A study conducted by an international team coordinated by Sapienza University of Rome and the Italian National Research Council (CNR) reveals the genetic origins of the Piceni and describes the genetic structure of one of the most fascinating civilizations of pre-Roman Italy.
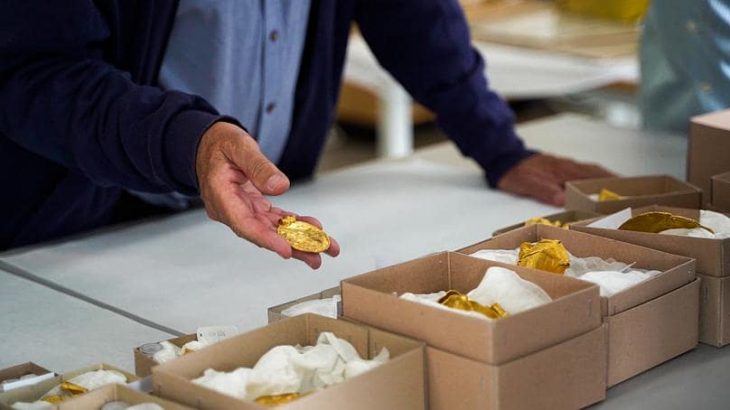
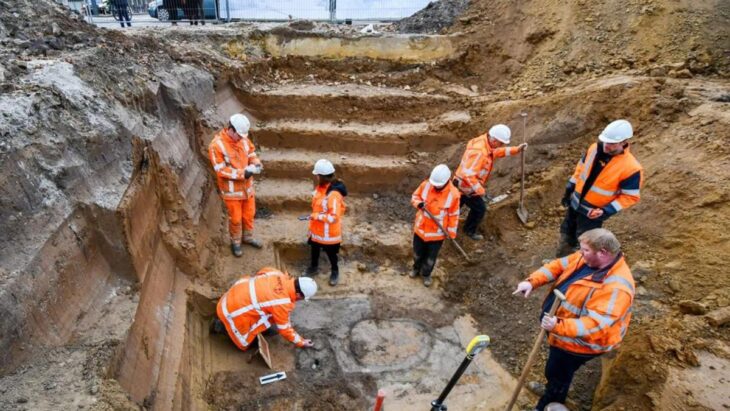
This study explores the DNA of over 100 skeletal remains found in ancient necropolises in central Italy, covering a period of more than a thousand years, from the Iron Age to Late Antiquity.
The findings, published in the journal Genome Biology, revealed a surprising genetic history that differentiates Adriatic from Tyrrhenian peoples and provides new insights into the genetic legacy of the Roman Empire, and its role in shaping genetic and phenotypic changes throughout the Italian peninsula.
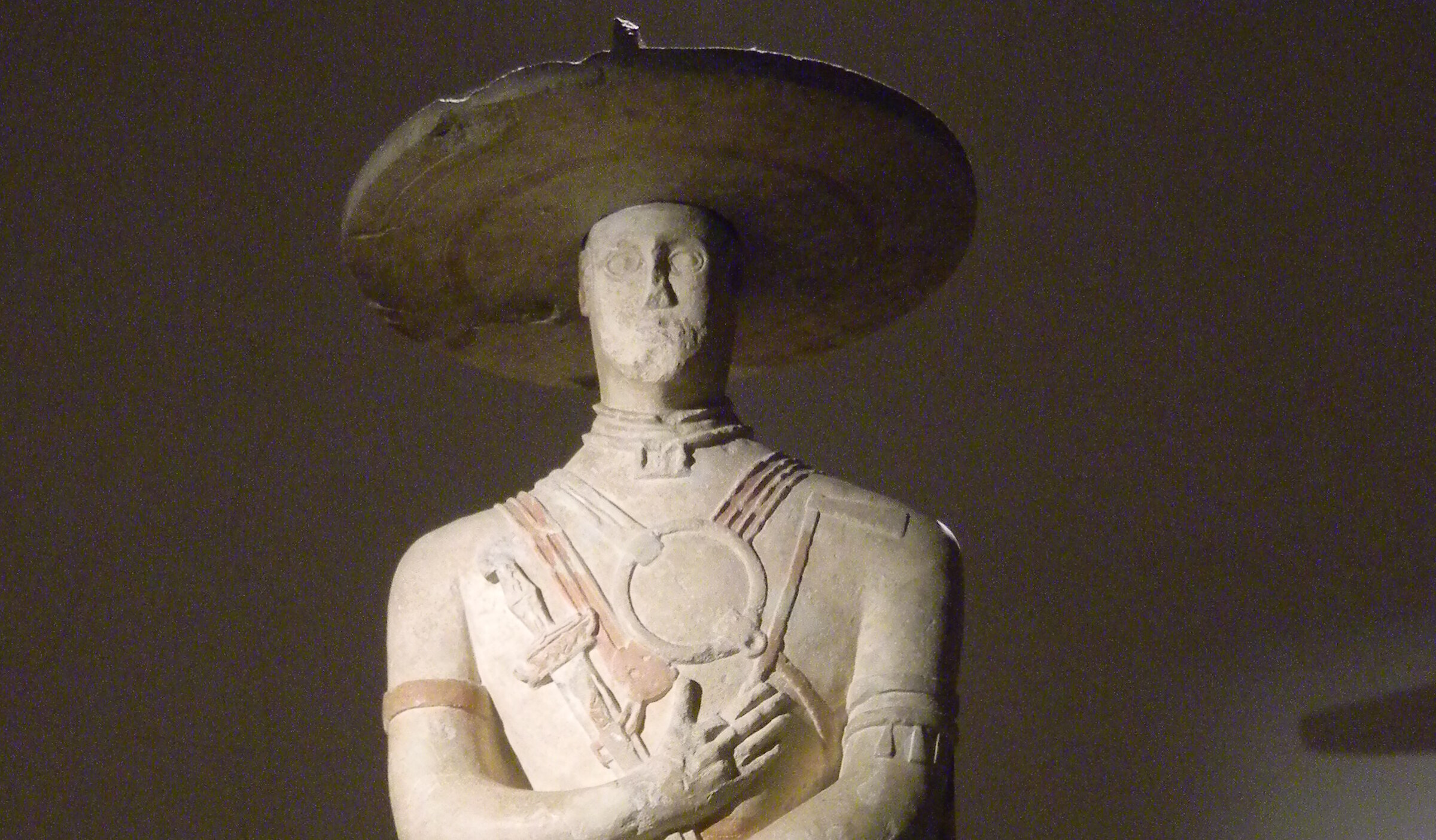
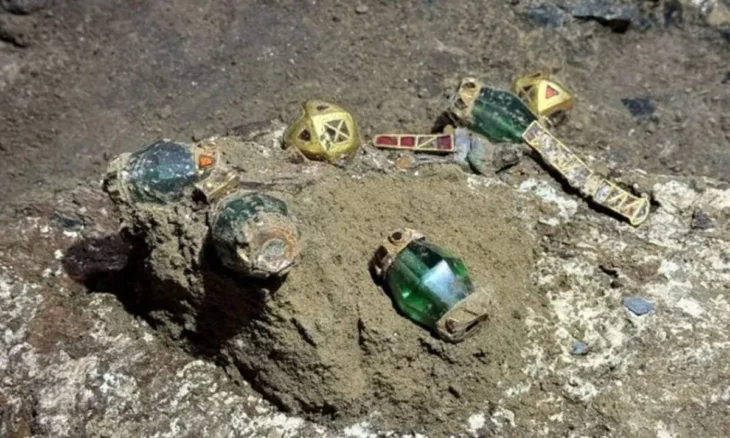
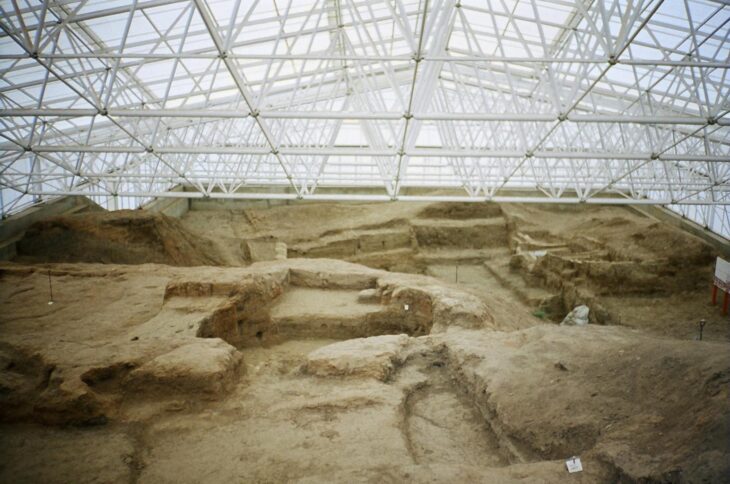
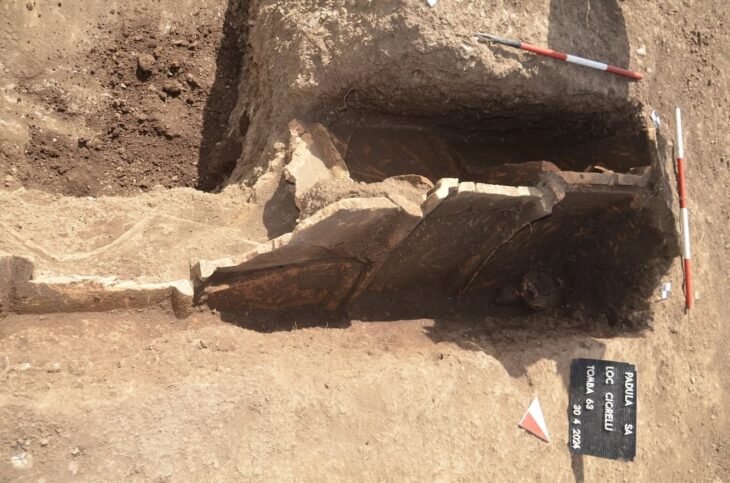
The ancient Italic people known as the Picentes or Piceni lived between the rivers of Foglia and Aterno from the ninth to the third century BC. The region was bounded to the east by the Adriatic coast and to the west by the Apennines. Their territory, known as Picenum, therefore included all of today’s Marche and the northern part of Abruzzo. Information on the Pictish civilization is based mainly on archaeological documents from necropolises, as well as settlement remains and votive relics.
The knowledge of the Picene civilization is mainly based on archaeological documentation, coming from (in primis) from necropolises but also from the remains of settlements and votive deposits.
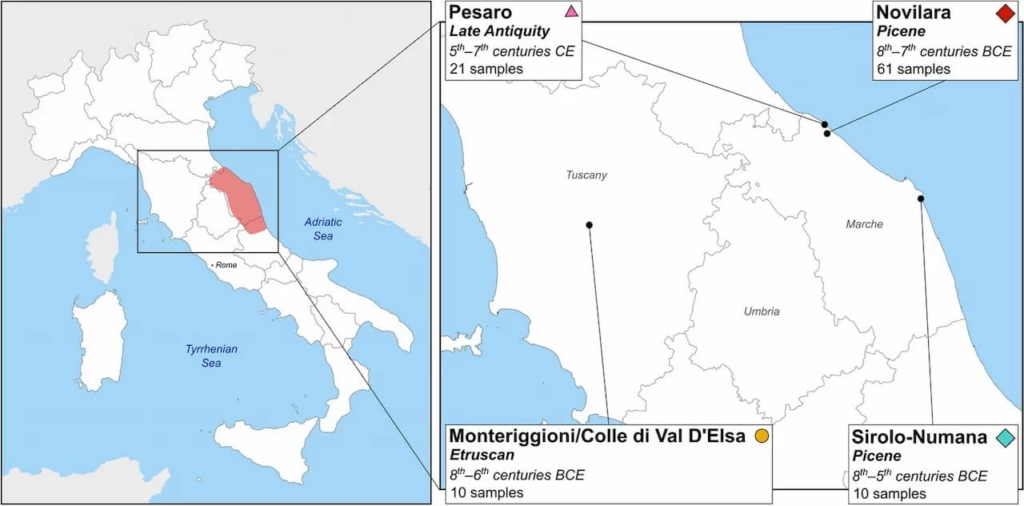
“We have a great phantom that has haunted us for many decades: on the Adriatic, this phantom is the Piceni”-that is how Massimo Pallottino, the scholar who has contributed more than any other to the study of pre-Roman Italy, expressed himself in 1975. Today, thanks to an interdisciplinary study that has seen the synergistic collaboration of archaeologists and geneticists, that “ghost” comes back to life, it provides an in-depth exploration of the origins, contacts, and evolution of the Piceni, one of the most fascinating civilizations of pre-Roman Italy.
The study found that the Piceni differ significantly from populations on the Tyrrhenian coast of the Italian peninsula in terms of genetic makeup, indicating that the geographical and cultural contexts of these two communities contributed to the development of unique traits.
One of the most fascinating aspects to emerge from the research is the phenotypic diversity of the Picenes compared to their neighbors. The study found that they showed a greater prevalence of phenotypic traits such as blue eyes and light hair, features much less common among coeval populations such as the Etruscans and Latins. This physical diversity, combined with genetic contacts with Northern European and Near Eastern populations, makes the Picenes a unique case in the study of pre-Roman Italy.

It appears that this physical diversity reflects the mix of genetic influences that this civilization has encountered as a result of its geographic location and interactions with other peoples. Because of the constant stream of migrants and traders into the area, the Piceni’s phenotypic diversity points to a degree of cosmopolitanism that may have grown stronger over time.
For Beniamino Trombetta, another author of the study and professor of Human Genetics at La Sapienza, the study opens up new possibilities for reinterpreting the peninsula’s history, showing that a cosmopolitan society began to form in Italy during the Iron Age and reached its peak during the Roman Empire.
Sapienza University of Rome (Università di Roma – Sapienza)
Ravasini, F., Kabral, H., Solnik, A. et al. The genomic portrait of the Picene culture provides new insights into the Italic Iron Age and the legacy of the Roman Empire in Central Italy. Genome Biol 25, 292 (2024). doi.org/10.1186/s13059-024-03430-4
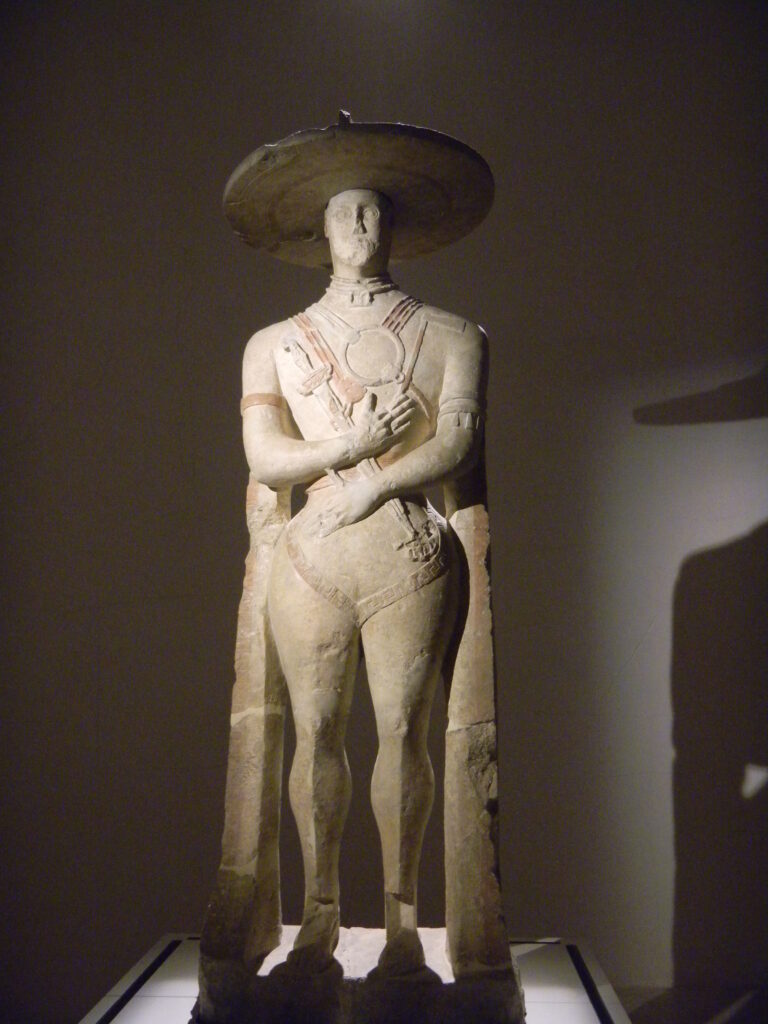
Cover Image: The Capestrano Warrior, created by the Picena culture. Credit: Elisa Triolo/ Wikimedia Commons