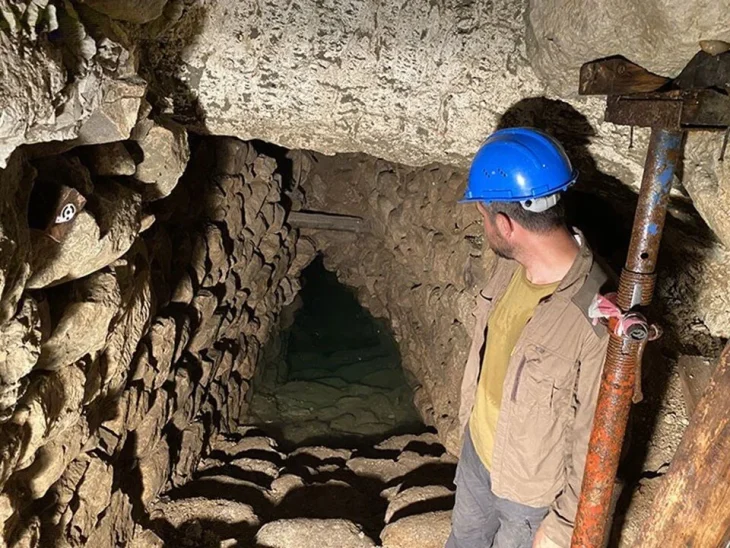
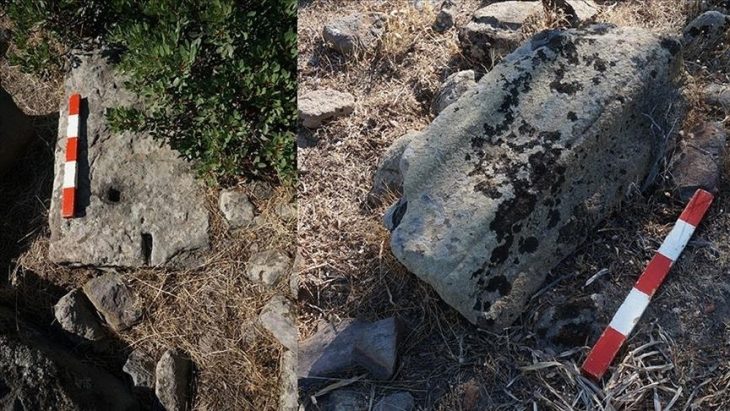
Recent archaeological excavations in the ancient Roman colony of Liternum, located in present-day Giugliano in Campania, Italy, have unveiled significant remains from the Imperial era, shedding light on the colony’s rich history. Among the discoveries are two well-preserved funerary enclosures, a quadrangular mausoleum, and a marble epitaph of a gladiator.
Established in the late 2nd century BC, Liternum flourished in the 1st and 2nd centuries AD, particularly due to the construction of the Via Domitiana, which transformed it into a vital trading center.
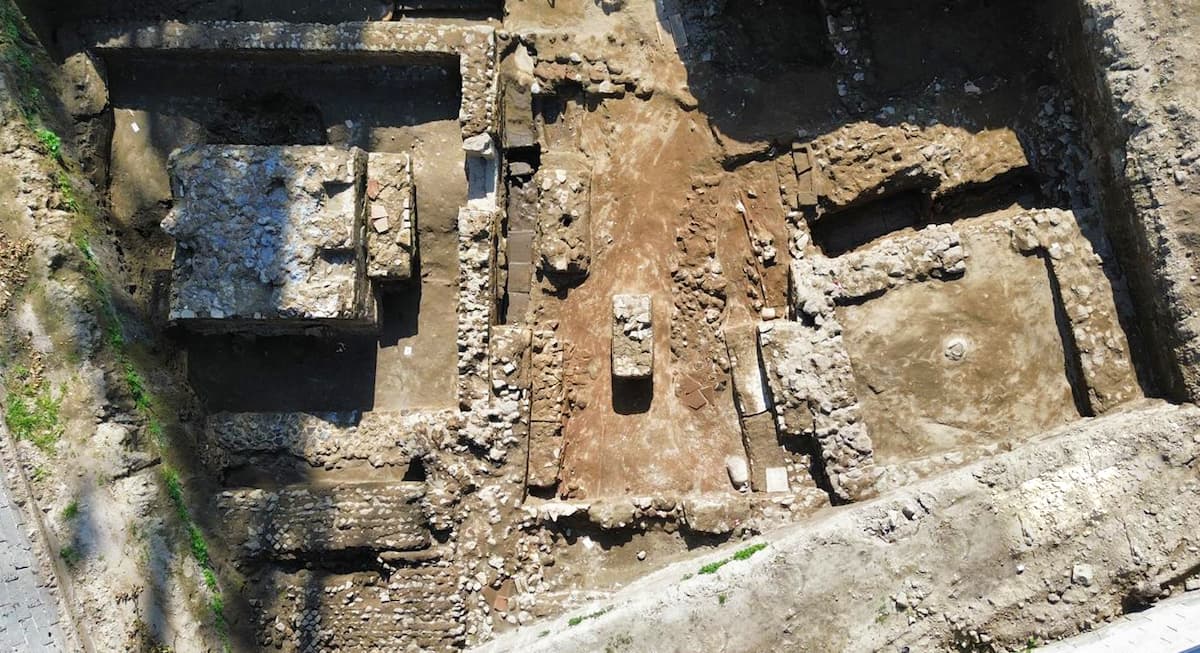
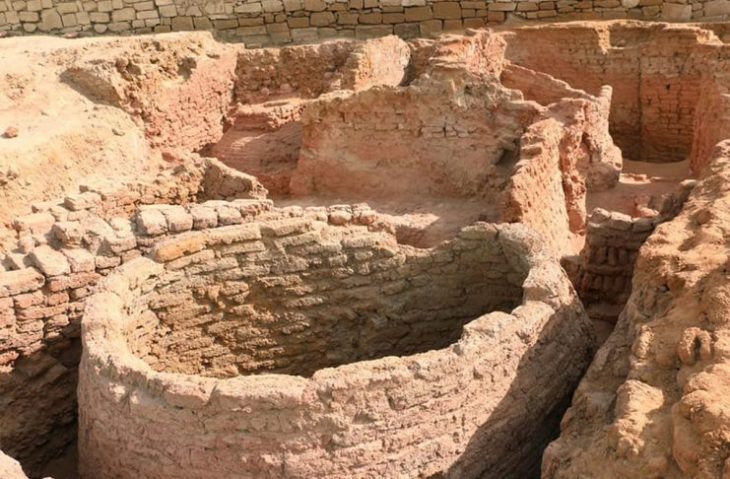
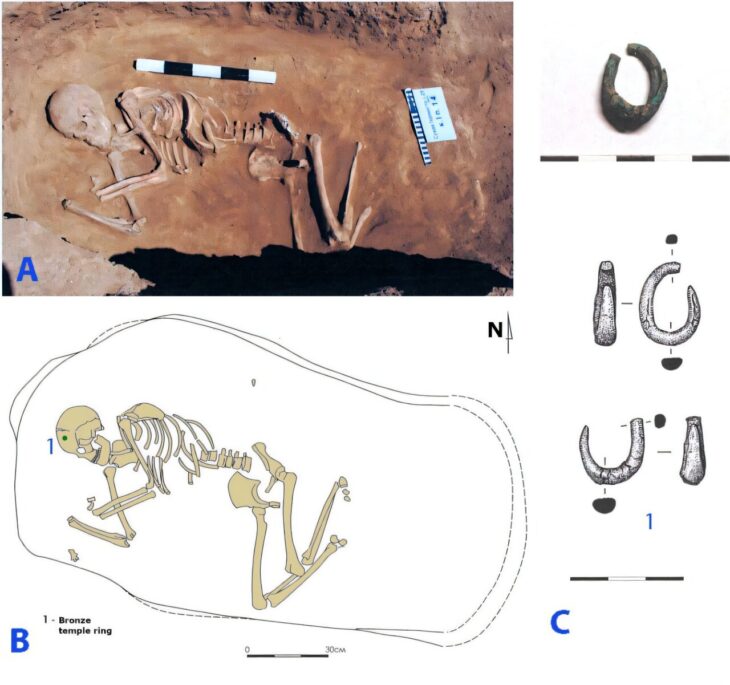
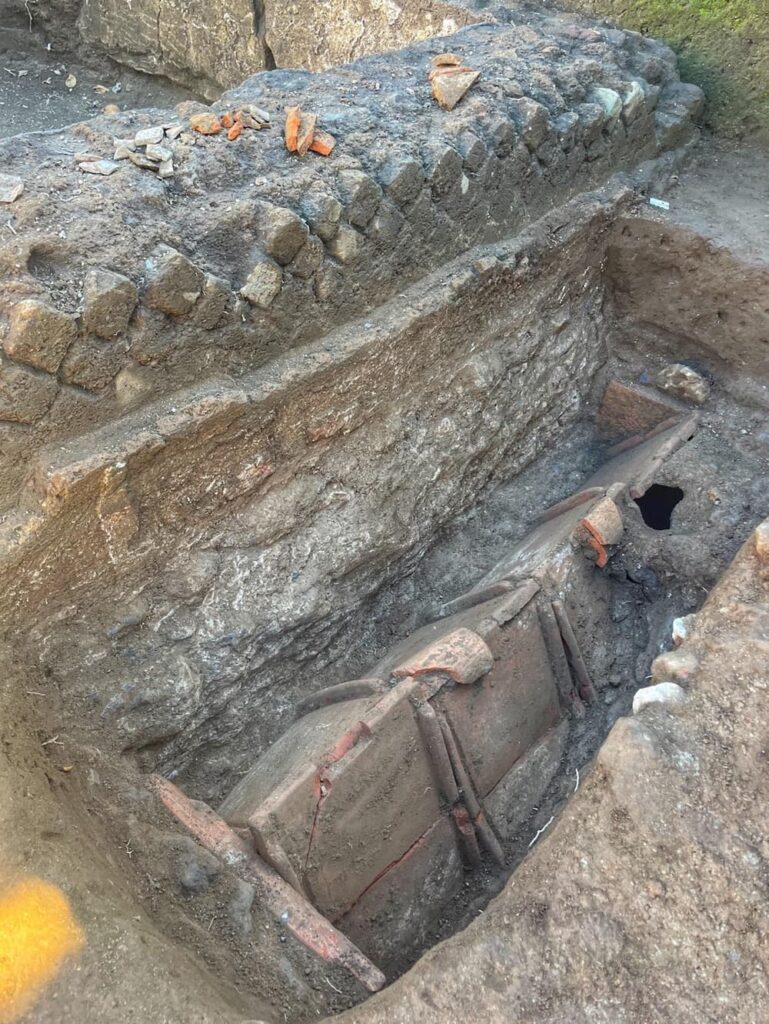
Under the direction of archaeologist Dr. Simona Formola, the excavation has revealed an extensive area of over 150 square meters, previously protected by a ministerial decree. Among the most notable findings are two high-status funerary enclosures, which retain large sections of their original cladding, and a quadrangular mausoleum constructed using the opus reticulatum technique. This mausoleum, measuring three meters per side, features plastered niches designed to house cinerary urns, indicating the necropolis’s prolonged use over generations.
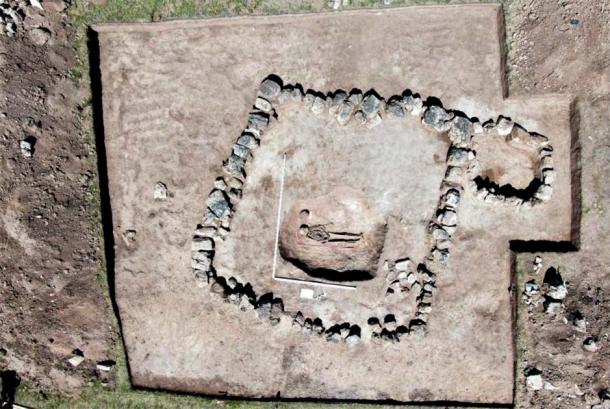
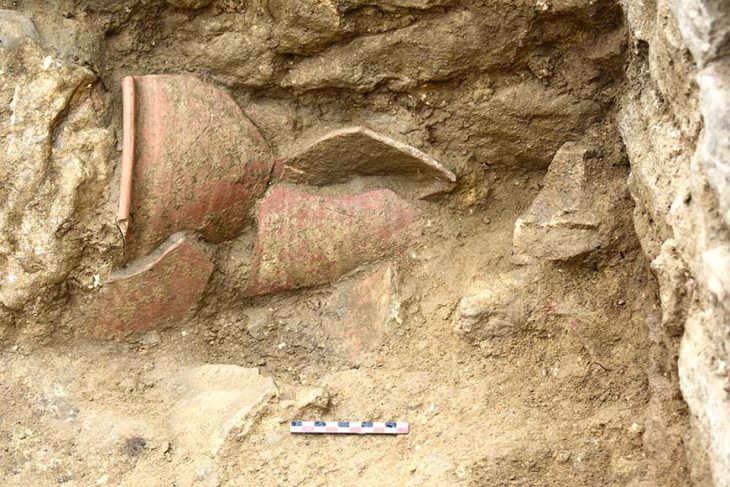
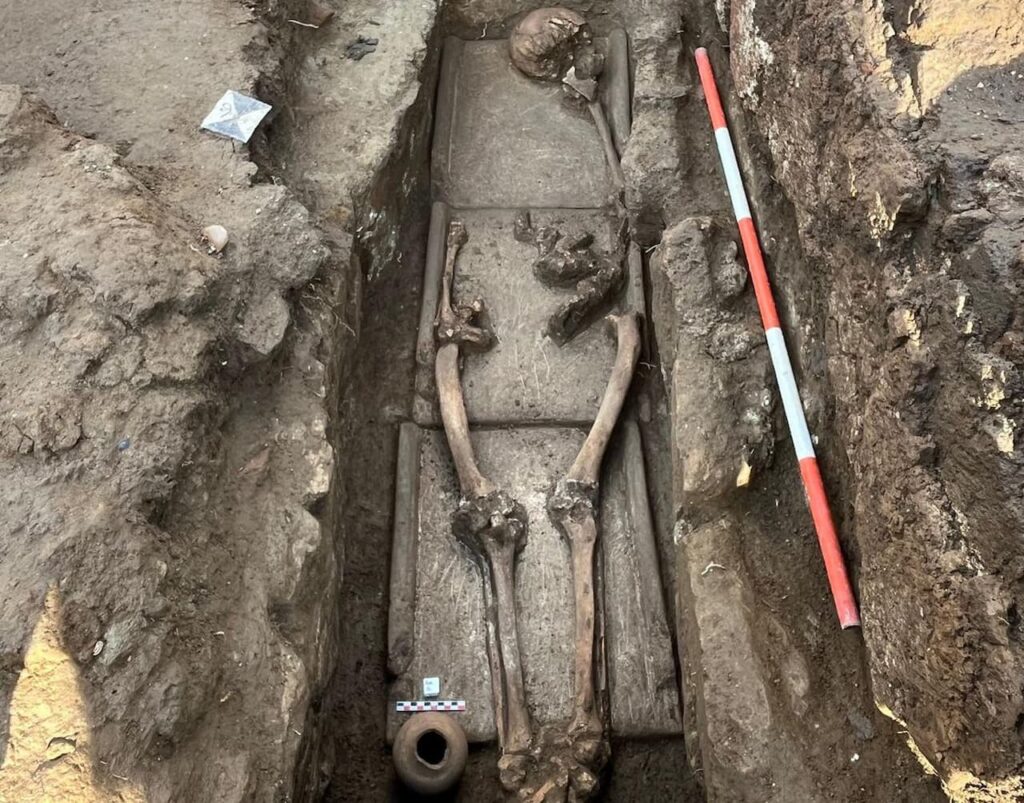
The excavation has also documented around twenty burials, showcasing various burial types prevalent in ancient Rome. These include inhumations in cappuccina tombs, ad enchýtrismos burials in large ceramic vessels, and intricately crafted box-shaped tombs. The stratigraphy of these structures, along with the discovery of grave goods such as coins, oil lamps, and small ceramic vessels, provides valuable insights into the funerary customs and social interactions of the Liternum community.

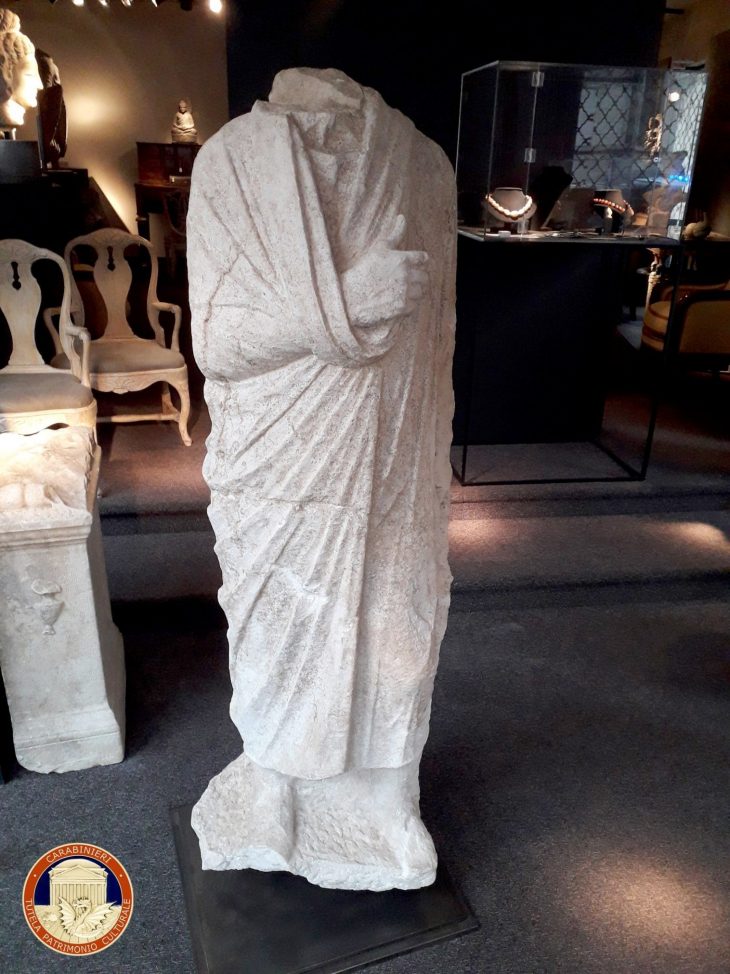
One of the most remarkable discoveries is a well-preserved marble funerary inscription mentioning a gladiator, offering a unique glimpse into the societal perception of these combatants in Roman culture. This finding suggests that Liternum was not only a residential area but also a resting place for gladiators after their careers in the arena.
Superintendent Mariano Nuzzo emphasized the importance of these findings, noting that the Giugliano territory is currently experiencing a remarkable period of archaeological discoveries. The quality and preservation of the structures enhance our understanding of Liternum’s history and the sociocultural context of the time.
The discoveries have also prompted new hypotheses regarding the spatial organization of the Roman colony, particularly concerning the layout of the ancient Via Domitiana, traditionally lined with necropolises. As excavations continue and materials undergo further study, it is anticipated that knowledge about this historically significant site will expand, contributing to the broader understanding of Roman life in Campania.

The Superintendency remains committed to protecting and disseminating these cultural assets, ensuring that the remains are preserved and accessible to both the scientific community and the public.
Cover Image Credit: Soprintendenza Archeologia Belle Arti e Paesaggio per l’area metropolitana di Napoli. (Superintendency for Archaeological Heritage, Fine Arts, and Landscape for the Metropolitan Area of Naples)