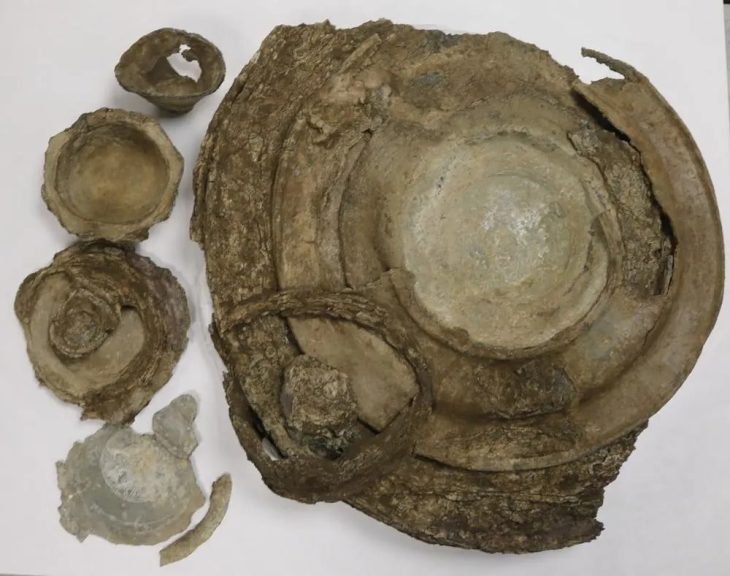
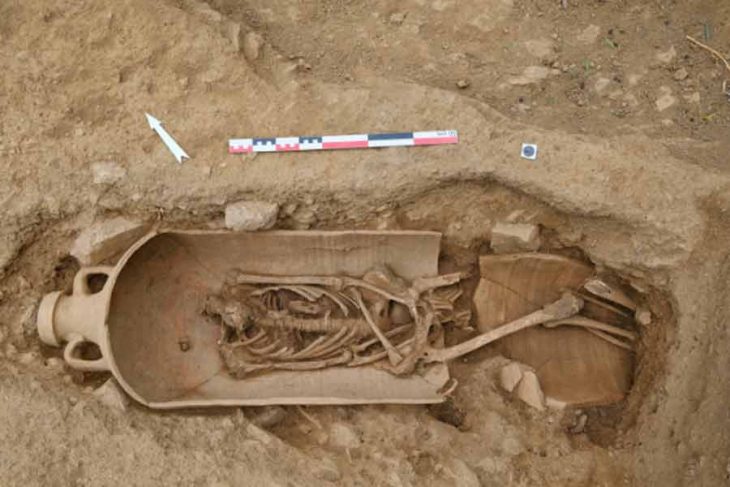
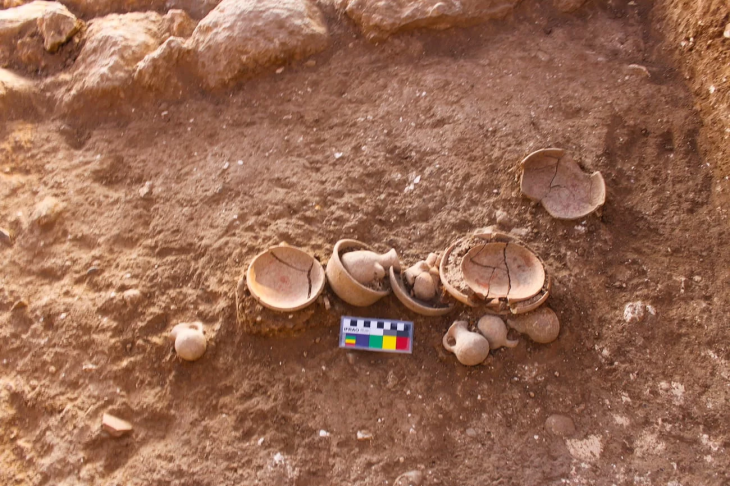
During the ongoing excavations in the Hasankeyf mound in Batman, one of the oldest settlements in the world, an 800-year-old healing bowl and two zihgir (archery rings) made of agate and bone used by archers were found.
Under the leadership of Zekai Erdal, associate professor in the Art History Department of Mardin Artuklu University’s Faculty of Literature, rare artifacts were discovered during the fifth period of excavations in the ancient area.
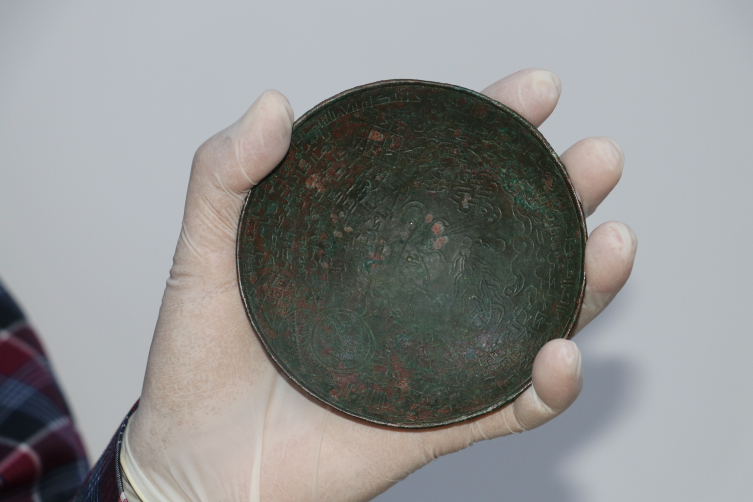
Associate Professor Zekai Erdal stated that there are only 22 healing bowls in the world, reaching 23 with Hasankeyf, and said that they unearthed a healing bowl made of bronze material used in folk medicine in the medieval Islamic world.
Assoc. Dr. Erdal said, “The healing bowl, adorned with talismans, seals, and verses, actually has a connection with Hasankeyf in one aspect. According to local belief, it is accepted that the people of Hasankeyf or the people who go to the castle are not bitten by scorpions or snakes,”
Stating that it is believed that the bowl, on which double-headed dragon, dog, snake, and scorpion motifs are engraved, protects in two ways, Erdal said, “It is believed that the person who drinks water from the healing bowl is protected against dog bites, snake and scorpion bites. Healing bowl is a material used to heal people who are exposed to dog bites, snake and scorpion bites.”
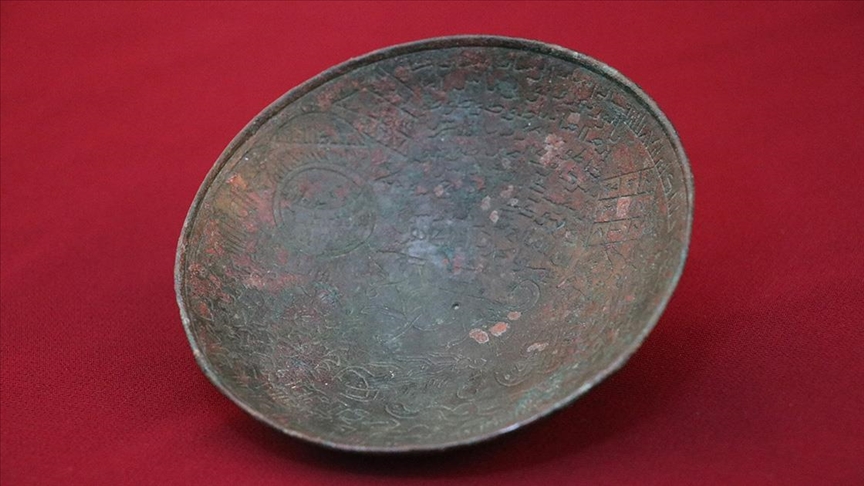

“It is possible to see examples of the healing bowl found in Hasankeyf in the Topkapı Palace Museum, Kayseri Museum and Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality Museum. Essentially, it’s important to evaluate the bowl in the context of folk medicine. After all, there are practices such as spells, amulets, and talismans in Islamic culture.
The purpose of the healing bowl was believed to protect individuals from natural dangers such as dog bites, snake, and scorpion stings. It was used in folk medicine with the belief that drinking water from it could provide remedies for those who encountered such animal-related harms.
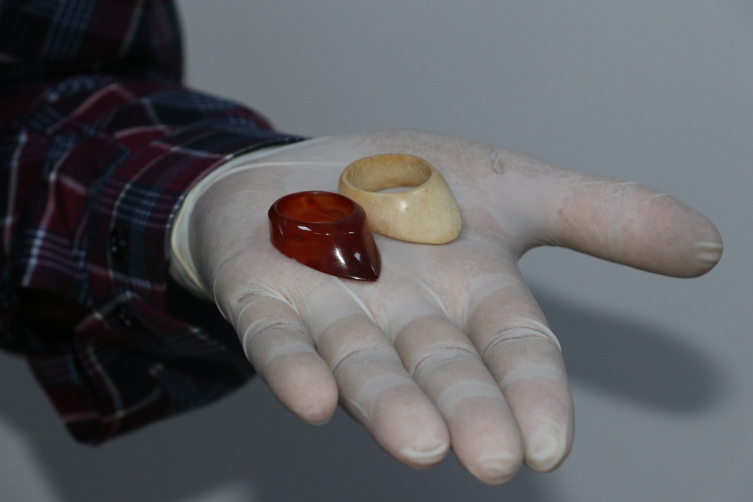
Erdal stated that they found two zihgir, similar examples of which they had not encountered in previous excavations, along with the healing bowl, and said:
“One of the Zihgir (archery rings) was discovered during an excavation at a shrine. This suggests that the individual buried there was of significance, although their identity couldn’t be determined. The Zihgirs were made of agate and bone. In the medieval, the zihgir was one of the most important elements used in the Islamic world and Turkish Islamic arts, particularly in archery. It was a ring-shaped tool worn on the finger during archery to prevent the bowstring from harming the finger.”
The artifacts were delivered to the Hasankeyf Museum Directorate and preserved.
















