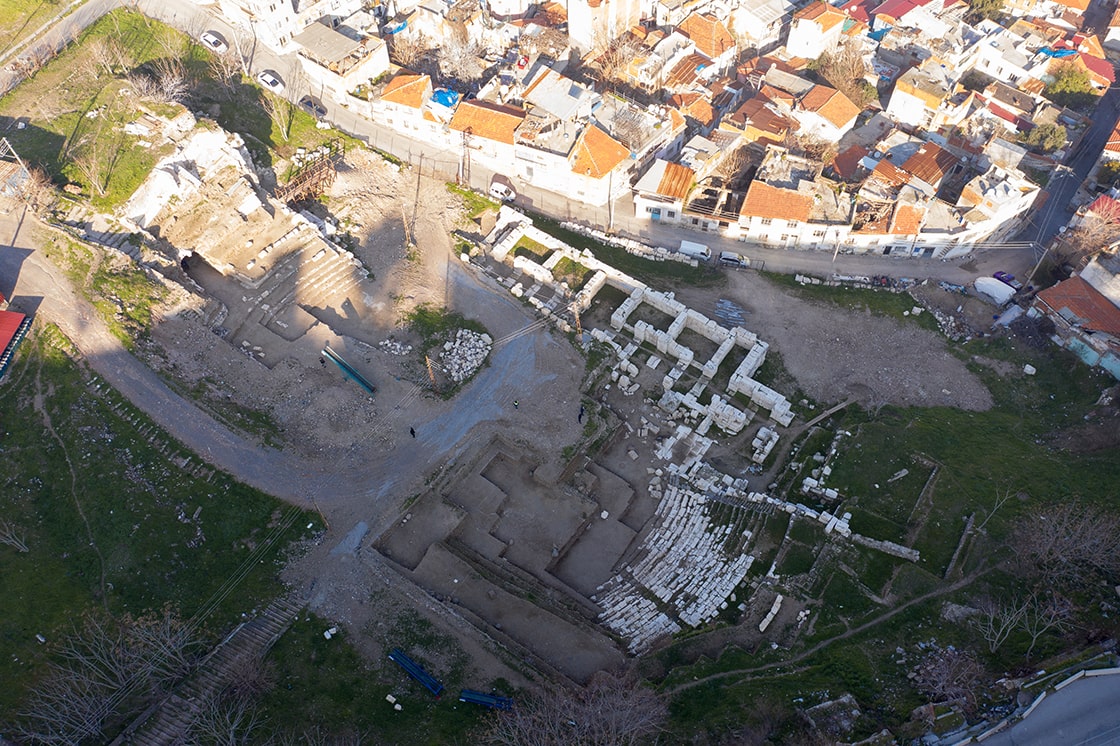
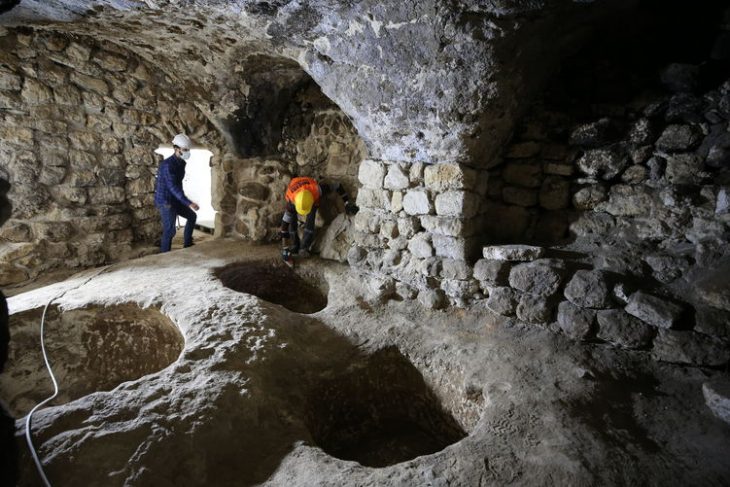
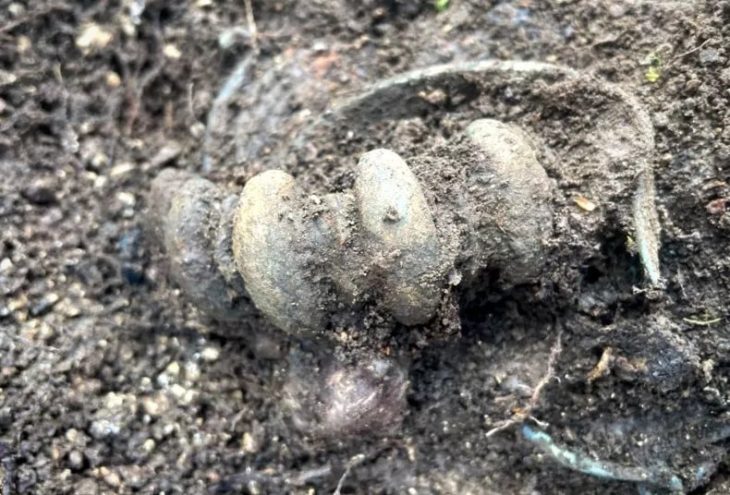
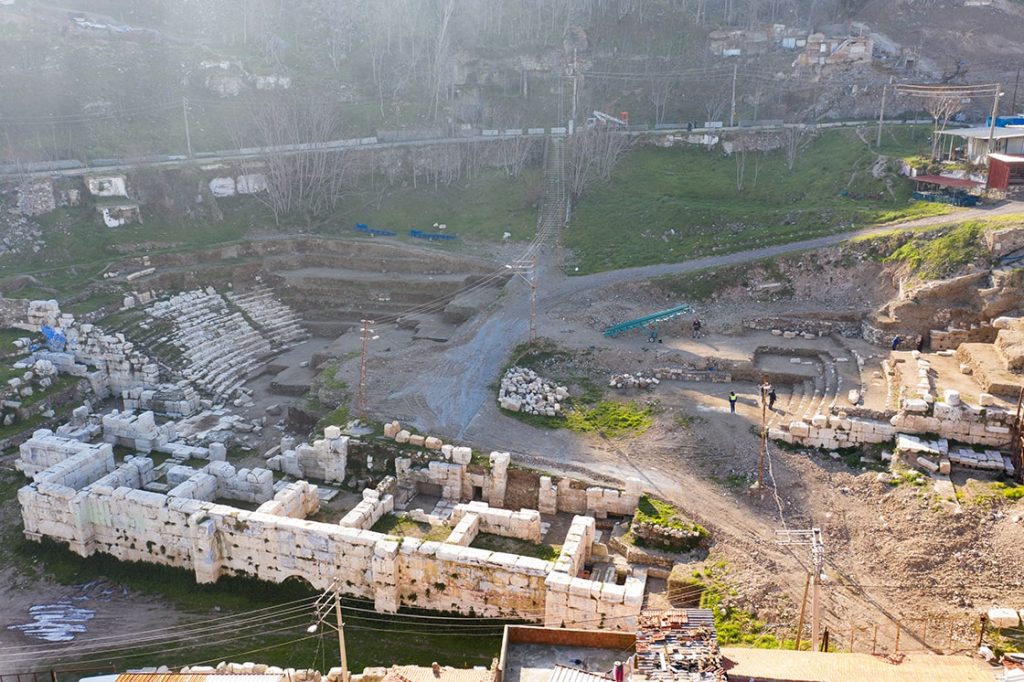
Archaeologists discovered a 2,000-year-old passage that was 26 meters long and constructed in an “L” form in the theater part of the ancient city of Smyrna, in the center of Izmir in western Turkey.
Uncovering an “artist toilet” where It can be used by 13 people sitting side by side, in 2021 in the stage building, the excavation team found a 26-meter passage shortly after this discovery.
The 4-meter-wide passage, built in an “L” shape, which allows the audience to reach the theater with a capacity of approximately 20 thousand people, was discovered 6-7 meters below the houses demolished by the expropriation method.
It was determined that the passage, called “vomitorium” by archaeologists, was built with the knowledge of arches and vaults to strengthen the rows of seats.

The head of the excavation, İzmir Katip Çelebi University (İKÇÜ) Turkish-Islamic Archeology Department Lecturer Assoc. Dr. Akın Ersoy told Anadolu Agency (AA) that they came across 2 very important finds during the excavations in 2021.
Stating that the first of the finds was the toilet area in the stage building, Ersoy noted the following regarding the works:
“If we express it in archeological terms, we identified a latrina, that is, a toilet. An example of a theater with a toilet in the stage building was not encountered in any other theater in the Mediterranean Basin. Then we found a vomitorium, or underpass. We noticed it in some photographs taken in the 1950s in the area. We focused our work on the entrance section of the theater. We reached an underpass used by the audience to reach the seating places of the audience coming from outside the theater.”
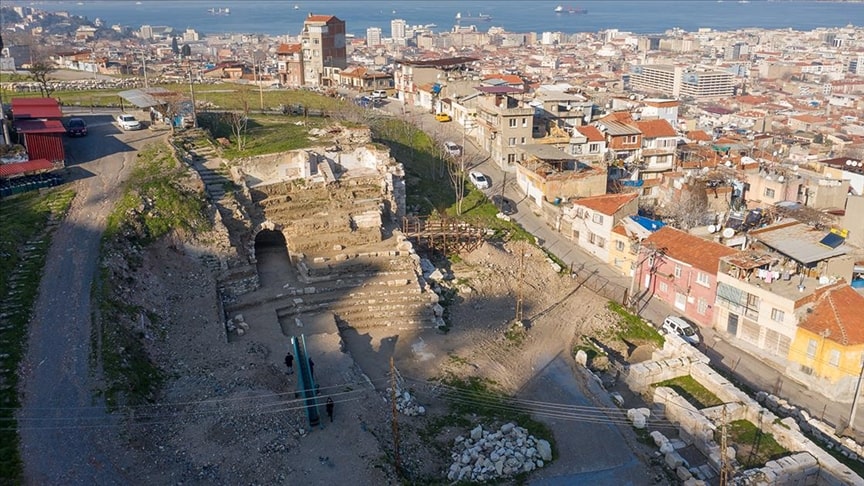

Expressing that they call the passage the “Western Vomitorium”, Ersoy said, “There must also be the Eastern Vomitorium. We hope that we will uncover it during the 2022 excavations, and thus we will encounter another architectural find that will highlight the 20 thousand spectator capacity of the Izmir theater.”
Pointing out that the passage in the Smyrna Theater was built with arch and vault systems, Ersoy said that the arch and vault systems were not used in Anatolia and the Mediterranean before the Roman Period, except for a few examples. Examples emerge with the Roman Period. He added that there are new construction technologies that bring together the science of mathematics and statics.
Cover Photo: Ömer Evren Atalay – Anadolu Agency