Near Hadrian’s Wall in northern England, archaeologists discovered a carved sandstone slab portraying a naked horseman.
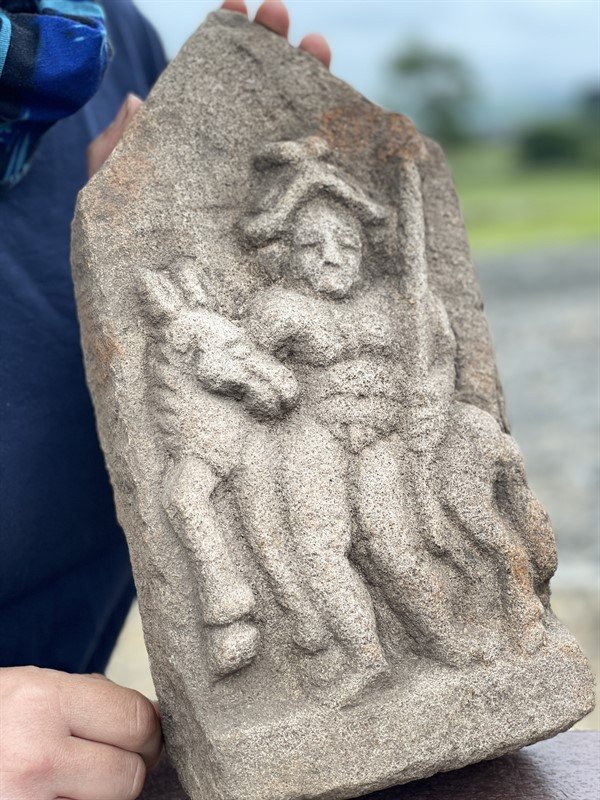
During the annual excavations at the Roman fort of Vindolanda near Hadrian’s Wall in Northumberland, a superbly carved sandstone relief depicting a naked male figure carrying a spear standing in front of a horse/donkey was discovered. The complete stone measuring 160mm by 315mm would have originally been fitted into a recess.
The Vindolanda Charitable Trust, which manages archaeological, conservation, and educational activities at the site, that there have been “no analogous discoveries” before now.
Site archaeologist Marta Alberti added, “The nakedness of the man means he is probably a god, rather than a mere cavalryman, he is also carrying a spear in his left arm, a common attribute of the God of War – Mars, however when you look at his head, the two almost circular features could be identified as wings: a common attribute of Mercury – god of travel. Horses and donkeys are also often associated with Mercury as a protector of travelers”.
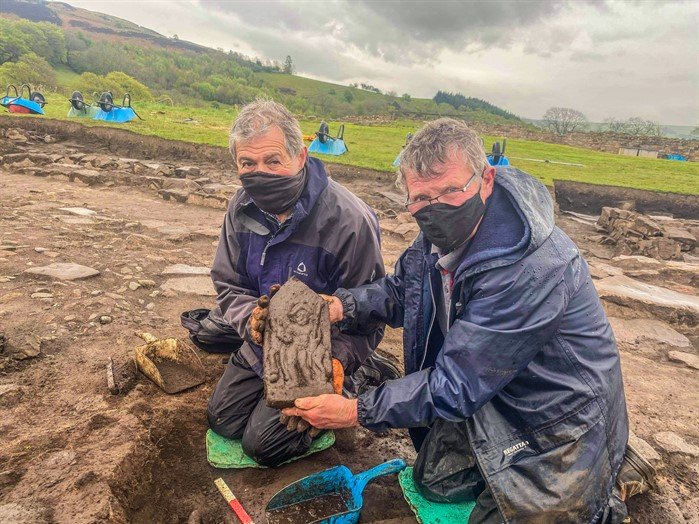

Marta commented, “this interesting relief may represent something we have not only never seen before but something we may never see again”.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
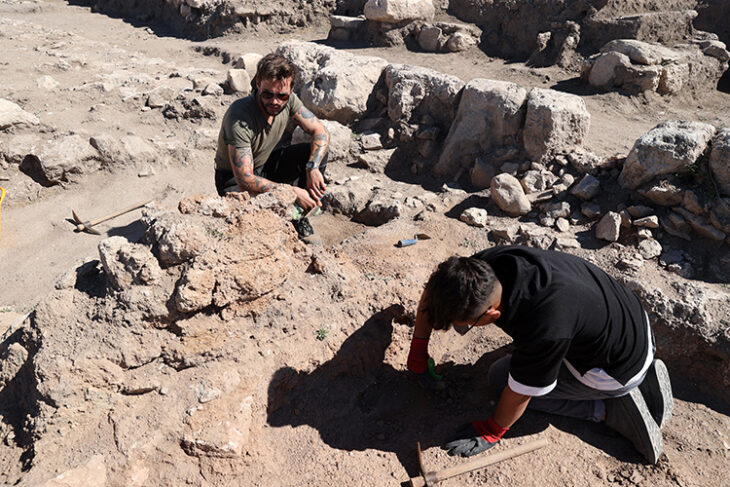
The stone was uncovered on May 20 this year, only inches under the topsoil, by two volunteers from Newcastle.
Richie Milor and David Goldwater had been assigned to uncover a flagged floor inside a 4th-century building of the ancient fort.
‘We are just absolutely elated, very proud to be part of this discovery, it was actually very emotional,’ Milor said.
The artifact can be seen in the current findings exhibition at the Vindolanda museum beginning July 1st and will be on display until the end of the 2021 season.
Source: Vindolanda Charitable Trust