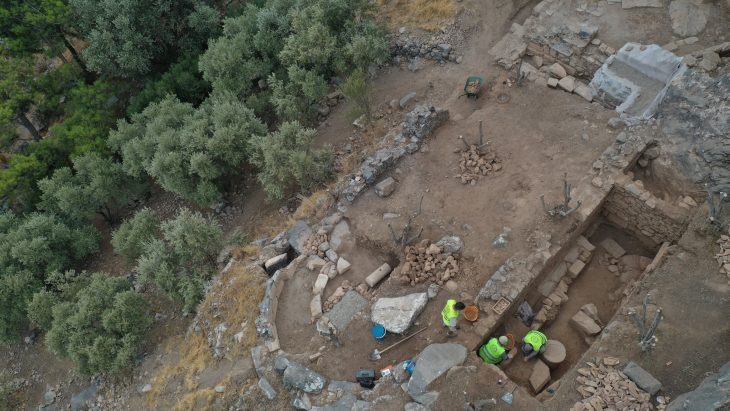
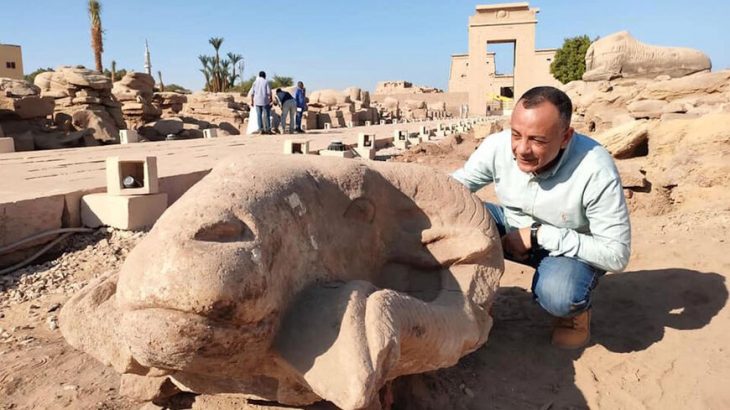
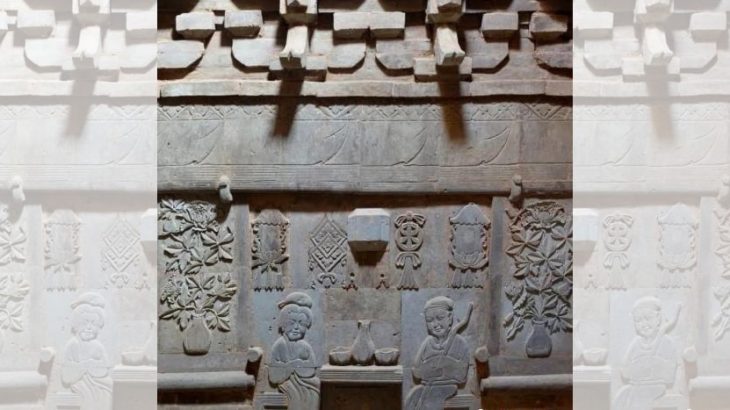
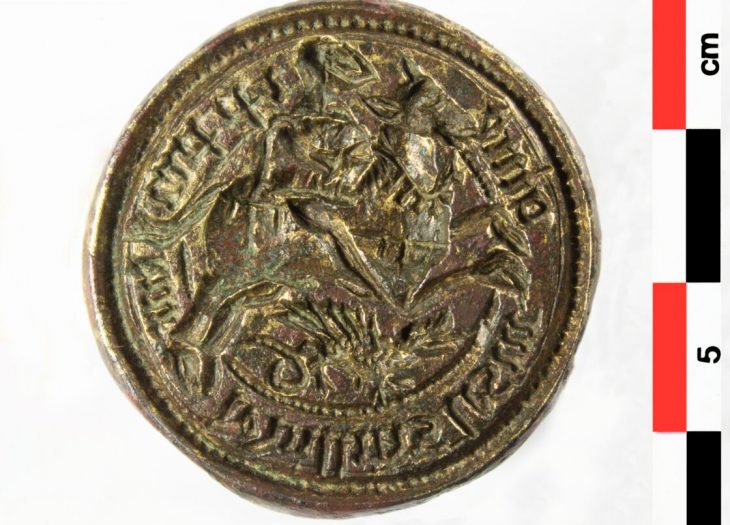
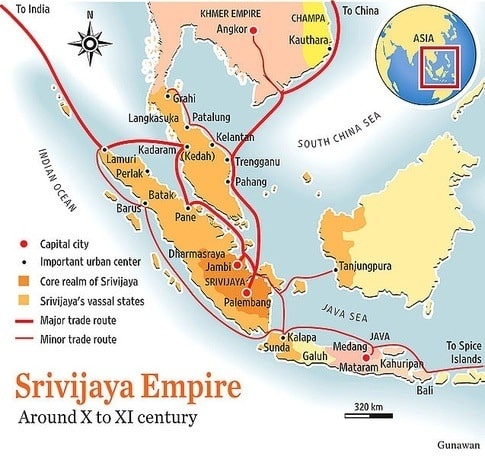
The site of the Srivijaya kingdom, known in ancient times as the Island of Gold, may have been found by local fishing crews doing night-time dives in Indonesia‘s Musi River.
The legendary kingdom inexplicably disappeared in the 14th century, taking its great fortune with it.
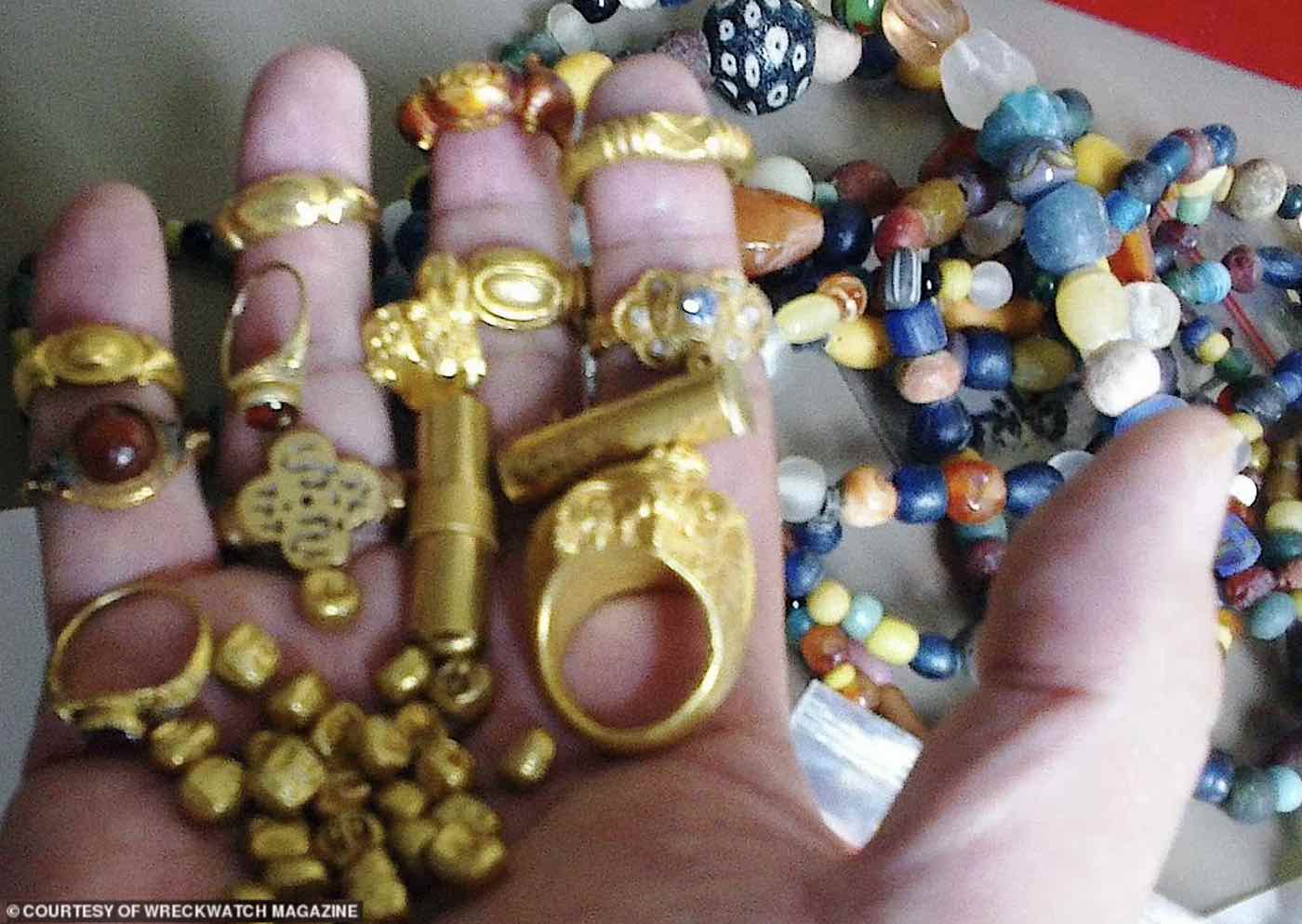
Dr. Sean Kingsley, a British maritime archaeologist, believes the discoveries, which include a ruby-studded life-size golden Buddha worth millions of dollars, represent the gradual rediscovery of a lost merchant palace city from the kingdom of Svirijaya, which ruled trade routes in large parts of Indonesia for 400 years.
The palace city, located around the town of Palembang, also known as “Venice of the East,” would have sat on a major artery of the maritime version of the Silk Road.
Dr. Sean Kingsley described the trove as definitive evidence that Srivijaya was a “Waterworld”, its people living on the river like modern boat people, just as ancient texts record: “When the civilization ended, their wooden houses, palaces, and temples all sank along with all their goods.”
Dr. Sean Kingsley said: “In the last five years, extraordinary stuff has been coming up. Coins of all periods, gold and Buddhist statues, gems, all the kinds of things that you might read about in Sinbad the Sailor and think it was made up. It’s actually real.”
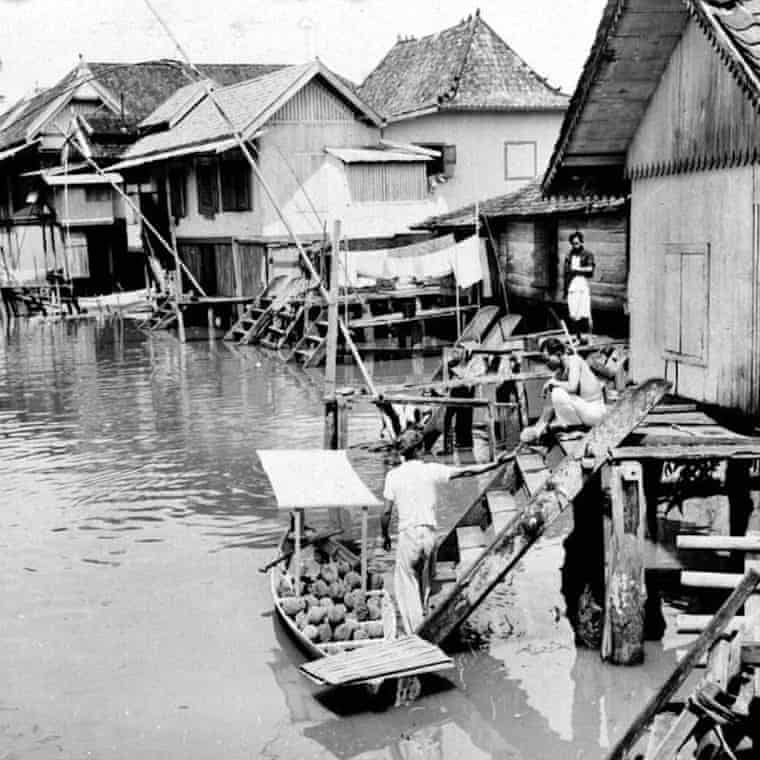

The findings will be published in the latest edition of Wreckwatch, which Kingsley edits. The Srivijayan research is part of a 180-page fall release on China and the Maritime Silk Road.
Dr. Sean Kingsley thinks Sumatra modern sea people, local fishermen, have finally figured out the Srivijaya mystery.
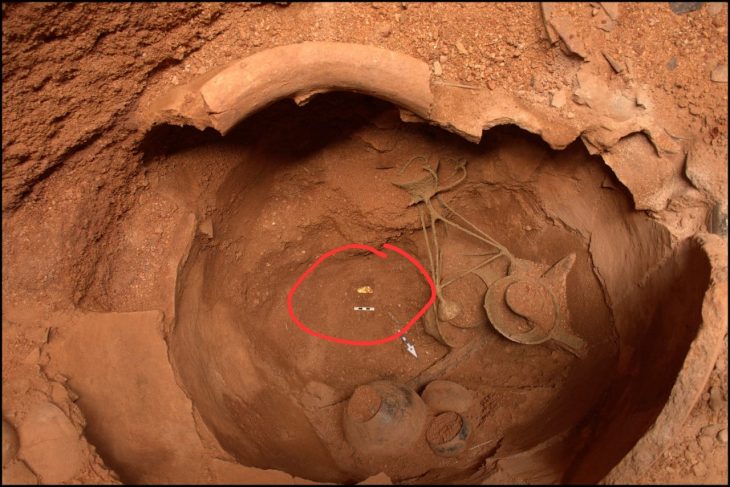
Previously, Australian archaeologists uncovered exquisite collections of pottery preserved in the river silt, reflecting an astonishing number of cultures—including every major Medieval power in Asia, as well as the Dutch, British, and Portuguese.
Kingsley noted that, at its height, Srivijaya controlled the arteries of the Maritime Silk Road, a colossal market in which local, Chinese and Arab goods were traded.
Dr. Kingsley picks up the narrative when he spoke with Dalya Alberge at The Guardian about his upcoming presentation on the lost city in Wreckwatch Magazine.
“From the shallows have surfaced glittering gold and jewels befitting this richest of kingdoms – everything from tools of trade and weapons of war to relics of religion. From the lost temples and places of worship have appeared bronze and gold Buddhist figurines, bronze temple door-knockers bearing the demonic face of Kala, in Hindu legend the mythical head of Rahu who churned the oceans to make an elixir of immortality. Bronze monks’ bells and gold ceremonial rings are studded with rubies and adorned with four-pronged golden vajra scepters, the Hindu symbol for the thunderbolt, the deity’s weapon of choice.”
The reason for the collapse of the kingdom is unclear. Kingsley speculates that it might have been Asia’s Pompeii, buried by Indonesia’s erupting volcanoes. The prevalence of volcanic activity in Indonesia could offer a Pompeii-like explanation, while it’s also possible that riverine activity could have swallowed the city up during a flood or mudslide.
Cover Photo: WreckWatch Magazine