In the Albanian port city of Durrës, archaeologists have uncovered a 1600-year-old Roman indoor pool, the first of its kind.
Durrës is Albania’s oldest economic and historic center, having emerged as a permanent gate between the east and the west. The city was known as Epidamnus by the Illyrians in the seventh and sixth centuries BC. The Greeks colonized the city in 672 BC and called it “Dyrrhachium,” or “The city between the two hills.”
The Romans took over the city around 230 BC. The city was known to the Roman historian Catullus as “Dyrrhachium Adria e Taberna,” or “The Adriatic Tavern.” Cicero, who took refuge in Durrës circa 57 BC, described the city as “admirable,” mainly because of his colorful and active lifestyle.
The archaeologists of the city of Durres are familiar with Roman remains, but the latest discovery surprised even them.
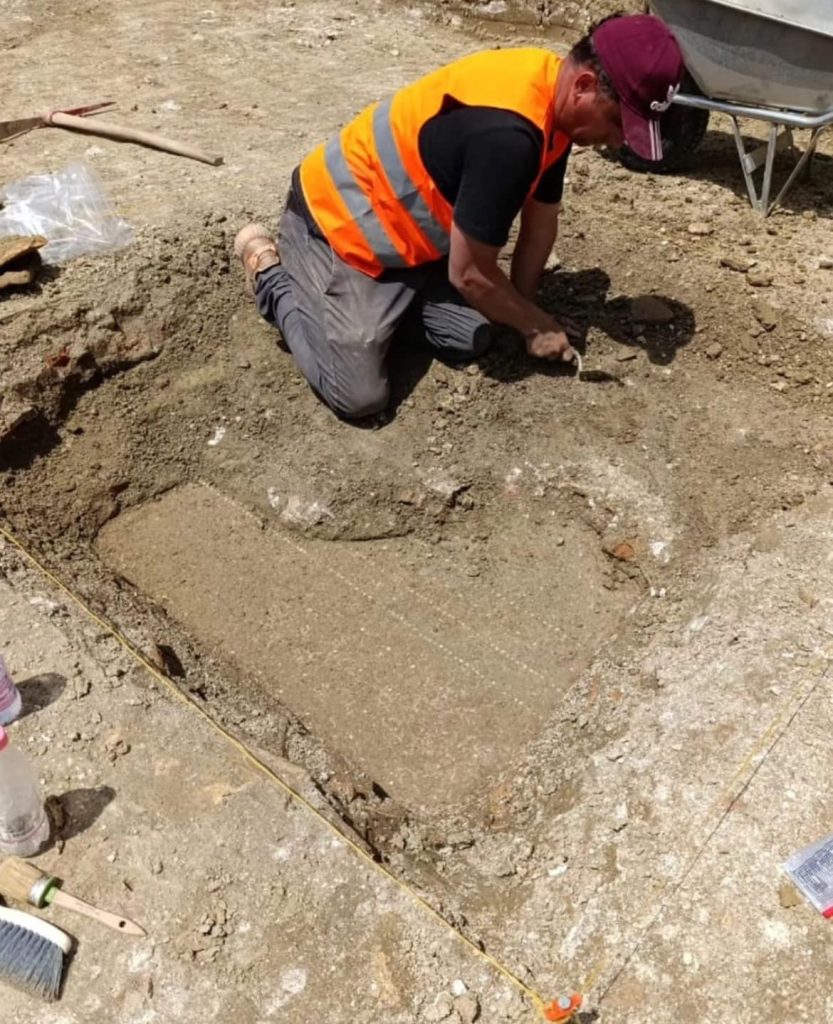

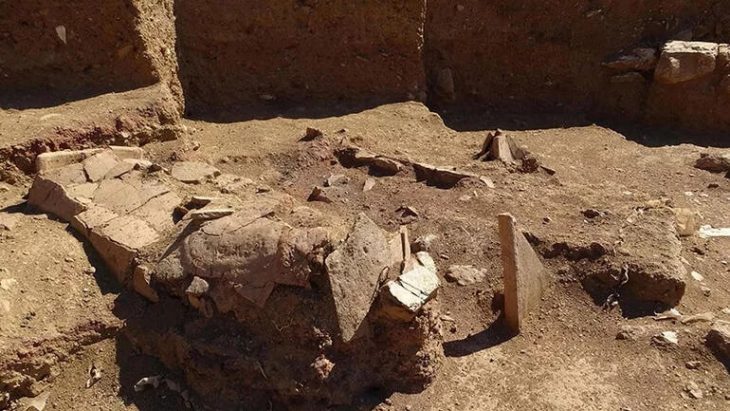
Prior to a school being built, archaeologists were excavating a site in Durrës when they discovered an aristocratic ancient Roman neighborhood, according to a May 9 Facebook post from Albania’s National Institute of Cultural Heritage.
The National Institute of Cultural Heritage said that the archaeological excavations, which cover an area of 1,200 m2, at this stage, have provided a unique panorama of the urban organization of the area, which is thought to have been a part of the city.
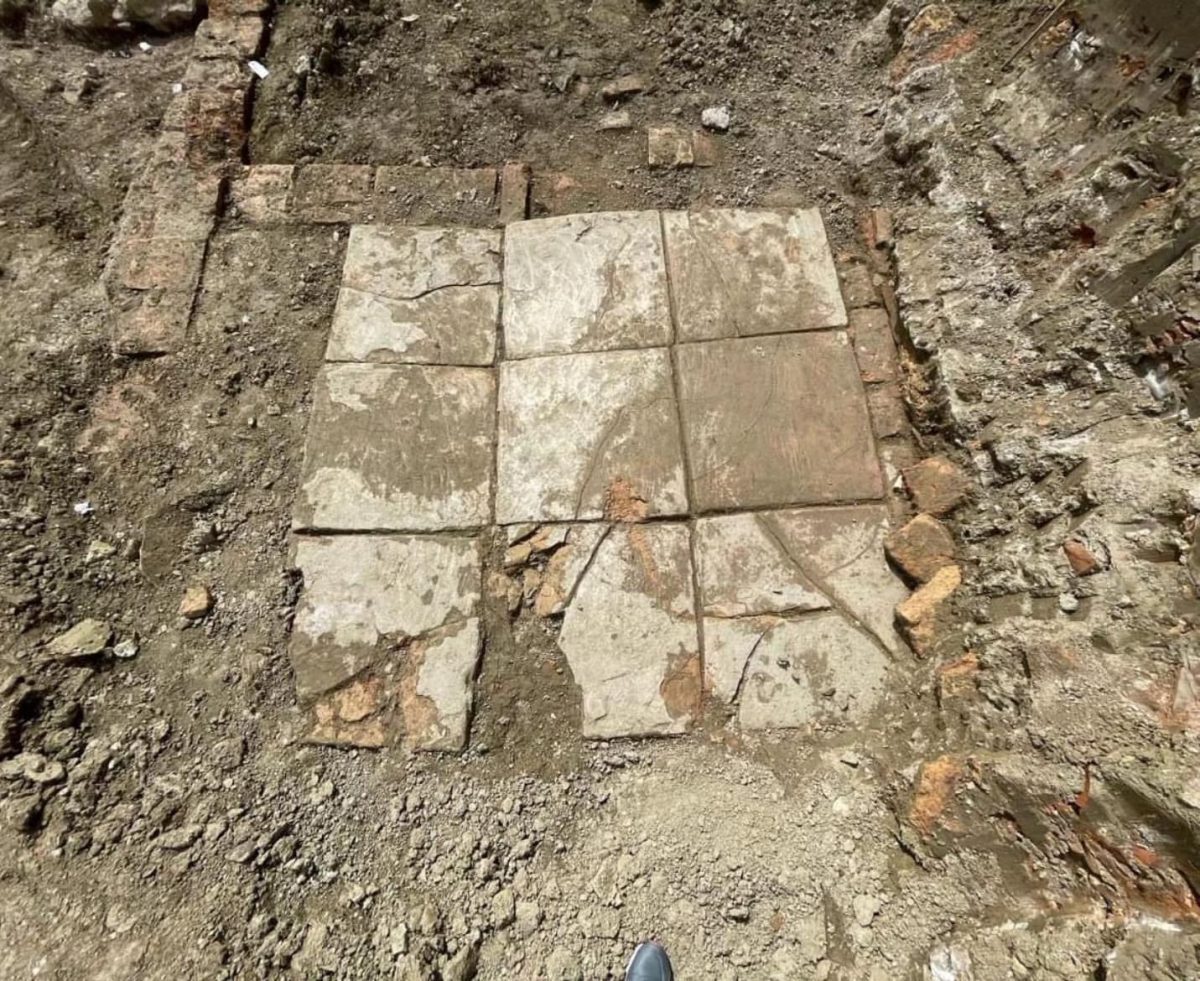
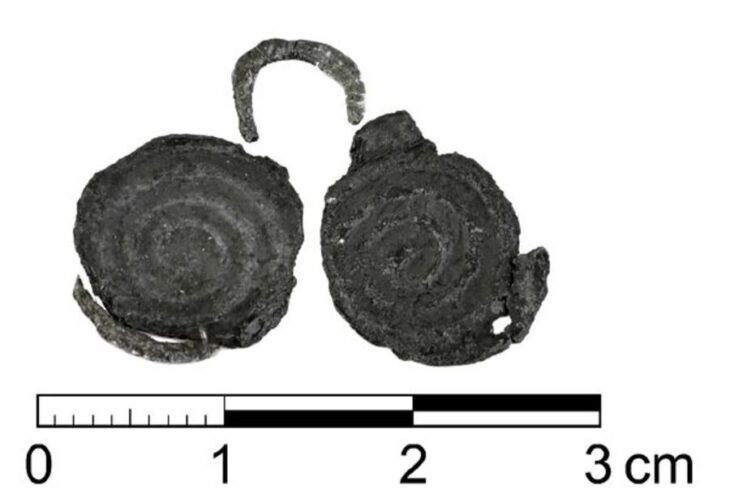
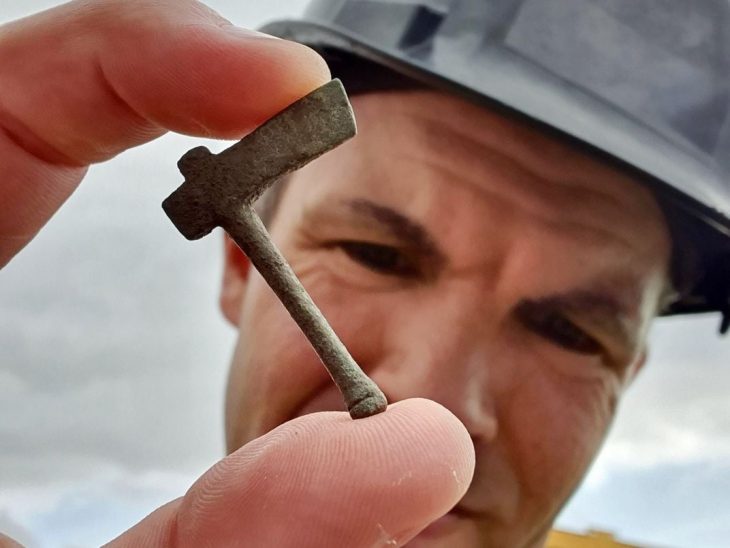
Among the ruins of an ancient Roman villa were traces of an indoor pool decorated with well-preserved mosaics, the institute said.
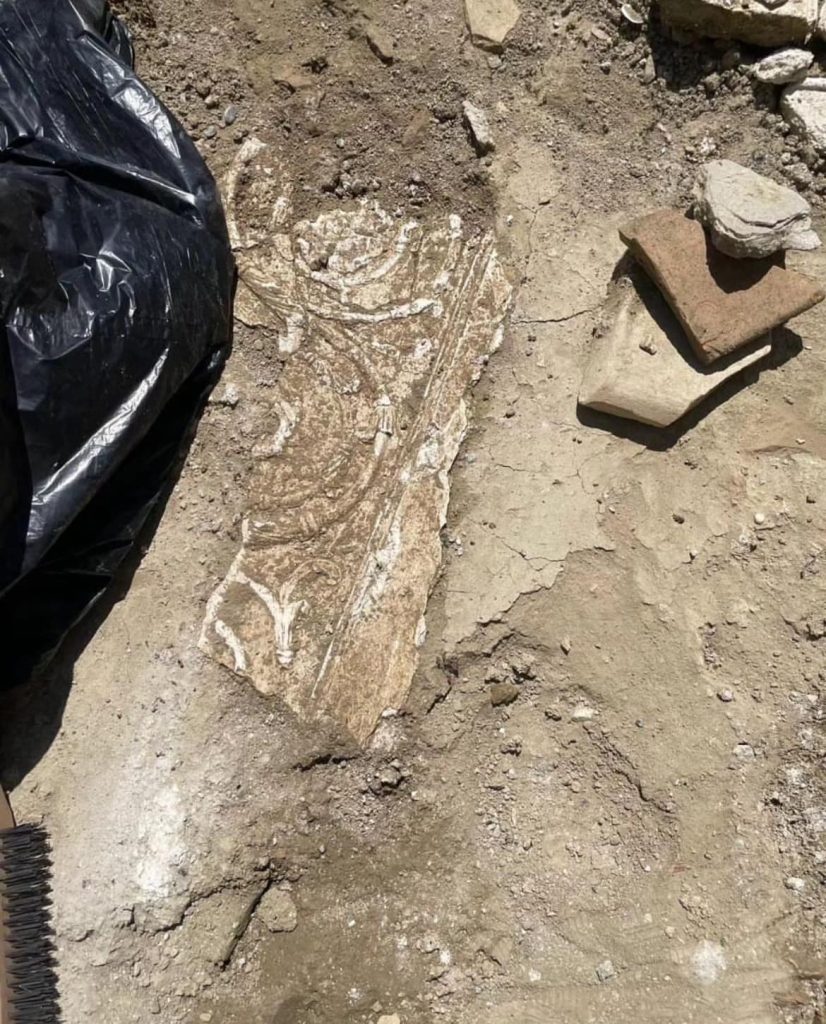

“From the excavations, the remains of an indoor swimming pool of a Roman period residence were discovered, the first of its kind discovered in Albania. It is decorated on its entire surface with colorful frescoes of a high artistic level.” The Institute underlined that the most important feature of the building is that it has a very well-preserved mosaic floor with geometric motifs made of marble, stone, glass, and ceramic tiles.
Archaeologists estimated that the Roman ruins were between 1 and 400 A.D. old, and at least 1,600 years old.
According to the institute, excavations at a different part of the site revealed several walls and a sizable brick floor that may be the remnants of a two-story ancient Roman bathhouse. Other fragments of walls, ceilings, and tile mosaics were also uncovered.
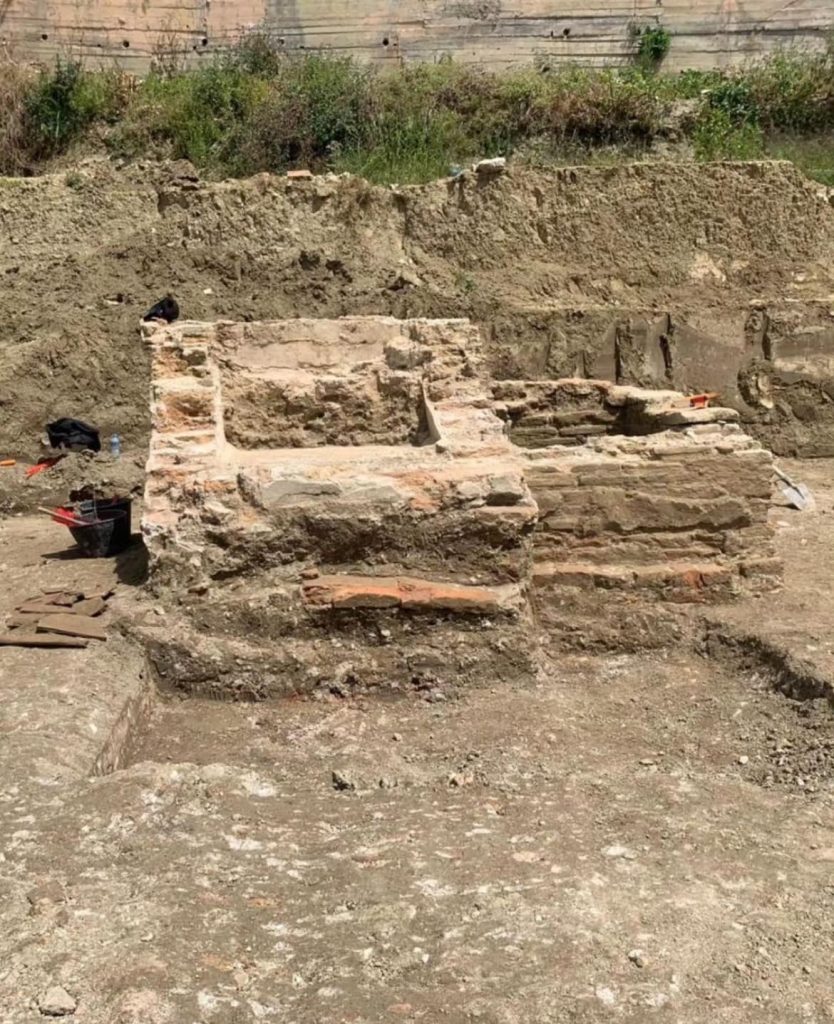

Excavations at the construction site are ongoing.
The Facebook post from Albania’s National Institute of Cultural Heritage was translated using Google Translate.
Cover Photo from Albania’s National Institute of Cultural Heritage