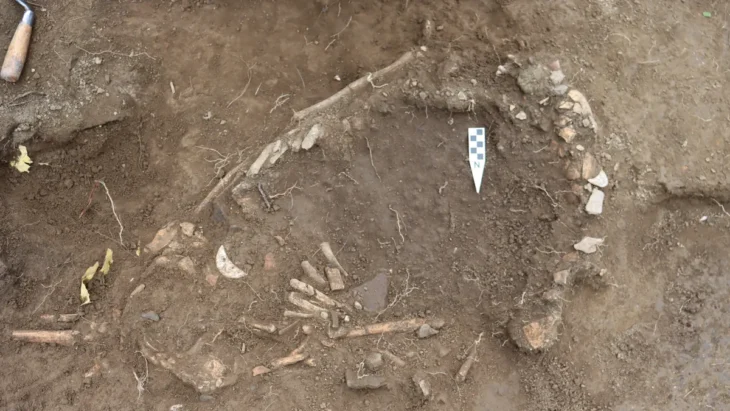
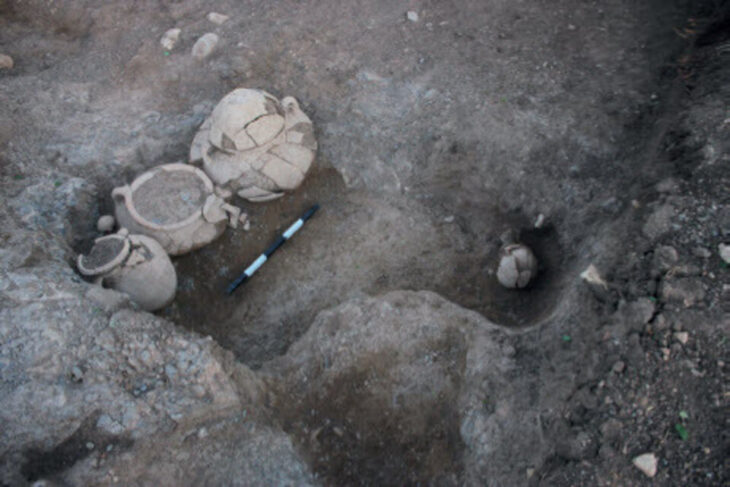
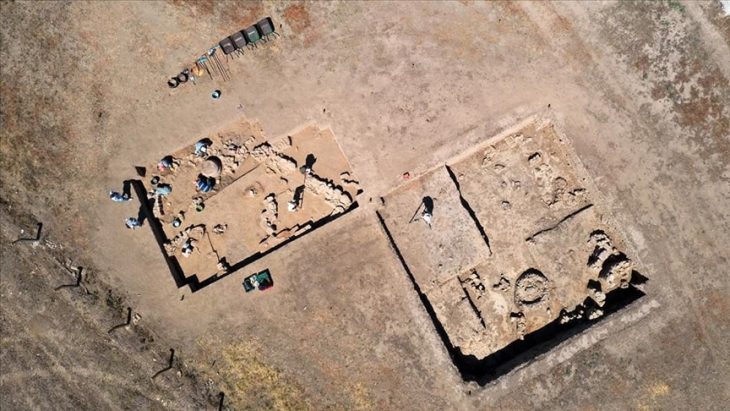
During the archaeological excavations in Yeşilova Höyük (Yeşilova Mound) in Bornova district of Izmir, an 8,200-year-old kohl made of stone material was found.
The Yesilova mound excavation in Türkiye’s Izmir province has been in progress since 2005. Archaeological excavations continue in the Yeşilova and Yassıtepe mounds with the support of the Culture and Tourism Ministry, İzmir Metropolitan Municipality, Bornova Municipality, and Ege University.
The findings are significant because they suggest that the historical settlements in the Izmir area go back 8,500 years, to 6500 BCE. The mound that is being excavated, has already revealed some critical traces of the Neolithic Age and much about the early settlers in the Izmir area off the Aegean coast, their surroundings, and their culture. For example, they lived in separate houses, with separate roof systems, unlike Catalhoyuk in middle Anatolia, where the houses are next to each other.
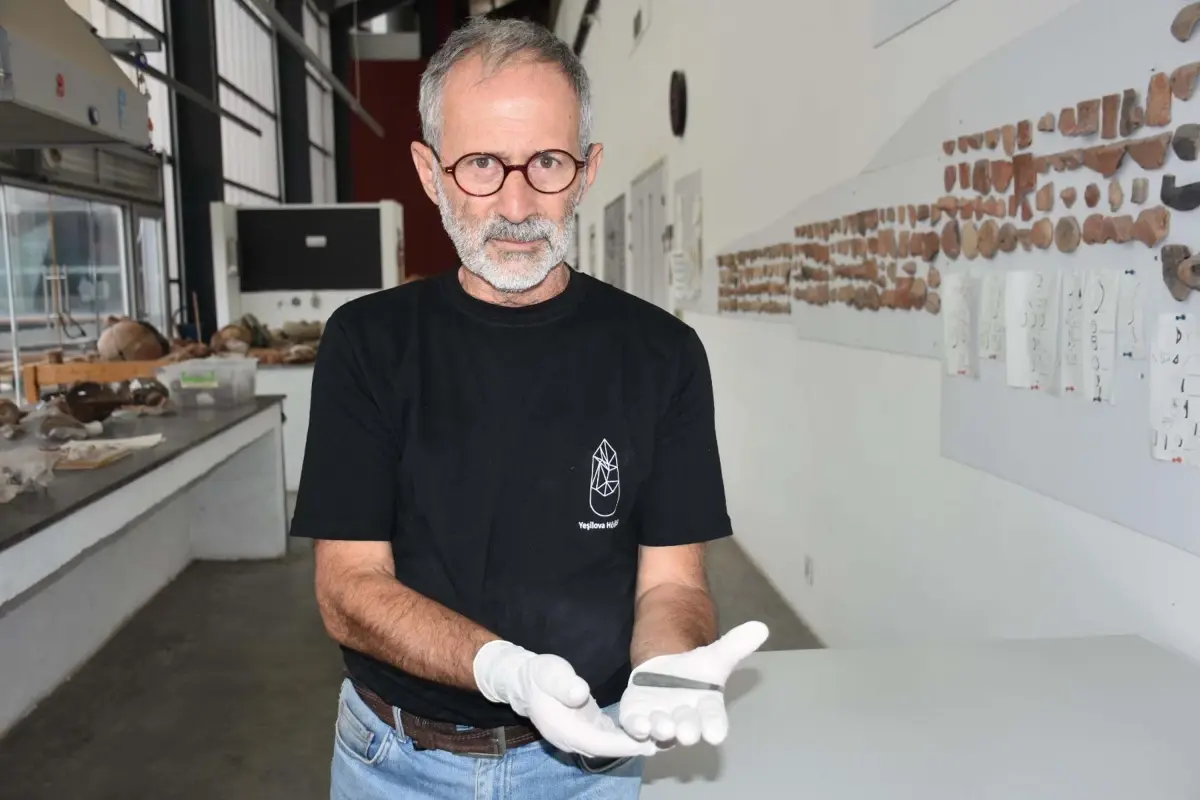
The excavation leader, Zafer Derin from Ege University, announced in a statement that an 8,200-year-old stone-made kohl pen was found during the ongoing archaeological works.
It was stated that the 9.5-centimeter-long find, made of stone, is the oldest dated kohl ever found.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
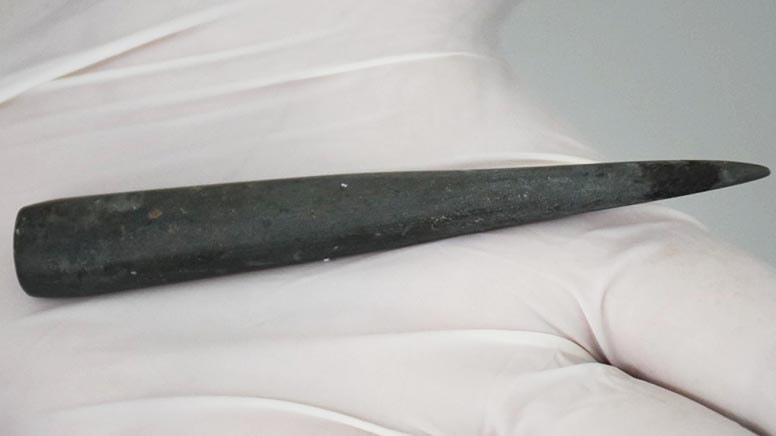

Excavation Head Assoc. Prof. Dr. Zafer Derin said, ‘There is a black paint residue on the tip of the find. These are called kohl. It is an ornamental tool. This shows that Aegean women 8,200 years ago also cared about their ornaments, were fond of their beauty, and took care of themselves.’
‘A sharpened stone pencil is used by dipping it into a container filled with paint. Today, this usage is still present in various parts of Anatolia. This is not our first artifact showing that Aegean women in the region attach importance to their beauty. We also found a vessel in which they put their ornaments. This shows that Aegean women were fond of their beauty and took care of themselves in the historical process. We have found similar artifacts as far back as 4 thousand years ago. This shows that this pen was used 8,200 years ago.’
The black substance at the tip of the find sent for analysis is thought to be manganese oxide. That powdered mineral was the main component of a cosmetic known as kohl, used as an eyeliner in ancient times.
Cover Photo: DHA