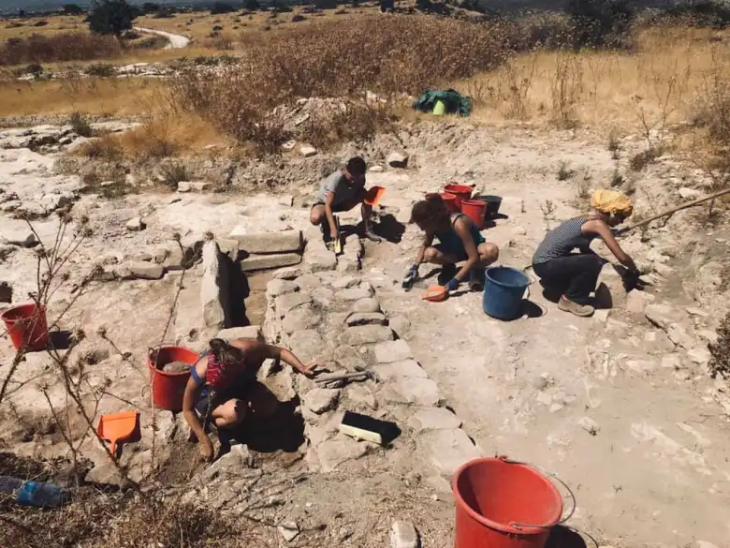
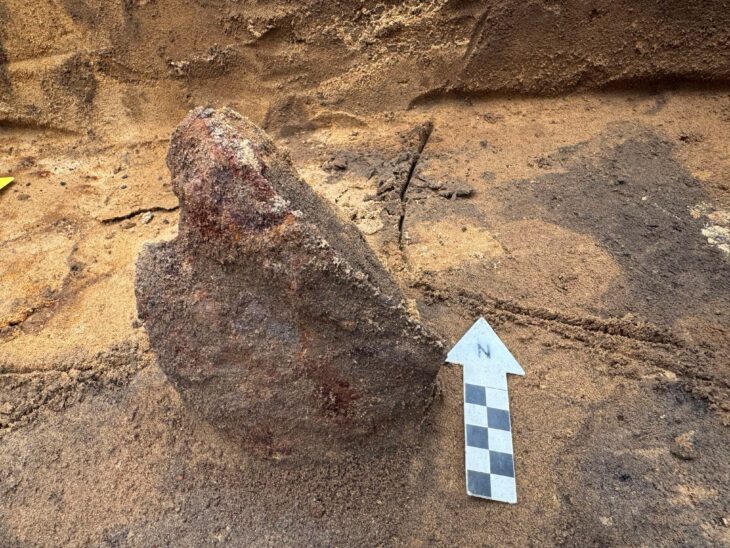
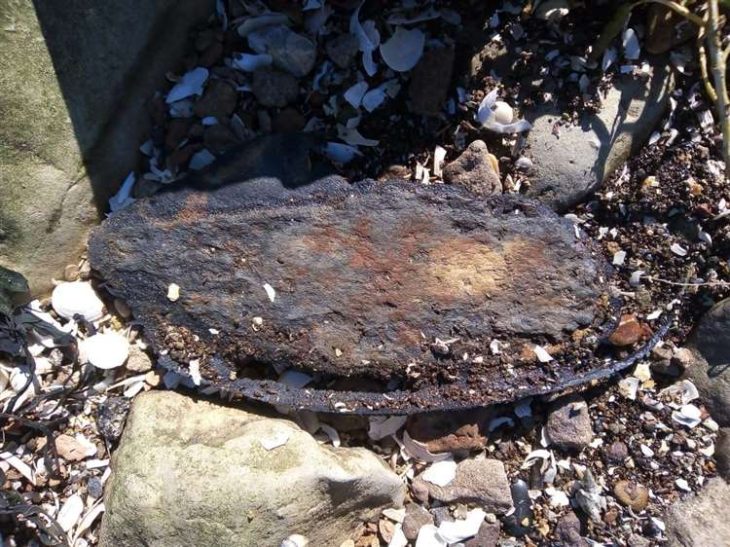
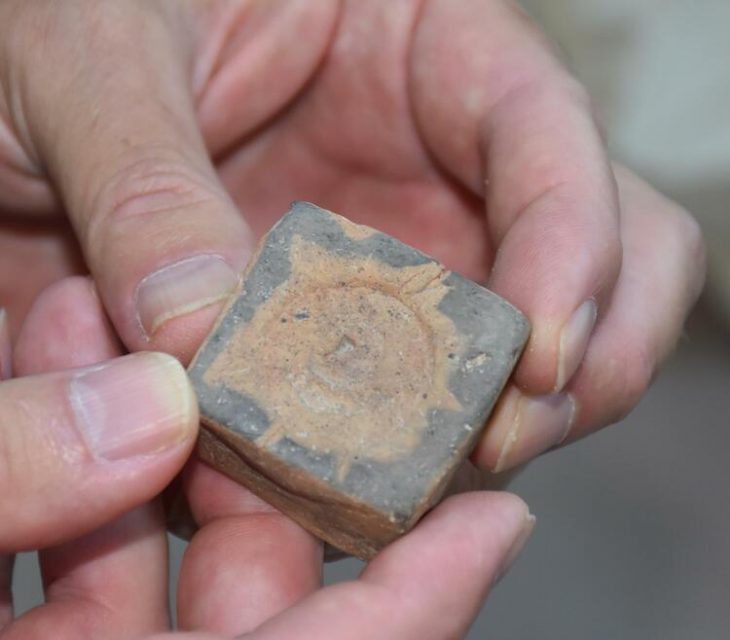
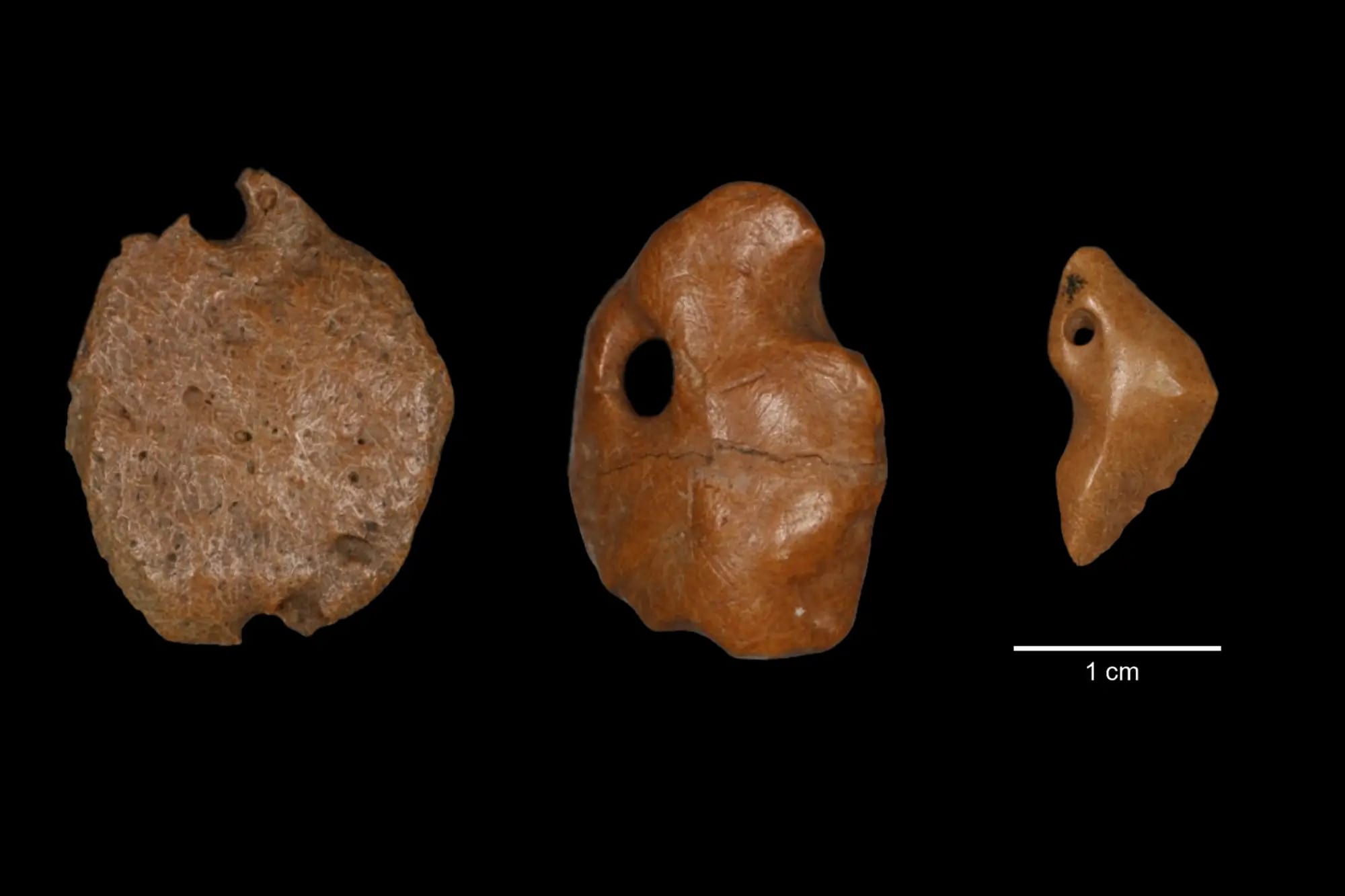
Archaeologists discovered three pendants made from the bony material of an extinct giant sloth in a rock shelter in central Brazil.
The pendants are believed to be between 25,000 and 27,000 years old, making them the oldest known personal ornaments in the Americas and the only ones made from giant sloth bone in the archaeological record.
New research suggests humans lived in South America at the same time as now-extinct giant sloths, bolstering evidence that people arrived in the Americas earlier than once thought.
Recent research has challenged the notion that humans migrated to the Americas about 13,000 years ago by crossing a land bridge from Siberia to Alaska.
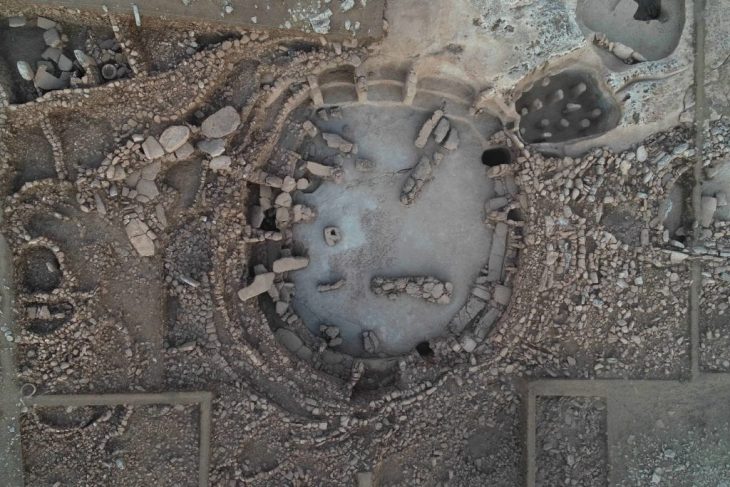
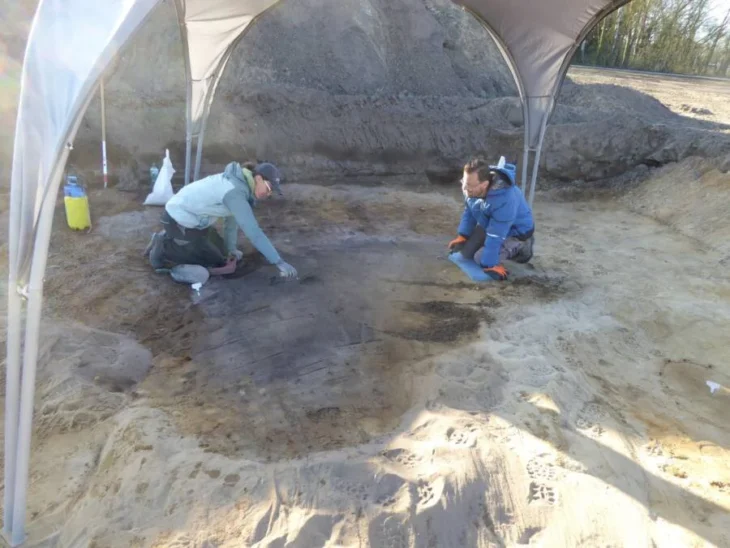
The ornaments were found about 30 years ago at a rock shelter in central Brazil called Santa Elina. The new study is the first to analyze them extensively and rule out the possibility that humans had found and carved them thousands of years after the animals perished.
The pendants were among thousands of osteoderms — hard bony deposits that form within the skin of certain animals —. The osteoderms belonged to a species of giant sloth known as Glossotherium phoenesis, which weighed around 600 kilograms (1,323 pounds) and had long clawed arms for digging.
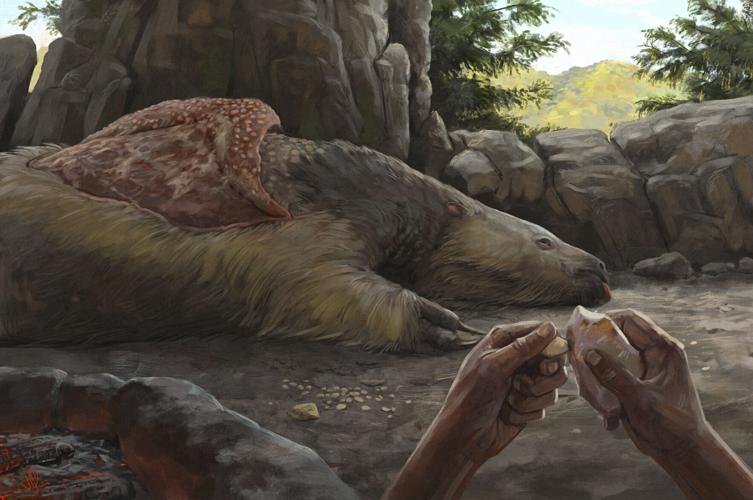

To ascertain how the pendants were created and altered by human hands, the researchers who discovered them analyzed them using a variety of methods and experiments. They found that the osteoderms were polished and had holes drilled into them, suggesting they were used for personal adornment, probably as necklaces or earrings. The holes were not caused by natural abrasion or predation, according to the study published in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
The team of researchers from Brazil, France, and the United States said their analysis shows this handiwork was done within days to a few years after the animals had died, and before the materials had fossilized. The researchers also ruled out natural abrasion and other things that might explain the shapes and holes.
Giant ground sloths could reach 13 feet long, weighed more than a thousand pounds, and were equivalent in size to an Indian elephant. According to the report, it walked on all fours and was one of the largest creatures in South America.
The discovery of the pendants has significant implications for our understanding of the Americas’ human history. It suggests that humans were present in South America thousands of years earlier than previously thought, coexisting with giant sloths and other megafauna that became extinct around 10,000 years ago.
“We now have good evidence — together with other sites from South and North America — that we have to rethink our ideas about the migration of humans to the Americas,” Mirian Liza Alves Forancelli Pacheco, study co-author and archaeologist at the Federal University of Sao Carlos in Brazil told The Associated Press.
Cover Photo: Thais Rabito Pansani/AP