned 16.
Batavi forces were critical to the conquest of Britain, but after they were withdrawn from Britannia in 66 A.D., tensions between the Batavi soldiers and Rome grew. Gaius Julius Civilis, the son of a Batavi chief who had spent 25 years in the Roman auxiliary, staged a rebellion. For a year, he effectively deployed Roman military techniques against them. In the autumn of 69 A.D., Civilis’ elite warriors ambushed 12,000 Roman legionaries and auxiliaries in their field camp at Gelduba on the Rhine’s left bank. The Batavi entered the camp and began murdering, but were unable to complete the task when Roman reinforcements arrived. Although Rome won technically, it lost so many men that the victory was rather tainted.

After the Batavi War, the Roman presence in Gelduba began almost uninterrupted until the end of the Roman Empire in the fifth century. The region on the Rhine proved to be strategically favorable. The Romans built many different forts there over the centuries. The site monument today, along with other sites in the Lower Germanic Lime, was recognized as a Unesco World Heritage Site in 2021.
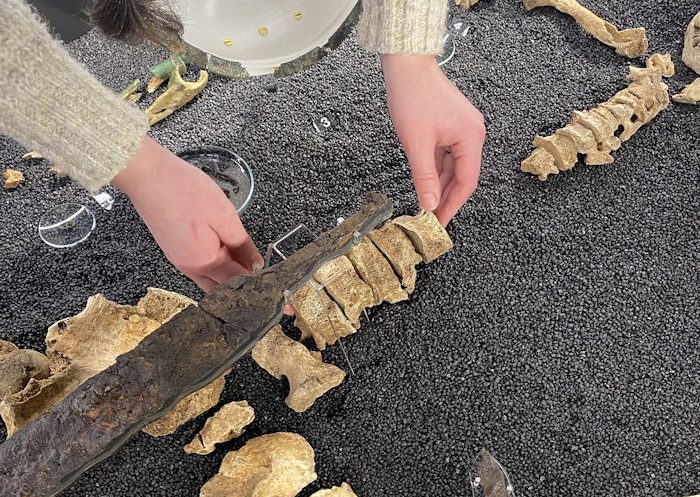
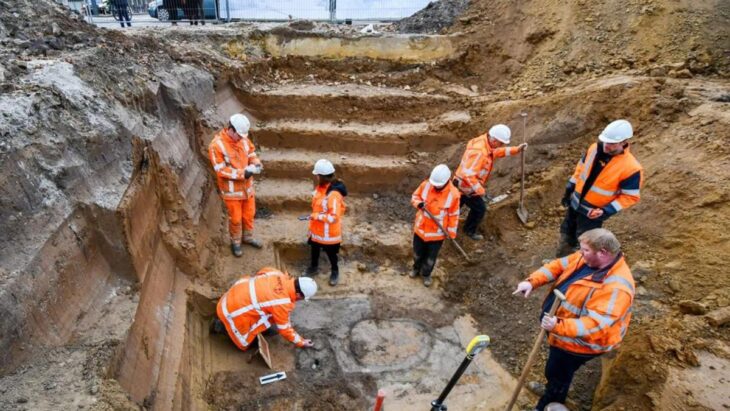
Excavations that began at Krefeld-Gellep in 2017 revealed the battlefield of Roman comrades who fought 2,000 years ago. At the excavation site, thousands of relics of the battle have been unearthed, including 200 horse skeletons, armor, and weapons.
The corroded, lumpy metal plate was brought to the Archaeological Museum in Krefeld for documentation, conservation, and study. When the piece was X-rayed, archaeologists recognized they had a part of a cavalry mask after spotting an eye slit, an ear, and a rivet where the helmet attachment was most probable.
Cover Photo: The mask fragment was found during an excavation at Krefeld-Gellep; here is the Batavi face mask and a replica of the helmet. Batavian cavalry mask. City of Krefeld, Press, and Communications