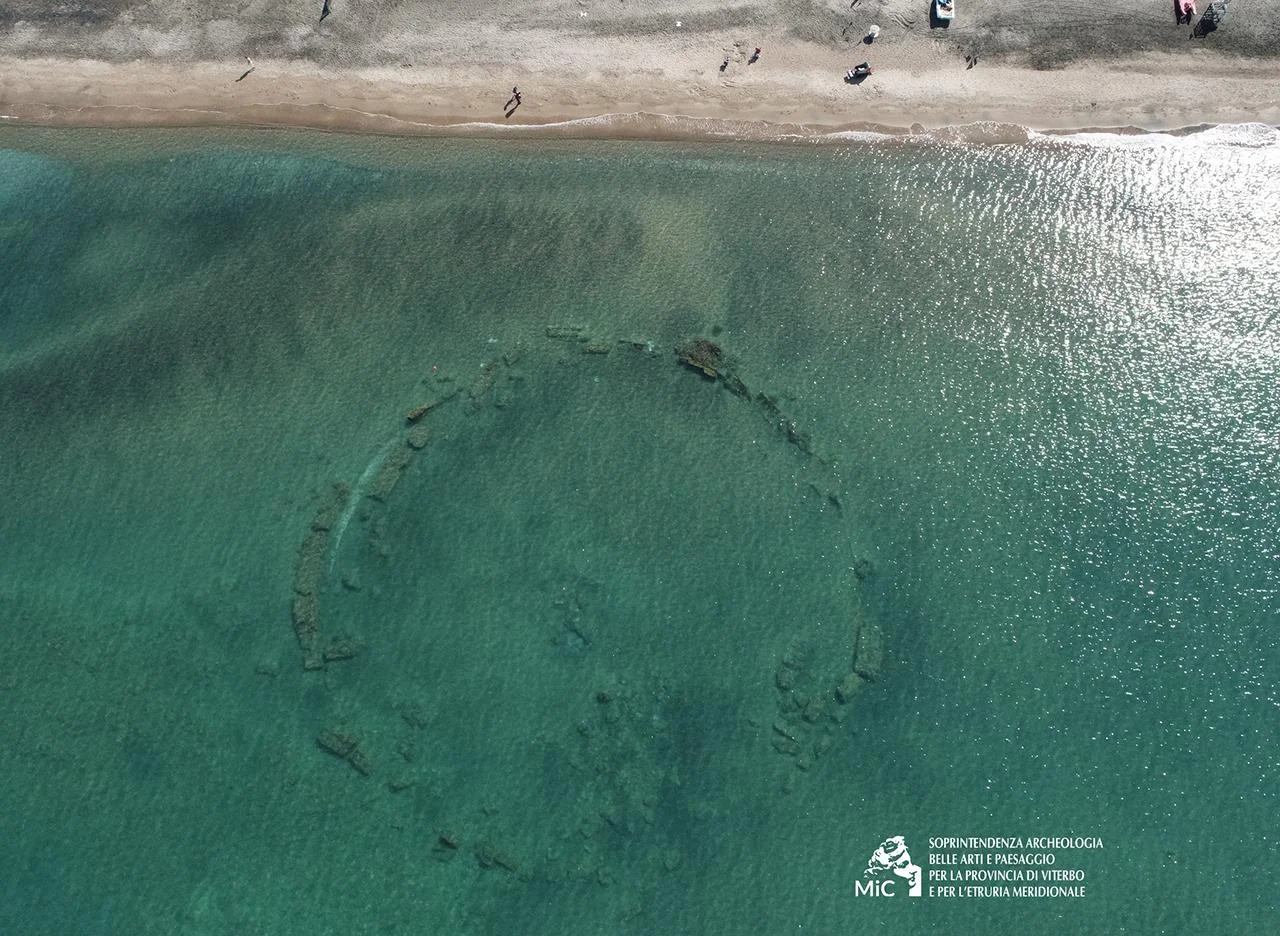
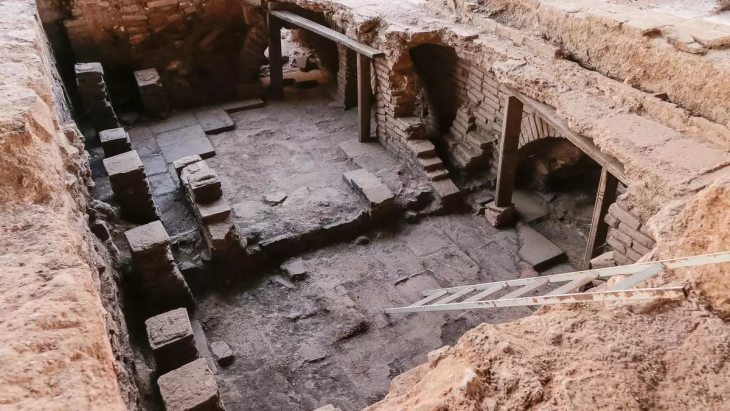
Archaeologists have recently uncovered a significant Roman-era structure submerged near the coastline of Campo di Mare on Italy’s western coast.
This discovery is part of a broader three-year program aimed at excavating and preserving the remnants of ancient Roman architecture that have succumbed to the sea over time.
In 2021, the area had already been the scene of discovering a Cipollino marble column with its Ionic capital. It was linked to a circular structure about 50 meters in diameter that is completely underwater, a few meters from the coast.
Experts believe it to be a maritime pavilion belonging to a Roman villa, whose extent and complexity are yet to be uncovered.
This ancient site, located in Campo di Mare, offers a fascinating glimpse into the Roman aristocracy’s luxurious lifestyles and the time’s advanced construction techniques.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
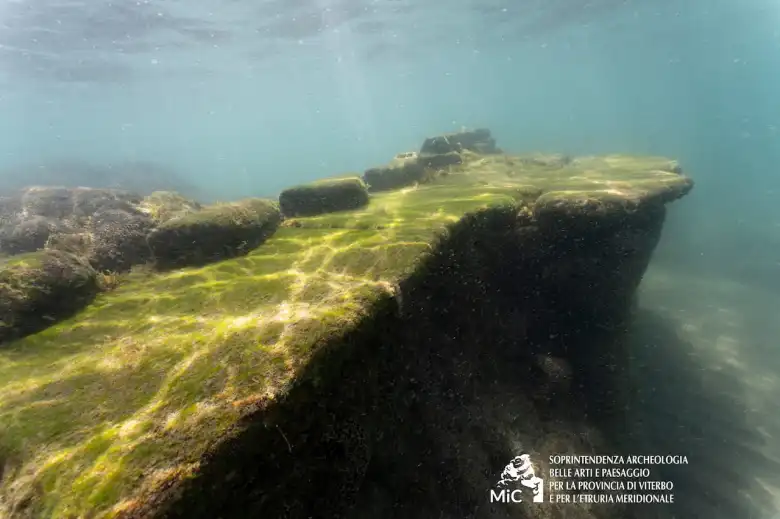

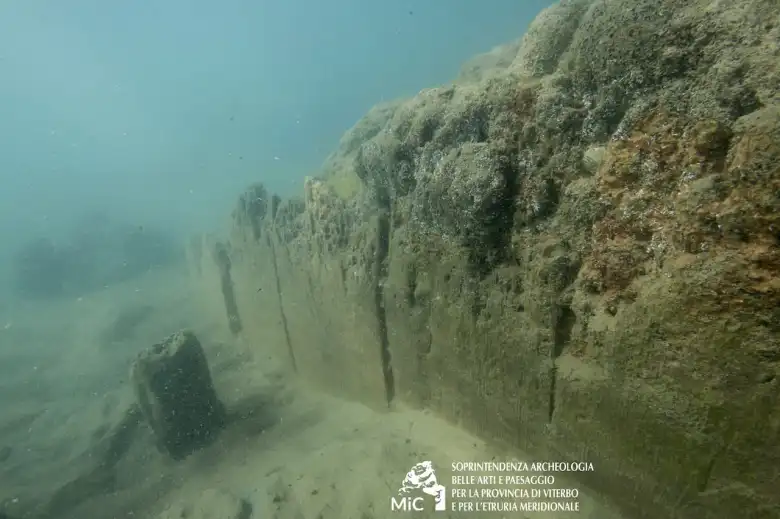
The Roman pavilion features a double belt of brick walls, separated by about three meters and founded on a clay layer. This clay foundation has preserved the wooden formwork and numerous foundation posts.
The walls, notable for their thickness, are constructed with a double layer of triangular bricks containing pebbles and mortar, connected by bipedal bricks. This construction method reflects advanced engineering and resilience against the harsh marine environment.

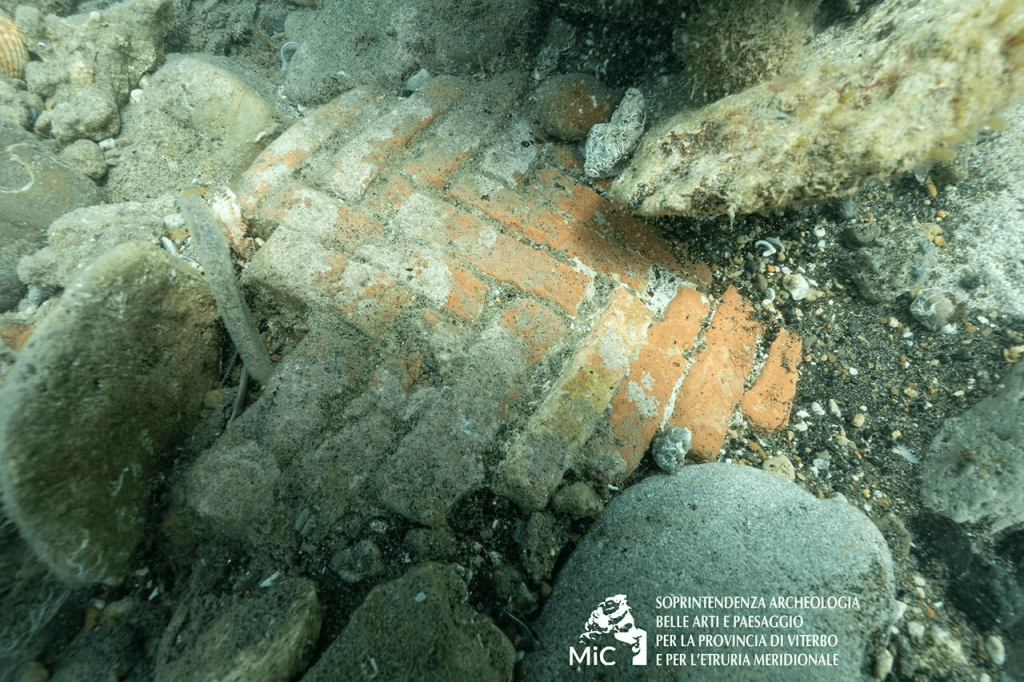
The structure preserves opus signinum coatings and opus spicatum pavements. Opus signinum was primarily used for its waterproofing properties in structures like baths, aqueducts, and cisterns. In the center, fragments of opus sectile pavement were found, indicating the richness and elegance of the construction. Opus sectile is a decorative technique using cut and inlaid materials to create intricate designs, often found in luxurious settings.
A press release from the Soprintendenza Archeologia Belle Arti Paesaggio Etruria Meridionale states that the pavilion’s architectural features highlight its significance in relation to Roman villa architecture. The extensive use of opus sectile and opus signinum, as well as the presence of opus spicatum, demonstrate the sophisticated building methods and aesthetic sensibilities of the time.
These components imply that the pavilion was an opulent and representative feature of the Roman villa, reflecting the occupants’ considerable wealth. The site’s strategic and prestigious location is further validated by its proximity to the historic Via Aurelia road.
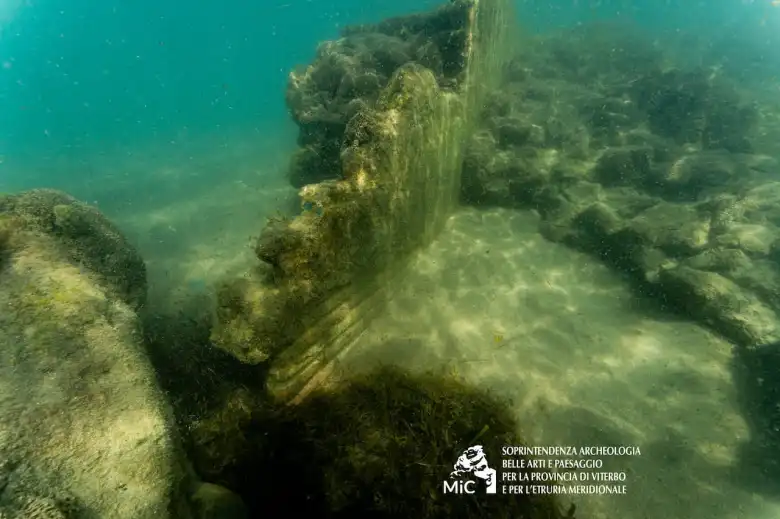

The Underwater Archaeology Service of the Superintendency carried out the project, with support from the company CSR Restauro Beni Culturali for the cleaning and restoration of the structures.
The company CSR Restauro Beni Culturali assisted with the restoration, while the Diving Unit of the Naval Station of Civitavecchia of the Guardia di Finanza provided crucial support during the operations. The Municipality of Cerveteri and the Port Authority of Civitavecchia facilitated the interdiction of the work areas for the safety and efficiency of the restoration efforts.

Future geophysical surveys are planned in collaboration with the National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology (INGV). These surveys aim to provide a thorough examination of the site and ensure its protection from relentless coastal erosion.
Soprintendenza Archeologia Belle Arti Paesaggio Etruria Meridionale
Cover Photo: Soprintendenza Archeologia Belle Arti Paesaggio Etruria Meridionale