A set of surgical tools indicating that the deceased was a surgeon was found in a funerary bundle found in a Sicán culture tomb in Lambayeque, Peru.
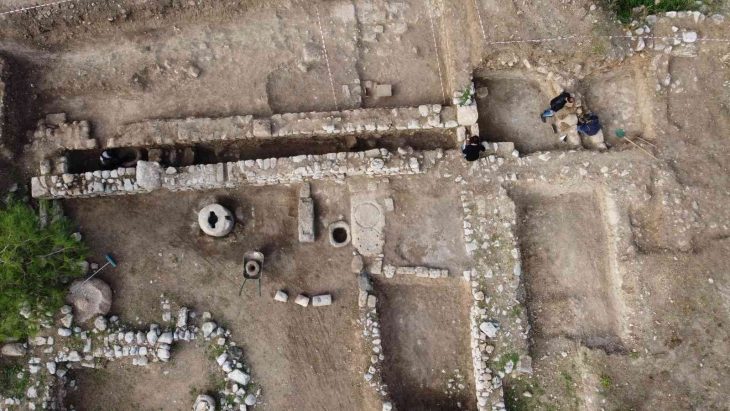
The tomb is from the Middle Sicán period (900-1050 AD) at the Huaca Las Ventanas archaeological site. This is the first such find ever made in Lambayeque or in northern Peru.
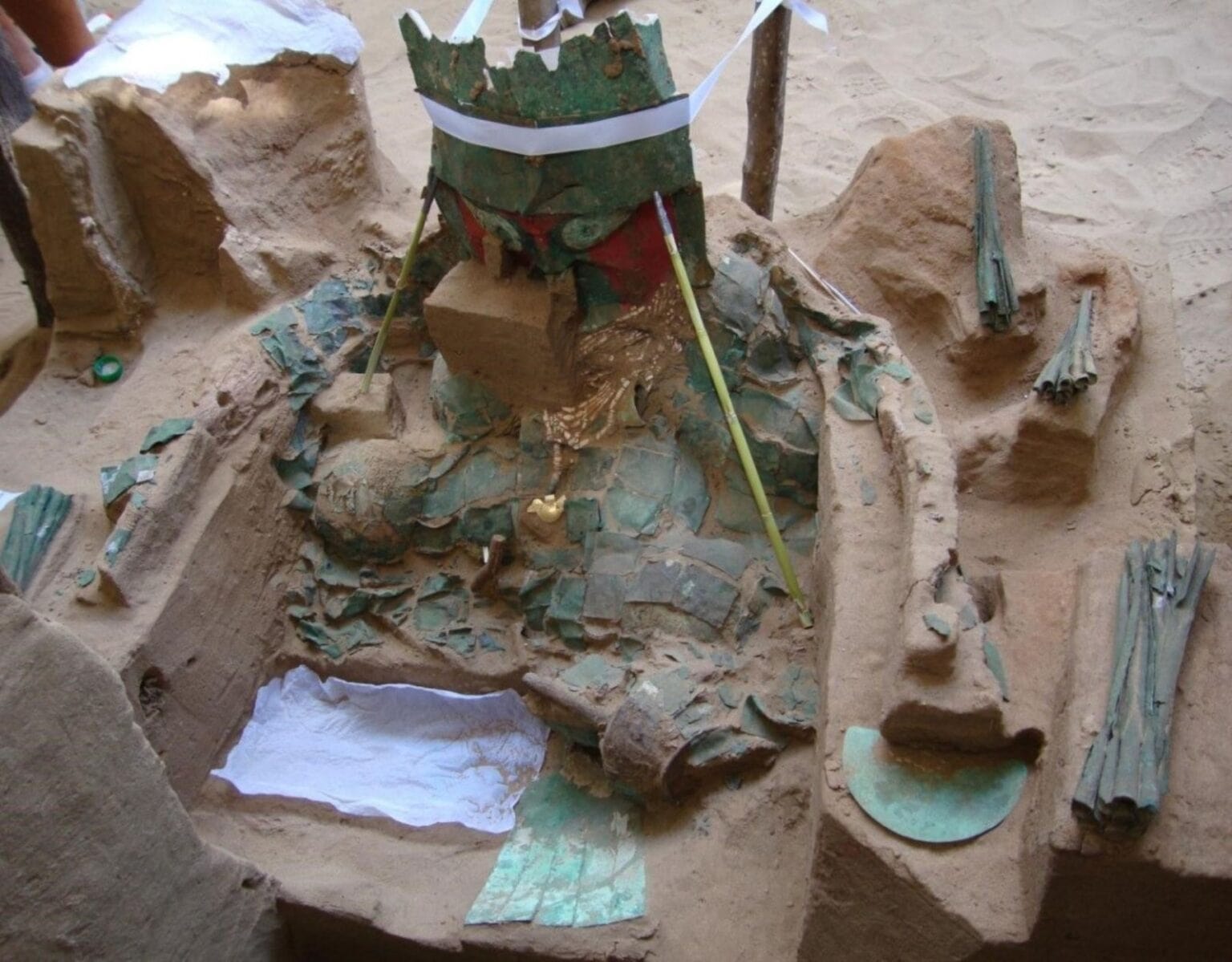
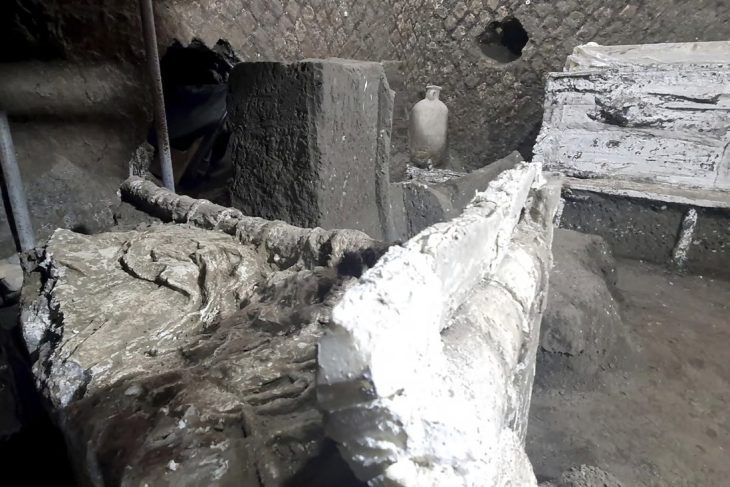
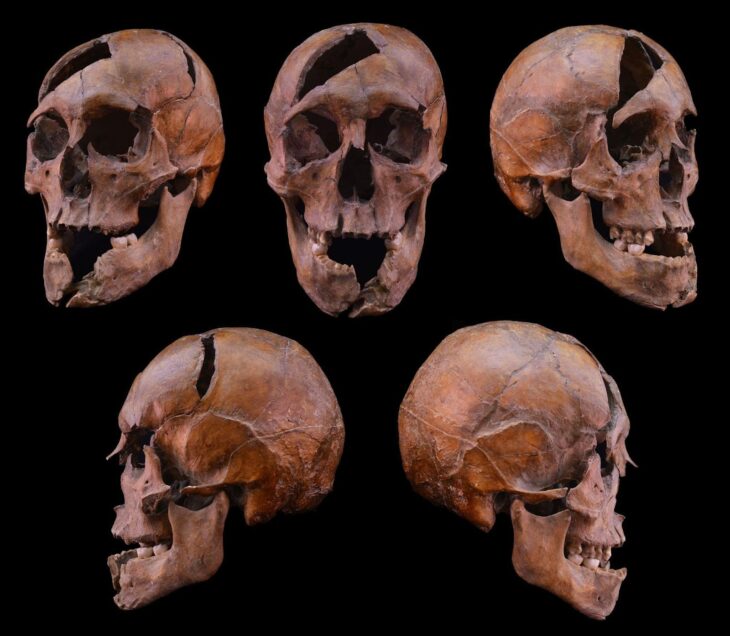
This surgeon contained in his grave various knives, needles and tumis, and was buried in a lotus flower position, sitting cross-legged.
This was discovered by a group of archaeologists in a ceremonial temple in the north, as the researchers reported. The discovery occurred at the end of 2021 at the Las Ventanas mausoleum temple, in the Pómac Forest Historical Sanctuary, in the Lambayeque region, about 800 km north of Lima.
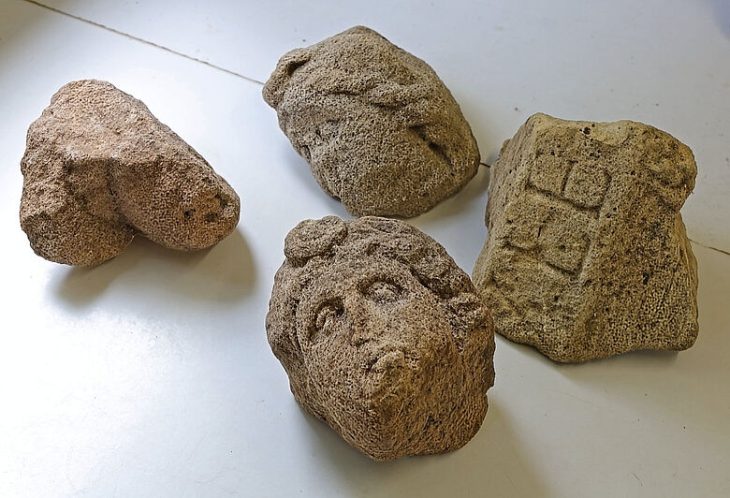
The tomb contained a golden mask with feathered eyes, a large bronze breastplate and other objects that speak of the status of the ancient character, who was buried in a lotus flower position, sitting cross-legged.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

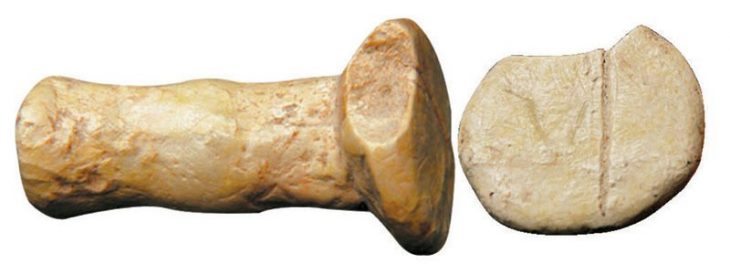
The surgical kit was of particular interest to archaeologists. It is large, containing a full set of awls, needles and knives of various sizes and configurations. There are about 50 knives in total, some with a single cutting edge. Most are a bronze alloy with high arsenic content. Some have wooden handles. There is also a tumi, a ceremonial knife with a half-moon blade. By the tumi was a metal planchette with a symbol associated with surgical instruments. Two frontal bones, one adult and one juvenile, were found next to the planchette. Marks on the bones indicate they were deliberately cut with trepanation techniques. This confirmed that the tools were intended for use in surgery.
“The character was a specialist in cranial trepanations and his surgical instruments were oriented to everything that was human skull surgery,” said archaeologist Carlos Elera, director of the Sicán National Museum.

Archaeologists stressed that these findings have a resemblance to what the Paracas culture did, on the southern coast of Peru (700 BC and 200 AD), famous for trepanations. However, the tools are made of different materials, however. The blades in the Paracas set were made with sharpened volcanic obsidian.
A piece of bark from an unknown tree found in the tomb may have been used for medicinal purposes as an analgesic or anti-inflammatory infusion, in the same way that white willow bark basically makes aspirin tea.
“We are comparing the instruments of a modern surgeon with these objects, to see what similarities they have,” Elera said.