Sometimes art and architecture challenge our perceptions of what was formerly thought to be feasible and what our forefathers were capable of.
An excellent example of this is the abandoned megalithic capital of Nan Madol, which is situated in a lagoon next to the island of Pohnpei in the Federated States of Micronesia in the Pacific Ocean.
The ruined city is one of today’s great archaeological enigmas and is sometimes called “Atlantis“, the “eighth wonder of the world,” or the “Venice of the Pacific”.
Few historic places in the Pacific are as intriguing as Nan Madol. Set apart between the main island of Pohnpei and Temwen Island, it was a scene of human activity as early as the first or second century AD. Islet construction had begun by the 8th or 9th century, with the development of the characteristic megalithic style commencing 1180-1200 AD.
Nan Madol was a prominent political and spiritual center for native Pohnpeians until it was abandoned. Between 1200 and 1700, the city operated as a religious center, a royal enclave, a stronghold, an urban marketplace, and the island of Pohnpei’s high seat of government.
Nan Madol was the capital of the Saudeleur dynasty, which unified all of Pohnpei’s estimated 25,000 people at its peak. The Saudeleur were a foreign tribe who arrived in Pohnpei and established themselves as the island’s rulers. The Saudeleur originally emerged about the year 1100, while Nan Madol was established around the year 1200.
Oral tradition on Pohnpei states that Olisihpa and Olosohpa, two brothers who traveled by canoe and wielded sorcery with the help of the gods to construct Nan Madol, were the first Saudeleur to land on the island. The local Pohnpeians were so moved by this that they encouraged the Saudeleur to join their tribe through marriage. Eventually, one of the brothers passed away, and the other crowned himself king. The Saudeleur built Nan Madol as a temple for the farm god Nahnisohn Sapw, the god worshipped by the Saudeleur nobility.
What is surprising is the relationship between this oral history, which has been passed down for centuries, and the evidence unearthed during archaeological excavations in the region. For example, oral traditions make references to small canals cut into the islets, allowing sacred eels to enter from the sea so that they could be honored through the sacrifice of captured sea turtles. Subsequent excavations have revealed traces of both the small canals and the sacrificial turtles.
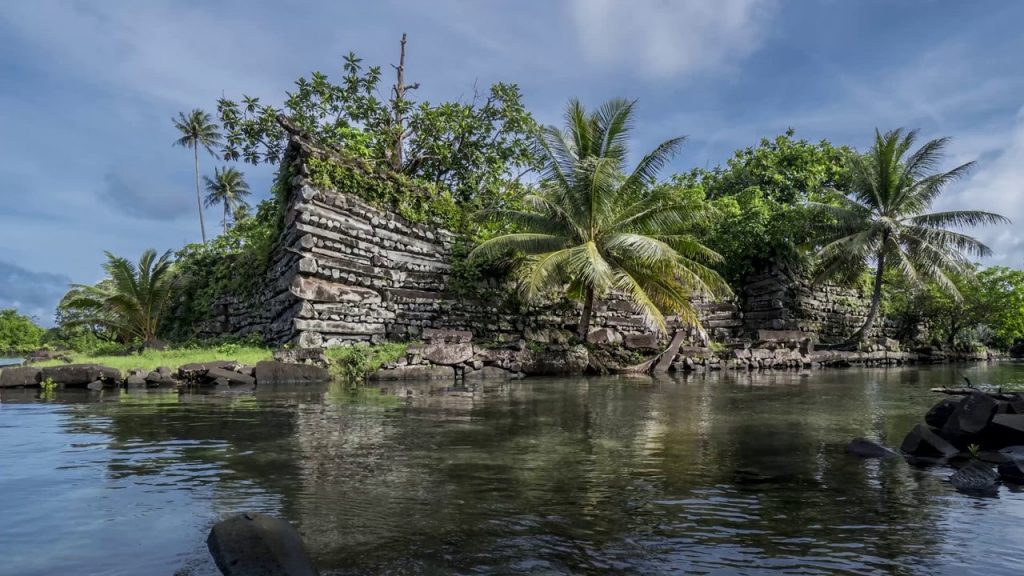

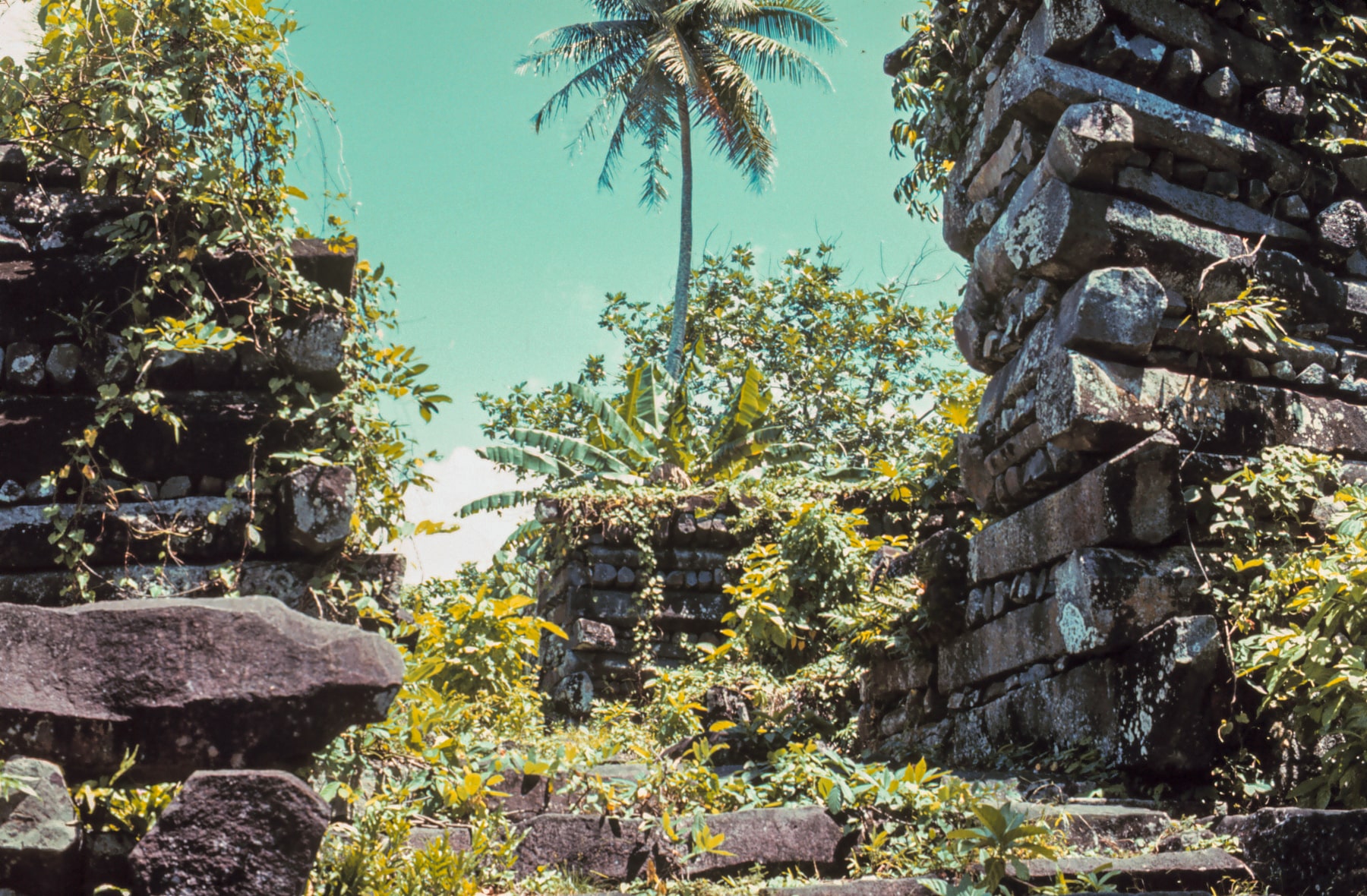
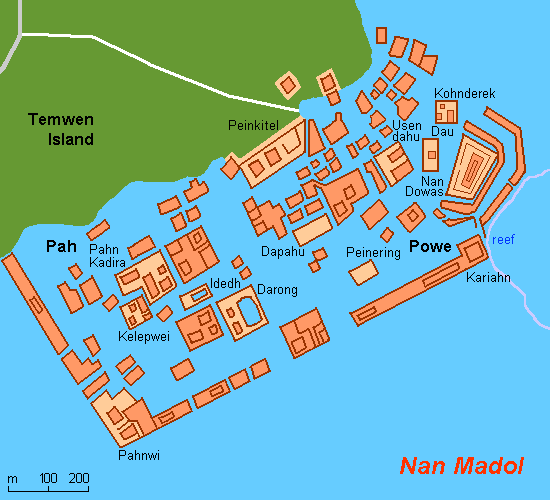
The city, constructed in a lagoon, consists of a series of small artificial islands linked by a network of canals. Nan Madol is the only extant ancient city built on top of a coral reef.
Nan Madol has been dubbed by some as the “eighth wonder of the world” and others as the “Venice of the Pacific”. The reference to Venice comes from the canals that connect 100 man-made islets spread over 200 acres built with basalt and coral boulders.
The site core with its stone walls encloses an area approximately 1.5 km long by 0.5 km wide and it contains nearly 100 artificial islets—stone and coral fill platforms—bordered by tidal canals.
Its basalt and coral rock structures were built from the 13th to the 17th century by a population of fewer than 30,000 people and their total weight is estimated at 750,000 metric tons.
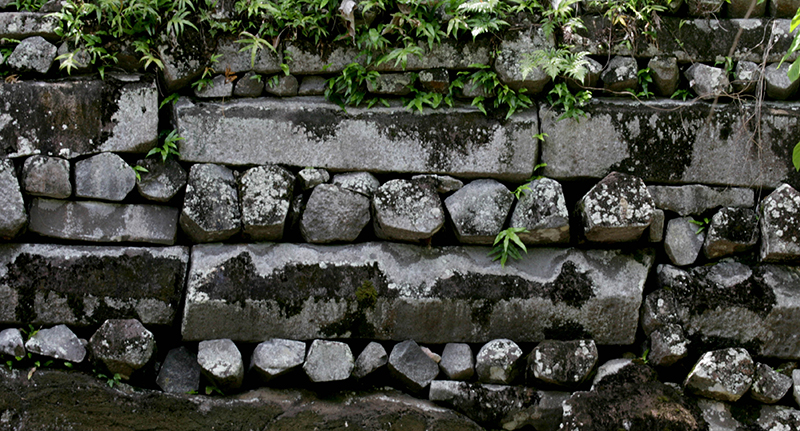

By stating that over a period of four centuries, the inhabitants of Pohnpei transported an average of 1,850 tons of basalt every year—and no one is entirely sure how they did it—archaeologist Rufino Mauricio helps us put these enormous amounts into perspective.
The natural coral foundation that is just below the water’s surface supports the structures. The Nandauwas, a royal temple encircled by 25-foot high walls, is the biggest building. The Pohnpeians used an unknown method to sink the massive stones into the lagoon because they lacked sophisticated diving gear and binding materials like concrete.
The building remains and canals are stable enough that even after centuries of abandonment visitors can still tour Nan Madol by boat. The complete building complex is a suitable homage to the advanced techniques used by its Pohnpeian builders. The scale and superiority of its stone architecture, its artificial islet construction, and the modification of the shoreline contribute to the significance of the site.
It seems that the Saudeleur Dynasty was deeply religious and sometimes cruel. According to oral history, later generations of Saudeleur aristocrats became increasingly oppressive, often forcing the native Pohnpeians into starvation.
Isokelekel, the warrior hero, led an invasion of Pohnpei in 1628 and conquered the Saudeleur tribe. According to Pohnpeian legend, Isokelekel was a demigod and the vengeful son of the Pohnpeian storm deity Nahn Sapwe, who had become tired of the tyranny of Nahnisohn Sapw and the Saudeleur. Historians say Isokelekel led a group of Micronesian settlers from the adjacent island of Kosrae. With the help of the oppressed Pohnpeian folk, Isokelekel led his battle band of warriors, women, and children to triumph. Nan Madol’s importance to Pohnpeians waned after the Sandaleur’s loss, and it was finally abandoned in the 18th century.
Cover Photo: Wikipedia
















