The Gribshunden, a 15th-century Danish royal warship, was uncovered to have been loaded with botanical materials, including the first archaeological evidence of saffron, ginger, and cloves in medieval Scandinavia, which was previously only known from sparsely written sources.
Furthermore, it is the sole surviving archaeological illustration of a complete Middle Ages royal spice larder. The saffron has been preserved so well that even after 527 years submerged, it still has its distinctive aroma.
In 1495, Denmark and Norway King Hans docked his ship Gribshunden off the coast of Sweden in preparation for a meeting with Swedish ruler, Sten Sture the Elder. His plan was to broker a deal that would give him control over Sweden as he had done with Norway, creating a united Nordic kingdom. Unfortunately for Hans and many of his crew, the ship caught fire and sank.
The King had loaded his ship with warriors and goods fit for a wealthy and powerful man in order to give himself the upper hand. The loss of the ship forced a change in strategy, and Hans decided to invade and conquer Sweden rather than negotiate for it. But the ship’s sinking also left a gold mine of artifacts for researchers in the modern era.

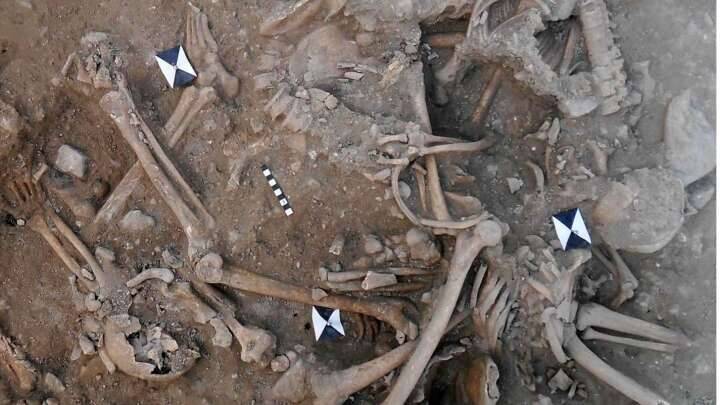
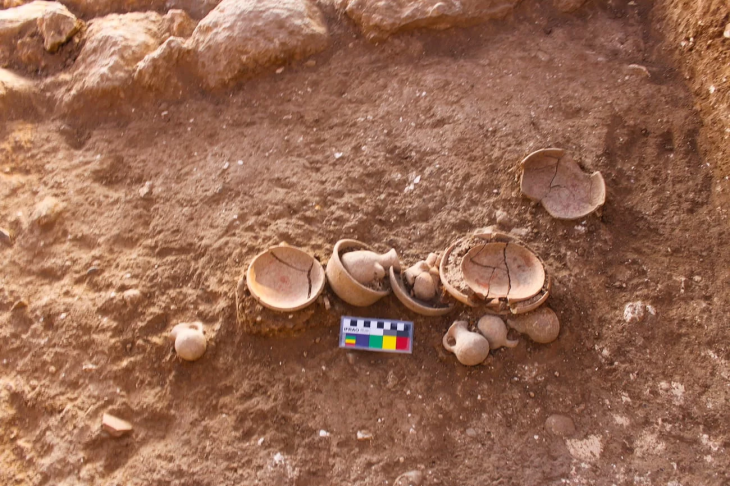
The wreck of Gribshunden was found during the 1960s and a new study was conducted from 2019-2021. Thanks to the unique environment of the Baltic Sea – with oxygen-free seabeds, low salinity, and an absence of shipworms – the wreck was particularly well preserved when it was discovered.
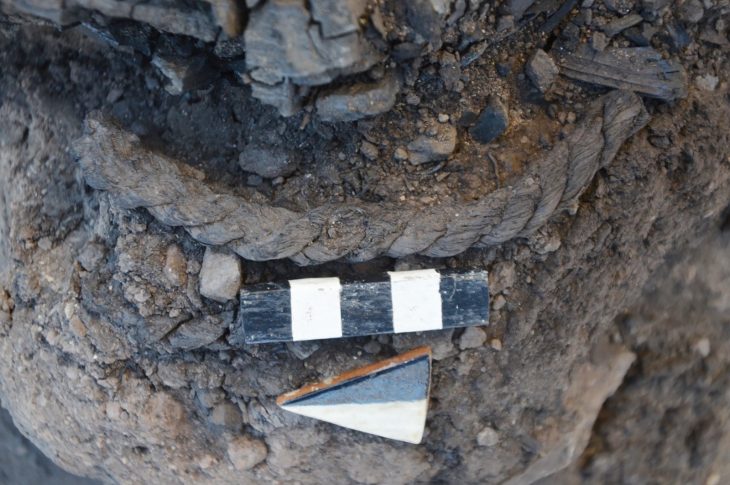
The team found that most of the expected artifacts had already been found in earlier expeditions, but something important had been overlooked—containers holding well-preserved plant material—more than 3,000 specimens.
The recent discovery of “exotic spices were status markers among the aristocracy in Scandinavia and around the Baltic Sea during the Middle Ages,” according to scientists from Lund University.
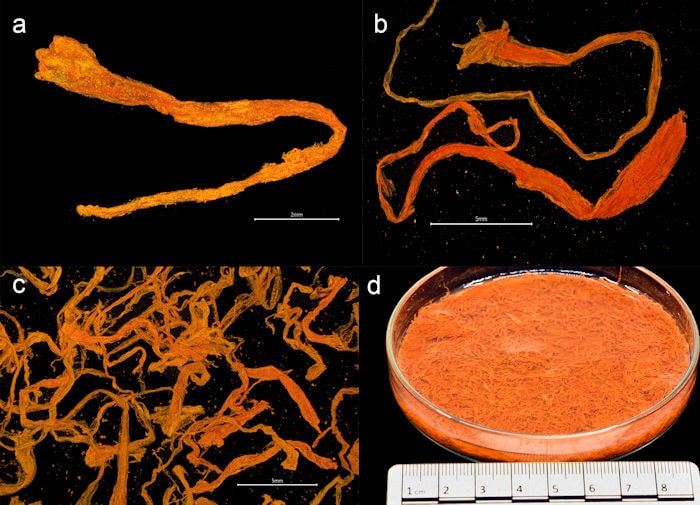
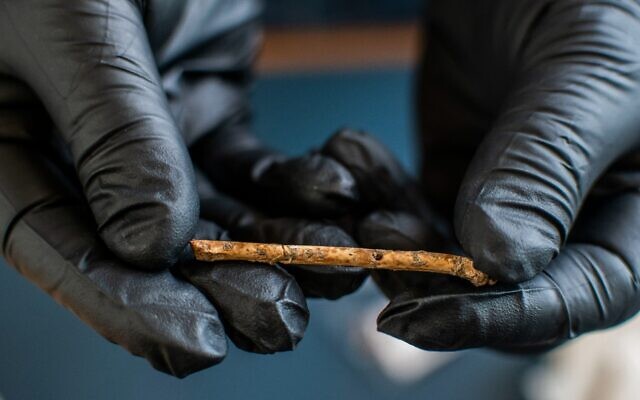
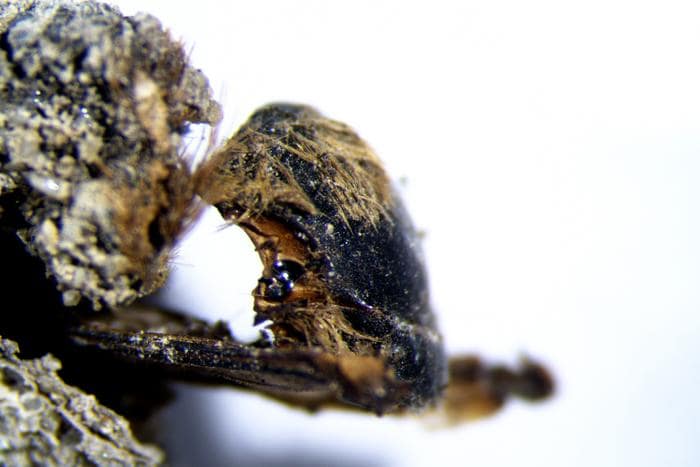
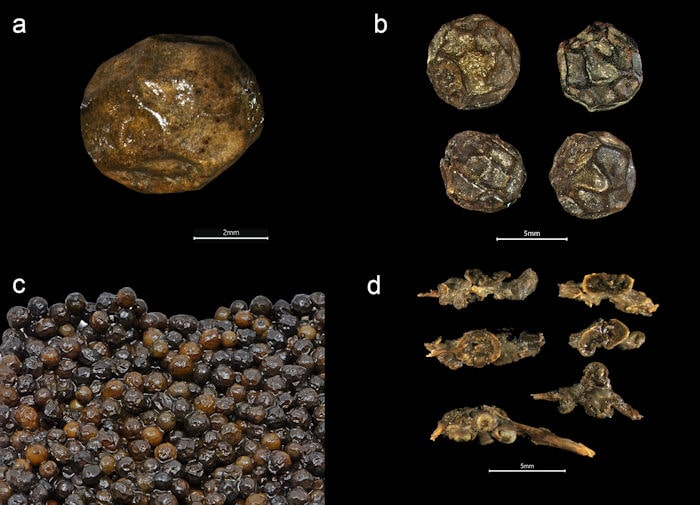
Researchers discovered herbs and spices like dill, nutmeg, and cloves. Additionally, they discovered samples of other plant materials, including almonds, saffron, ginger, and peppercorns. It is possible that some of the spices came from as far away as Indonesia, indicating that King Hans had established a sophisticated trade network. Additionally, the researchers discovered snacks like dried blackberries, raspberries, grapes, and flax, each of which revealed just how wealthy and influential Hans had grown to be. The researchers also discovered henbane, a non-edible plant that was once used medicinally.
The study identified 3097 plant remains from 40 different species in total. Spices make up the majority of the mixture (86%).
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281010
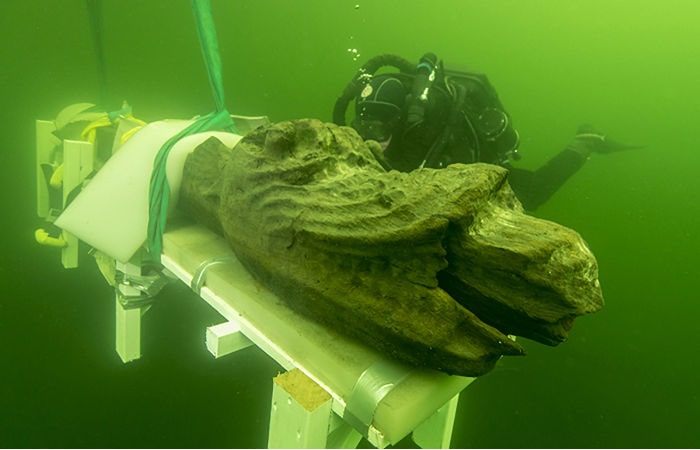
Cover Photo: Gribshunden’s figurehead was salvaged in 2015. Photo: Blekinge Museum