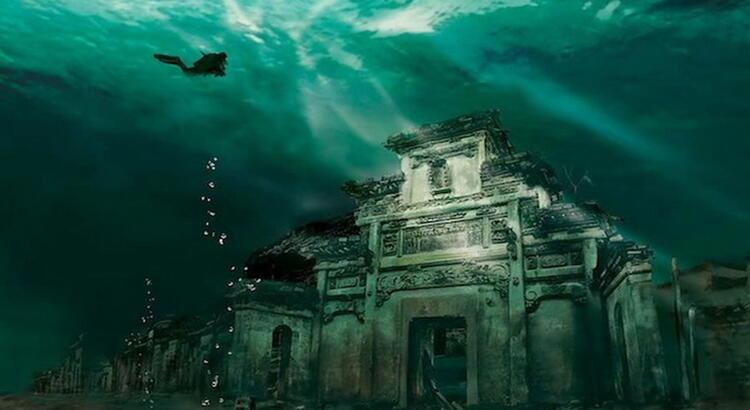
Thonis-Heracleion (Egyptian and Greek names of the city) is a port city lost between myth and reality until 1999.
Few people now have heard of Thonis-Heracleion, as opposed to Babylon, Pompeii, Truva, or the legendary Atlantis. Indeed, until recent discoveries, it was possible that the waves of the Mediterranean would condemn not only the city’s physical ruins but also its memory, to history.
The city was presumably established in the 8th century BC, experienced several natural disasters, and eventually sank completely under the waters of the Mediterranean in the 8th century AD.
Most historians thought Thonis-Heracleion were two different conurbations, both of which were located on the modern Egyptian mainland, until 1933 when an RAF captain flying over Abu Qir saw ruins in the sea.
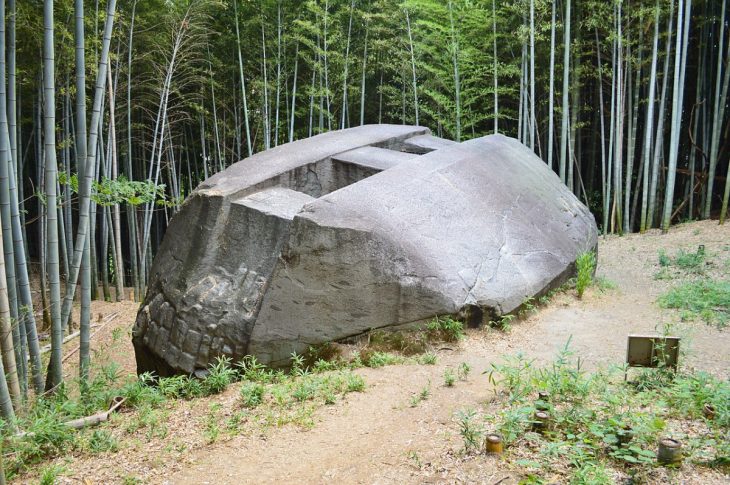
The ruins submerged in the sea were located and explored by the French underwater archaeologist Franck Goddio in 1999, after a five-year search.
Thonis-Heracleion founded approximately 2,700 years ago on the location of present-day Abu Qir bay, 15 miles north-east of Alexandria, preceded its better-known neighbor as the region’s major emporium (trading port) by several centuries and was a center for international commerce.
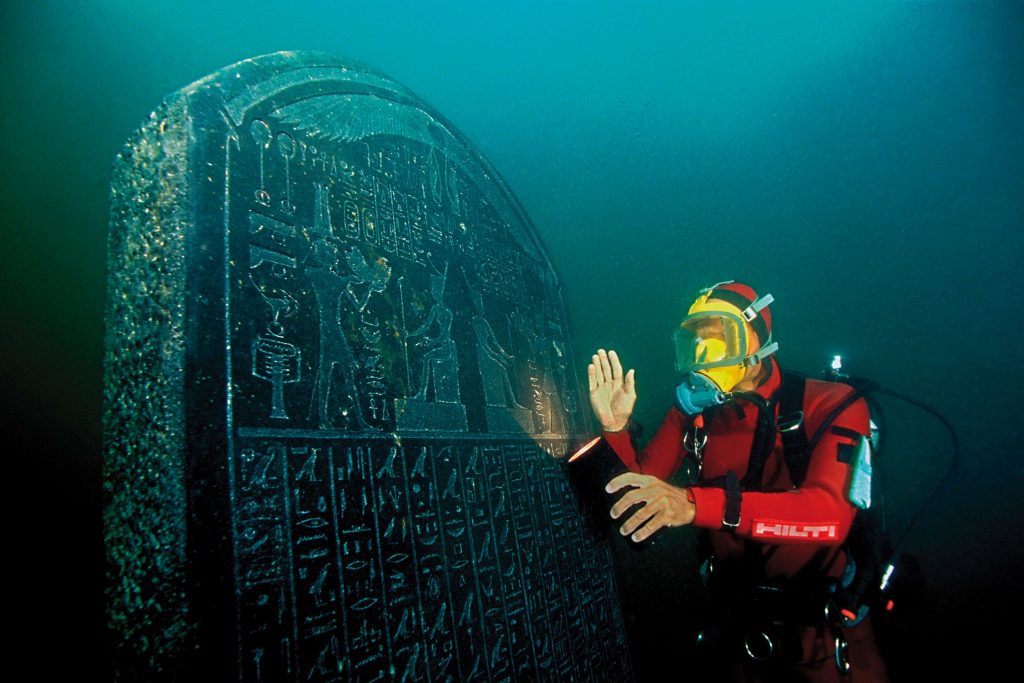

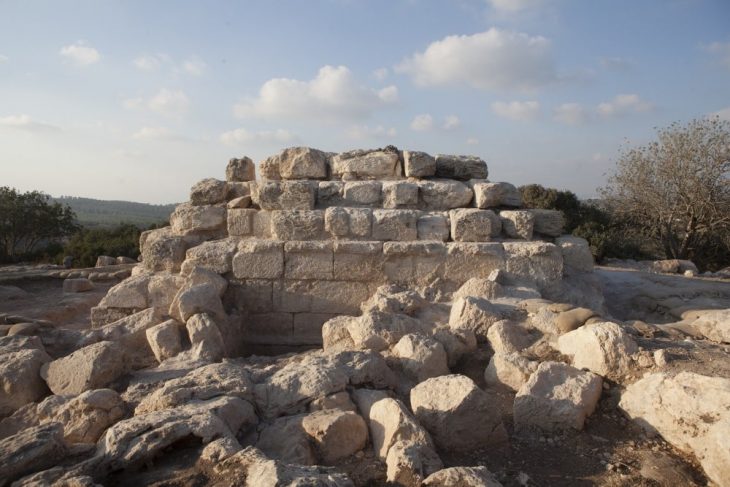
The city, crisscrossed by canals and populated with harbors, wharves, temples, and tower-houses – all linked together by a network of ferries, bridges, and pontoons — controlled the majority of the nautical commerce entering Egypt from the Mediterranean. Goods would be inspected and taxed at the customs administration center before being transported further inland, either to Naukratis – another trading port nearly 50 miles up the Nile – or via the Western Lake, which was connected by a water channel to the nearby town of Canopus and provided access to many other parts of the country.
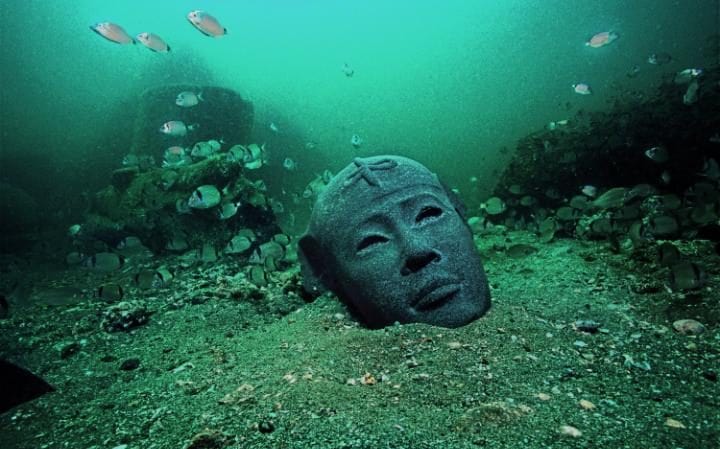

Thonis-Heracleion had a huge temple dedicated to Khonsou, son of Amun and known as Herakles to the Greeks. Amun worship grew increasingly popular later on. During the sixth and fourth centuries BC, when the city was at its peak, a huge temple dedicated to Amun-Gereb, the Egyptians’ supreme god of the period, stood in the heart of the city.
Thonis-Heracleion and Canopus was a city described by many great historians of antiquity, from Herodotus to Strabo and Diodorus.
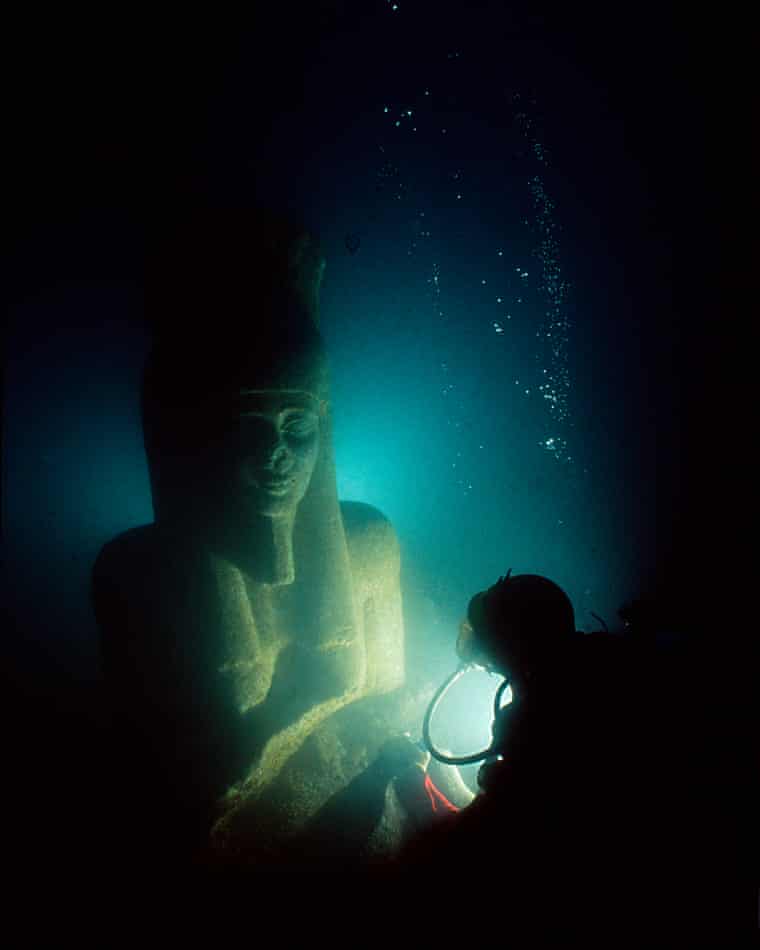

During the second century, BC Alexandria superseded Thonis (Heracleion) as Egypt’s primary port. According to the Greek historian Herodotus (5th century BC), a magnificent temple was constructed where the famed hero Herakles first set foot in Egypt. He also mentions Helen’s journey to Heracleion before the Trojan War with her lover Paris. More than four centuries after Herodotus’ journey to Egypt, the geographer Strabo noted that the city of Heracleion, which held the temple of Herakles, is located directly east of Canopus at the entrance of the Canopic branch of the Nile.
Thonis-Heracleion’s of pomp and glory was waning by the second century BC. Along the coast, the new metropolis of Alexandria was quickly establishing itself as Egypt’s foremost port, while the hybrid foundation of land and sea upon which Thonis-Heracleion was constructed was beginning to seem less secure. The city was destroyed not by a single natural calamity — an earthquake, tsunami, increasing sea levels, or subsidence – but by a mixture of them all.
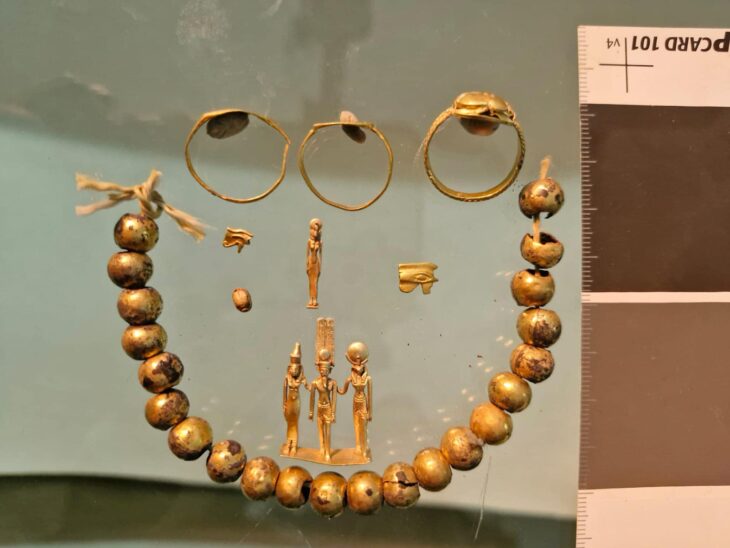
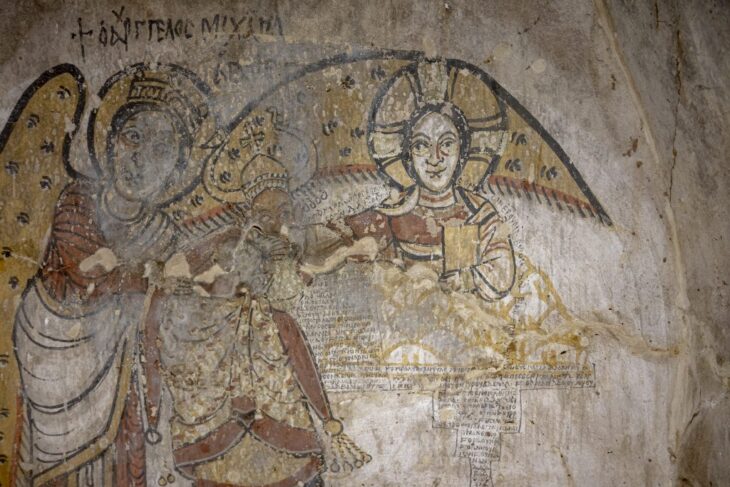
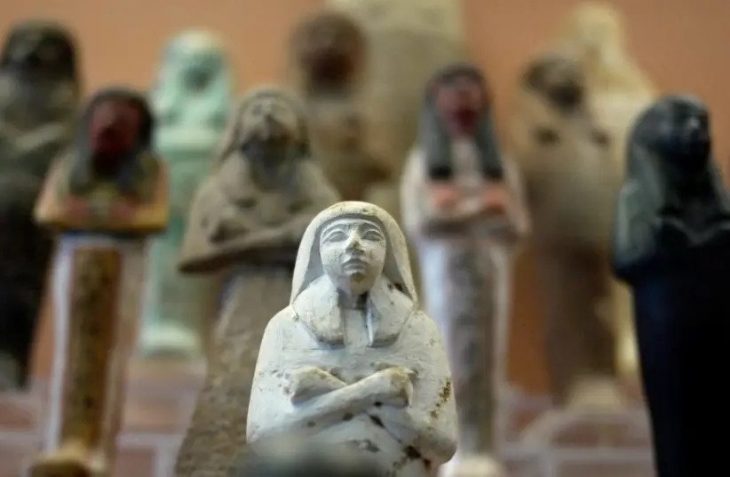
The excavated items depict the city’s beauty and splendor, the magnificence of their enormous temples, and the richness of historic evidence: colossal sculptures, inscriptions, and architectural components, jewelry and coins, ritual goods, and ceramics – a civilization trapped in time.
The most striking artifact among the city finds is undoubtedly the 5.4-meter-high statue of the god Hapy.
The underwater archaeological excavations at Thonis-Heracleion are still underway. Only 5% of the city, according to Franck Goddio, has been uncovered.