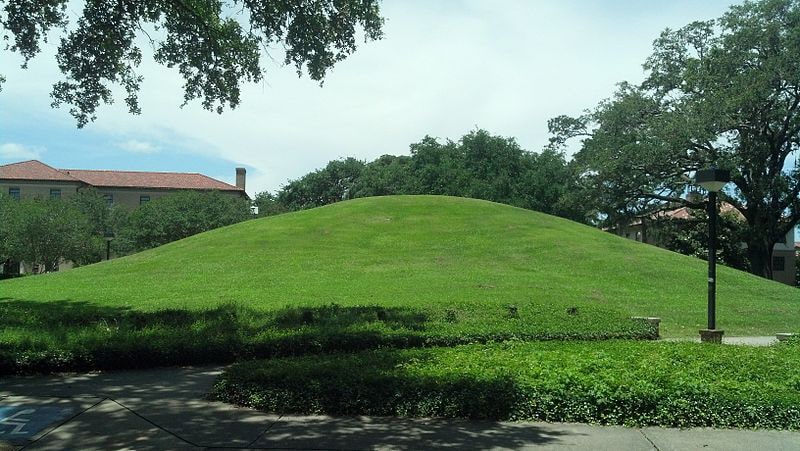
According to new research published in the American Journal of Science, two six-meter (20-foot) high mounds on the campus of Louisiana State University (LSU) are the oldest human-made structures ever discovered in North America.
Using radiocarbon dating, the researchers determined that the construction of the mounds began around 11,000 years ago and was completed over several millennia.
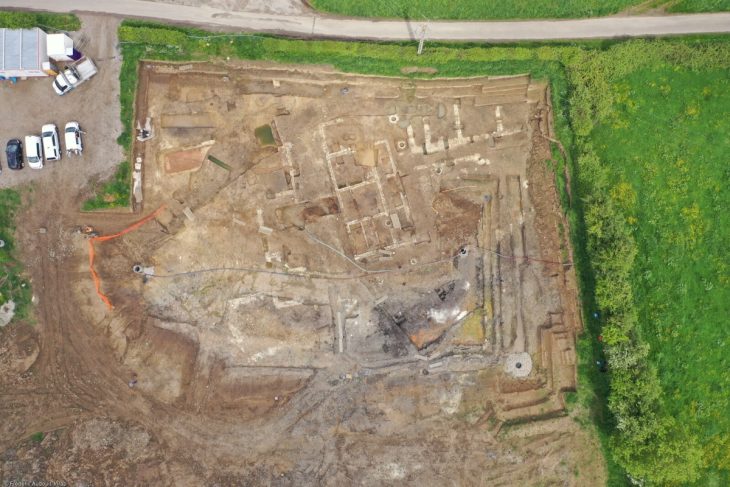
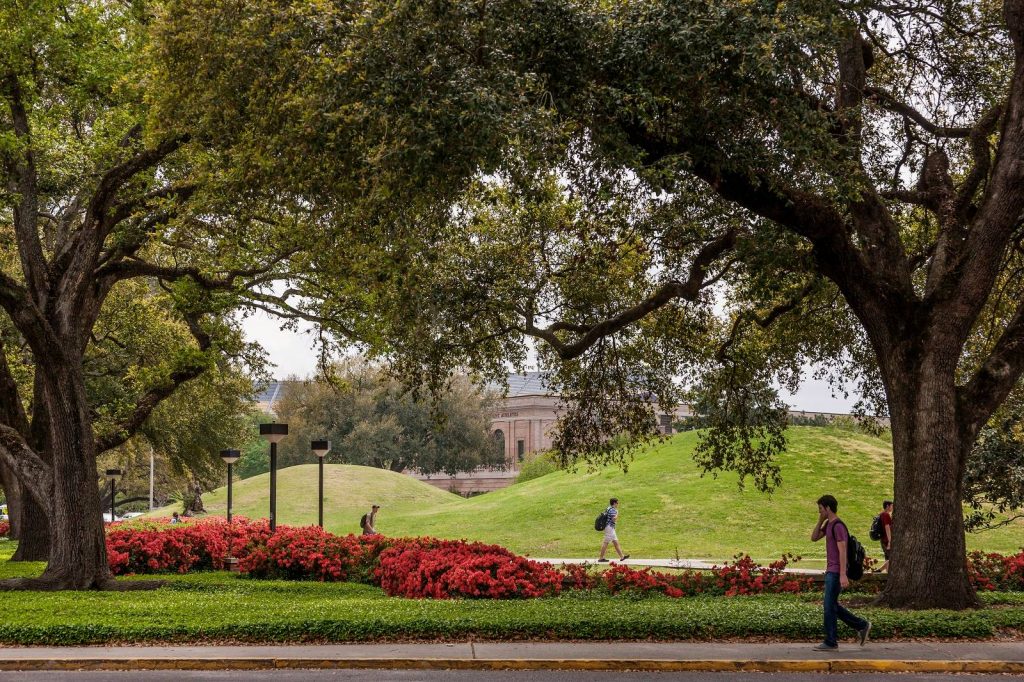
The two large, grassy mounds on LSU’s campus, are among the more than 800 human-made, hill-like mounds in Louisiana, built by ancient indigenous people. While many mounds in the region have been destroyed, the LSU Campus Mounds have been preserved and are listed on the National Register for Historic Places.
“There’s nothing known that is man-made and this old still in existence today in North America, except the mounds,” said LSU Department of Geology & Geophysics Professor Emeritus Brooks Ellwood.
Ellwood and colleagues collected sediment cores from the two LSU Campus Mounds to learn more about them. Layers of ash from burned reed and cane plants, as well as burned osteons, were discovered in the cores. Radiocarbon dating of the layers of material indicates the mounds were built over thousands of years.

These findings indicate that the first mound was constructed around 11,000 years ago. Because of a large depression in the ground behind LSU’s Hill Memorial Library, the scientists believe the sediment for the southern mound, dubbed “Mound B,” was taken from there. The mound was built up layer by layer over a few thousand years to about half its current height.
“The layers of reed and cane phytoliths, containing very small numbers of osteons, are indicative of very hot fires,” write the authors. Such infernos would have been too hot for cooking, and are therefore likely to have served a ritual function. “This finding supports the argument that the fires were used for ceremonials or cremations,” continue the researchers.
Tantalizingly, the team was unable to determine whether the osteons were of a human or animal origin. The team said they sought permission to perform DNA tests on the microscopic bone materials found, but were not granted permission by the Native American tribal communities contacted.
Around 8,200 years ago, the southern Mound B was abandoned. Tree roots found in the 8,200-year-old sediment layer indicate that the mound was not used for about 1,000 years. Also around 8,200 years ago, the northern hemisphere experienced a major climate event with temperatures suddenly dropping on average by about 35 degrees Fahrenheit, which lasted about 160 years.
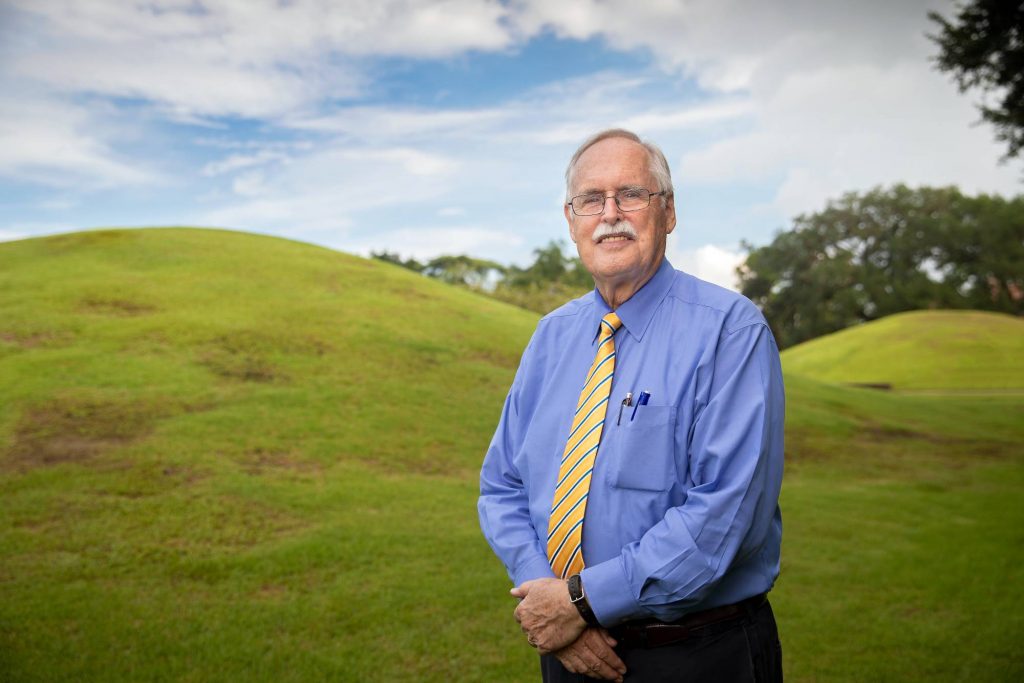

“We don’t know why they abandoned the mounds around 8,200 years ago, but we do know their environment changed suddenly and dramatically, which may have affected many aspects of their daily life,” Ellwood said.
Then, around 7,500 years ago, the indigenous people began to build a new mound just to the north of the first mound. However, this time, they took mud from the floodplain where the entrance to LSU’s Tiger Stadium is currently located, which at that time was an estuary. With this mud, they built the second mound, “Mound A,” layer by layer, to about half of its current height. Mound A contains mud that is saturated with water, which liquefies when agitated. As a result, Mound A is unstable and degrading, which is why it is critical to stay off the mounds to preserve them.
According to the new analyses of the sediment layers and their ages, it looks like indigenous people cleared the abandoned first-built Mound B and began to build it up to its current height before completing Mound A. Both mounds were completed around 6,000 years ago and are similar in height.
According to the researchers, the structures are aligned with a point on the horizon that is 8.5 degrees east of true north. Six millennia ago, the red giant star Arcturus – which is among the brightest stars in the sky – would have risen at this very point.
Study author Brooks Ellwood, “the people who constructed the mounds, at about 6,000 years ago, coordinated the structures’ orientation to align with Arcturus, seen in the night sky at that time,” said.
The two small hills have withstood the test of time, leading the authors to speculate that “the LSU Campus Mounds may represent the oldest known and still intact, human-made structures on Earth.”
The study was published in American Journal of Science
Cover Photo: LSU