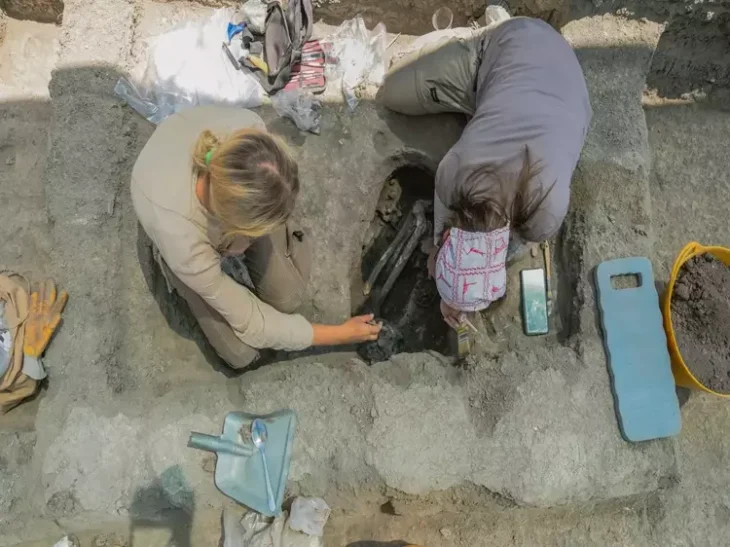
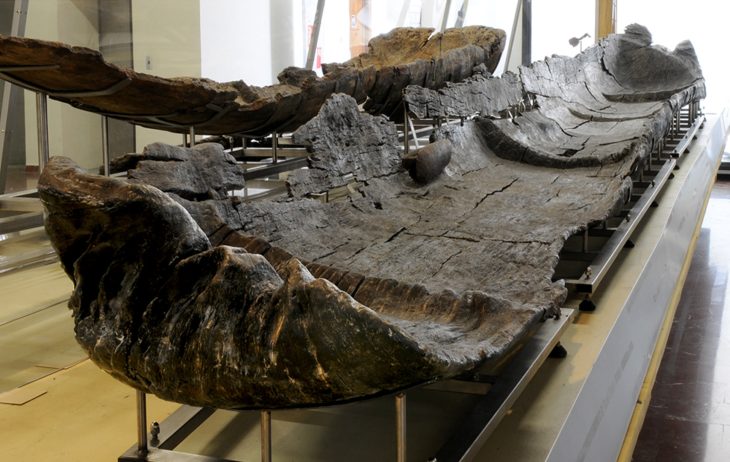
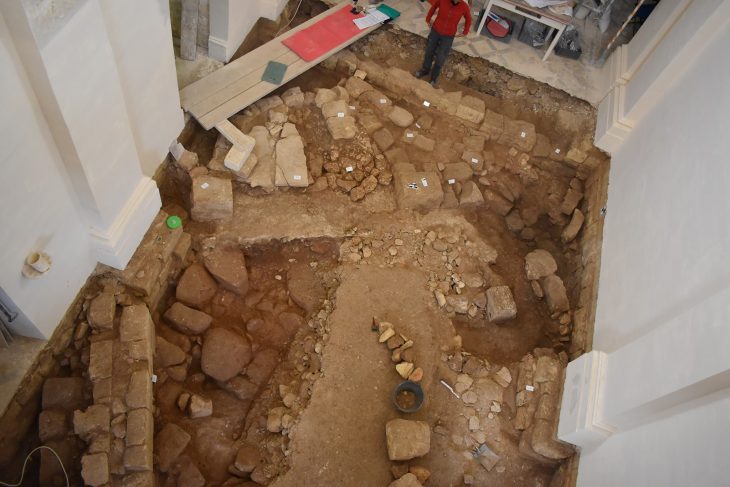
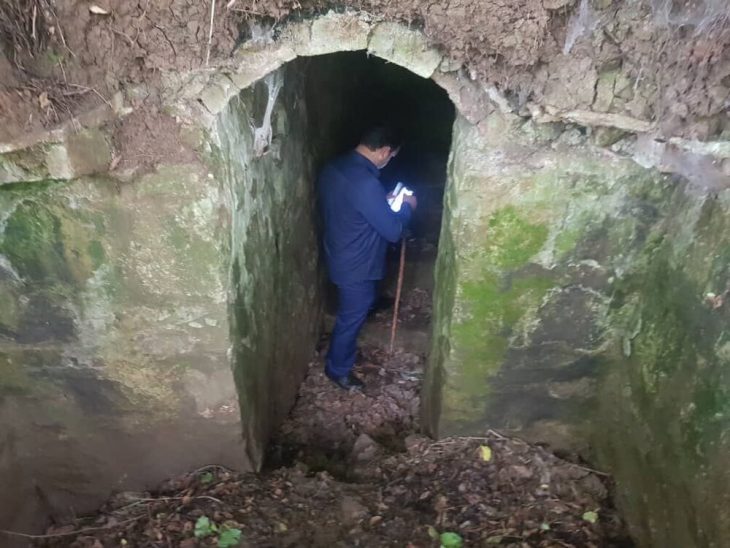
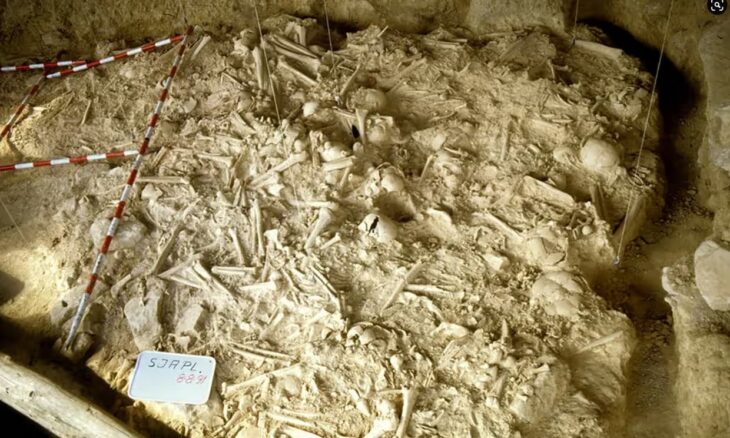
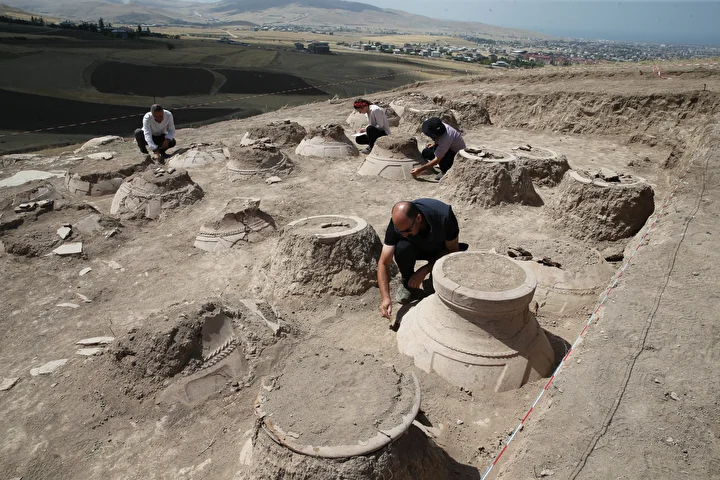
Excavations at the ruins of Kevenli Castle in Van’s İpekyolu district have brought to light the largest known storage center in Van to date. Archaeologists uncovered 76 massive pithoi, each carefully marked with cuneiform measurements, providing rare insight into how the Urartians stored and recorded agricultural products such as oil, grain, and beverages.
A Major Storage Center of the Urartian Era
The pithoi—massive storage jars—were used during the Urartian period (9th–7th centuries BC) to store oil, grain, and beverages. Experts believe the recently unearthed collection represents the largest storage facility ever identified in Van. Despite Kevenli Castle being relatively small in scale compared to other Urartian fortresses, the sheer volume of pithoi indicates that it functioned as a central depot for agricultural goods produced across the Van Plain.
Associate Professor Rıfat Kuvanç of Iğdır University, who is leading the scientific team, explained:
“Although Kevenli Castle is a small fortress, the discovery of 76 pithoi shows us that its storage capacity was far greater than expected. This suggests the castle played a vital role as a storage and distribution hub for agricultural products. For Van, this is the largest storage area ever identified so far.”
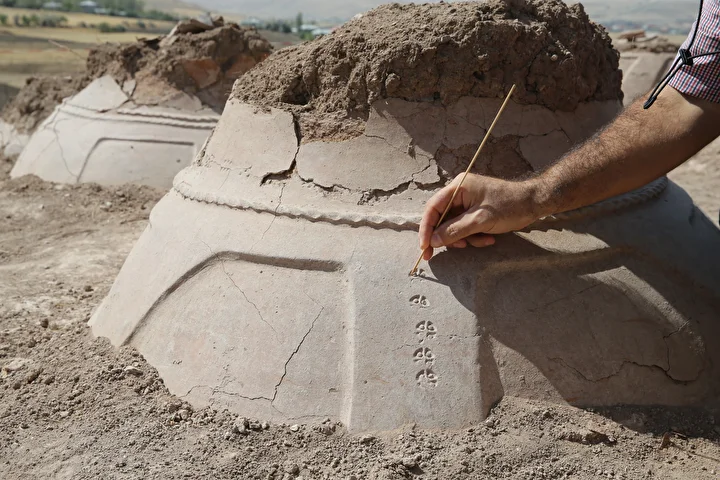

Evidence of Advanced Storage and Measurement Systems
Preliminary analysis has revealed that the pithoi were symmetrically arranged and inscribed with cuneiform signs. These inscriptions provide crucial information about the volume and types of goods stored inside, demonstrating the Urartians’ advanced methods of inventory management. Archaeobotanical studies are also underway: researchers found traces of seeds inside some of the jars and plan to conduct ancient DNA analysis to better understand the agricultural economy of the region.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The excavations also uncovered part of a terracotta water conduit (küng) that likely supplied liquid to the storage chambers. This find highlights the engineering capabilities of the Urartians, who constructed complex water and storage systems across their fortified settlements.
Wall Paintings and Ceramics Add Cultural Depth
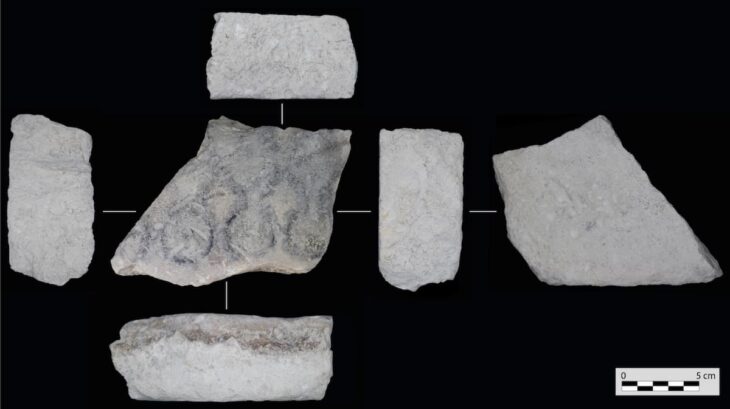
Beyond storage, Kevenli Castle has yielded fragments of painted plaster in red and black, indicating that some walls were adorned with murals. This suggests the fortress held administrative or ceremonial functions alongside its role as a depot.
Among the ceramic finds, archaeologists identified examples of “palace ware”, a fine red pottery style associated with Urartian elites. One shard even depicted a lion figure, underscoring the symbolic and cultural value embedded in daily objects.

The Strategic Role of Kevenli Castle
Kevenli Castle is located only about 10 kilometers from Van Castle (ancient Tushpa), the Urartian capital built by King Sarduri I in the 9th century BC. Its strategic position on the slopes of Mount Erek allowed it to both guard the fertile Van Plain and serve as a logistical support point for the capital.
Covering approximately 4,500 square meters and fortified by defensive walls, the site combined military protection with resource management, a dual-purpose design typical of Urartian strongholds.
A Landmark Discovery for Urartian Studies
The discovery at Kevenli Castle adds significantly to the growing body of evidence that the Urartians were not only skilled warriors and builders but also master organizers of agricultural resources. The combination of cuneiform-labeled pithoi, water infrastructure, and decorated walls makes Kevenli one of the most informative Urartian sites discovered in recent years.
As Dr. Kuvanç noted, “Every jar, every inscription brings us closer to understanding the organization and daily life of the Urartians. Kevenli Castle has already proven itself as one of the most significant Urartian discoveries in Van.”
Excavations will continue in hopes of uncovering additional storage facilities, murals, and artifacts that will further enrich our knowledge of this Iron Age civilization.
Cover Image Credit: Mesut Varol – AA