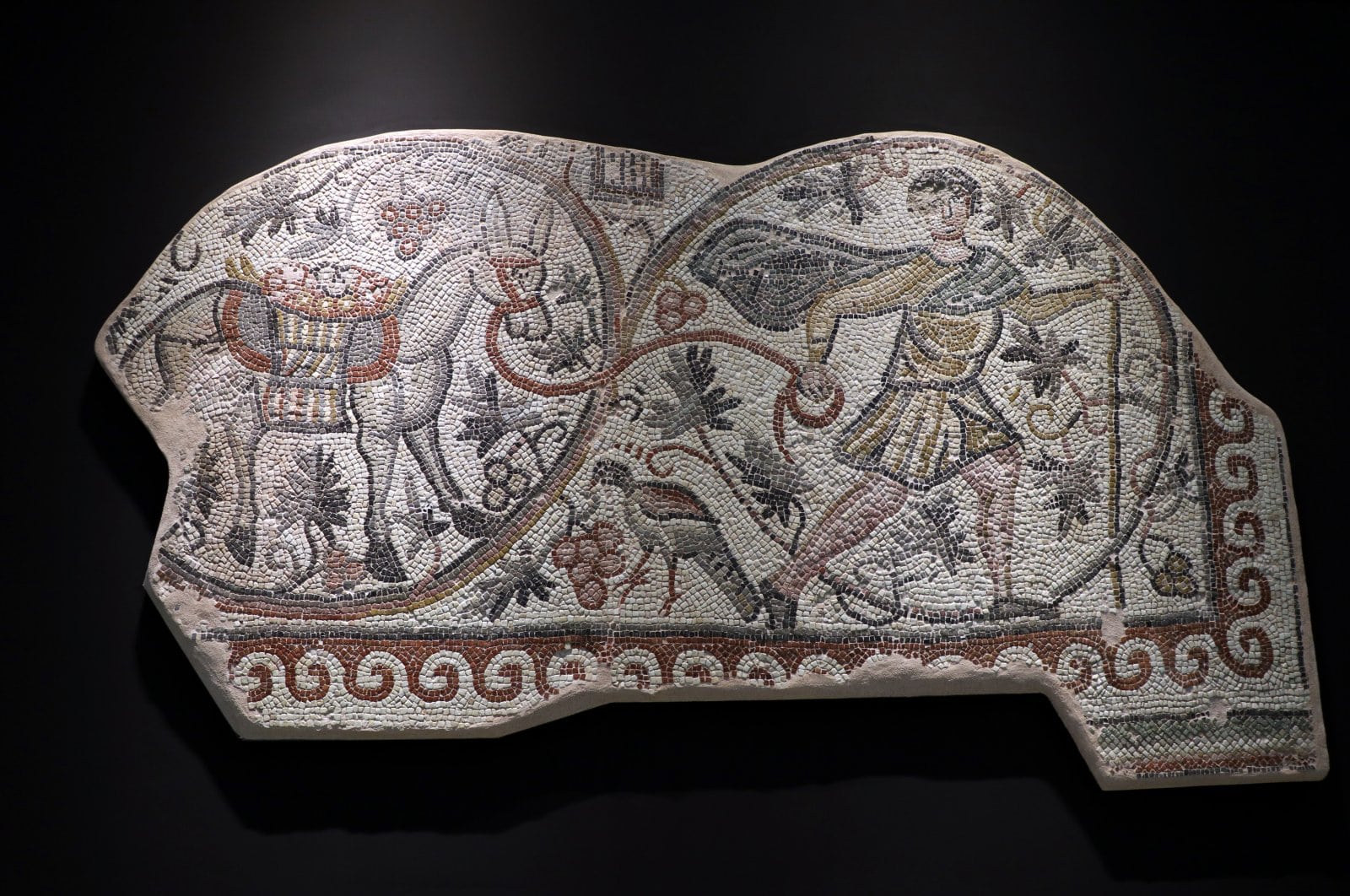
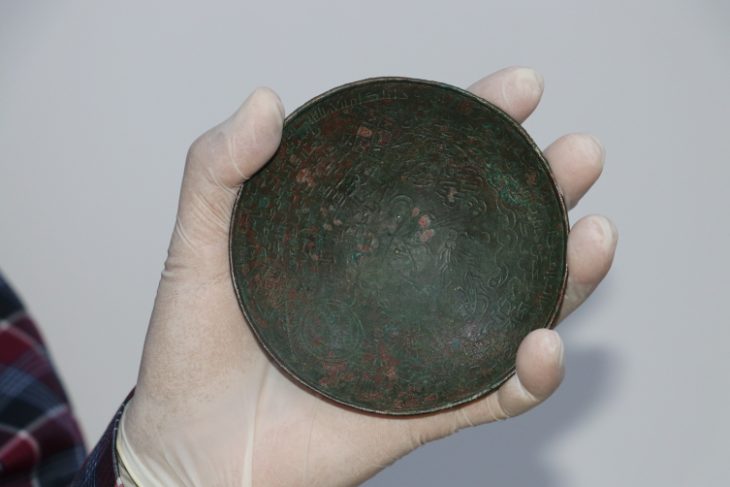
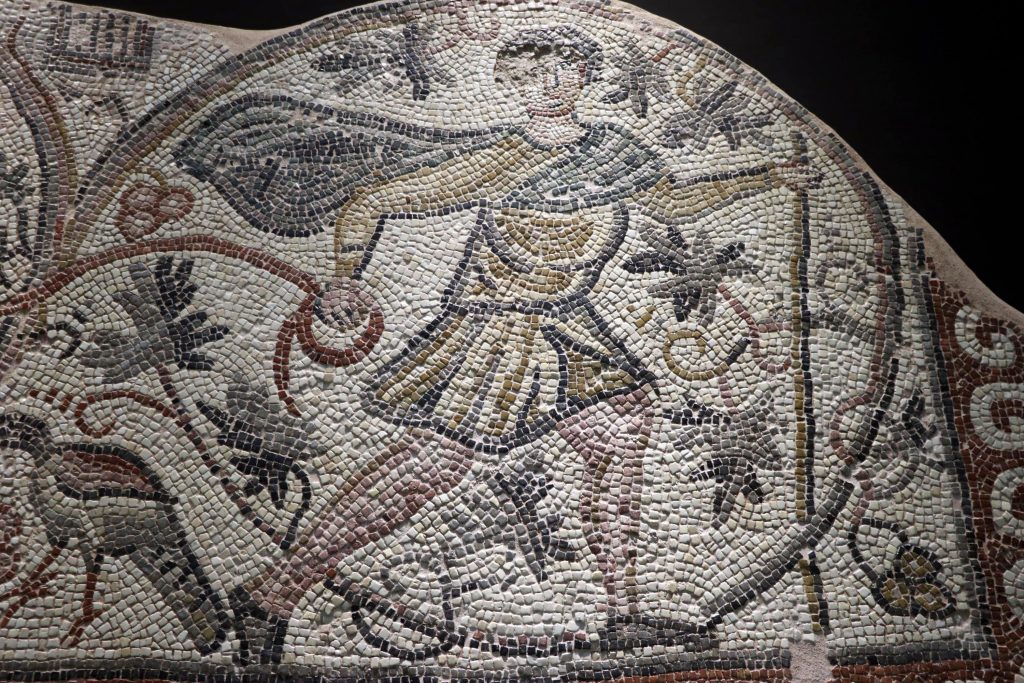
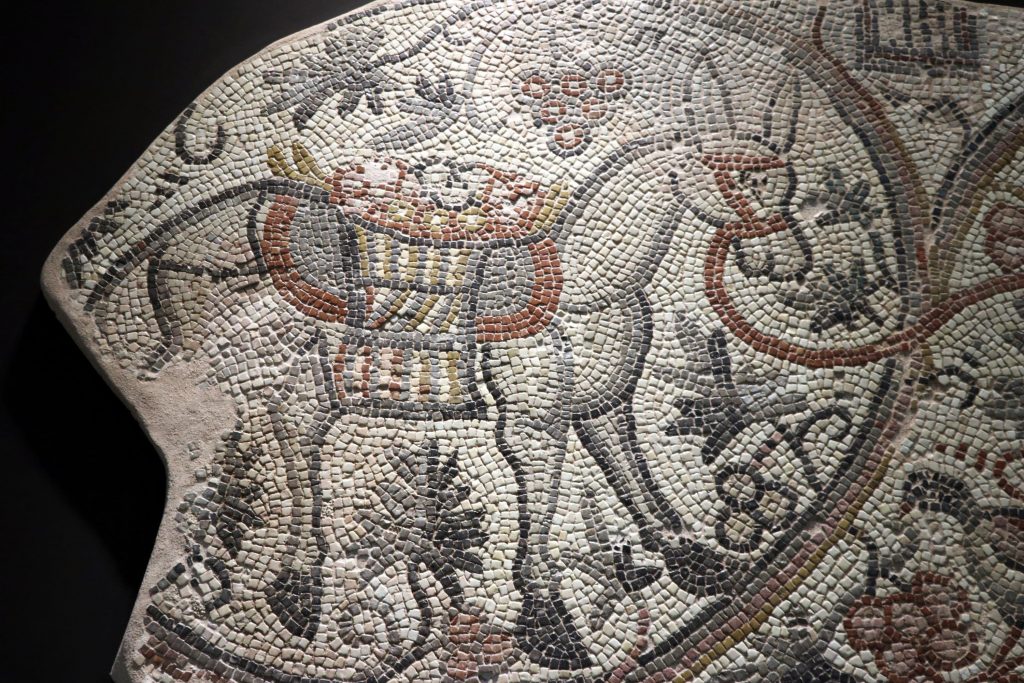
The mosaic depicting the grape harvest, which is considered to date from the Late Roman period, equivalent to the 5th and 6th century AD, will be shown at the Hatay Archeology Museum, according to a statement issued by the museum’s directorate.
The 6-square-meter (64-square-foot) mosaic was discovered during illegal excavations in the Hassa district southern Hatay province, an area with a long history of grape cultivation, and later moved to the Hatay Archaeological Museum’s warehouse in 2016.
After six months of restoration, the mosaic was moved to the temporary exhibition hall of the museum under the name “Mosaic of the Vine Harvest.”
The mosaic, made ready for display with its illustrations of grapes, which had an important place in agricultural activities in the late Roman period, will be introduced to local and foreign tourists.

Ayşe Ersoy, director of the Hatay Archaeological Museum, told Anadolu Agency (AA) that the artifact was found as the floor mosaic of a church.
She said the work has been kept in the museum’s warehouse for about five years.
“A grape harvest is depicted on it. It reflects the grapes carried in a donkey’s basket by a Roman. From this mosaic, we see that grapes had a very important place in the economy and as a food source in our district of Hassa in those years.”
“Our mosaic comes to the fore every year during the grape harvest in our Hassa. Based on this, we wanted to introduce it to the visitors. As part of our project ‘The Traces of Olives and Grapes Engraved in History Come to Light,’ the importance of olives in the Hatay region and their spread to Anatolia and Europe as well as the importance of grapes for our province will be explained in our temporary exhibition hall,” Ersoy added.

Ersoy, who said the “Mosaic of Vine Harvest” was made ready for display after six months of long and meticulous work, noted that a copy of an olive mosaic found during the excavations in the ancient city of Epiphaneia is also located in the temporary exhibition hall.
Emphasizing that they are eagerly waiting to welcome visitors, Ersoy said: “Actually, our hall was scheduled to open in September, but unfortunately, we could not meet that date. I hope our mosaic will be showcased to visitors in November.”
“It’s going to be a big opening. It is a very important hall. In particular, the people of the Mazbanlı neighborhood will be brought here to draw attention to the importance and value given to ancient artifacts and to provide them with a tour of the artifact and our museum.”