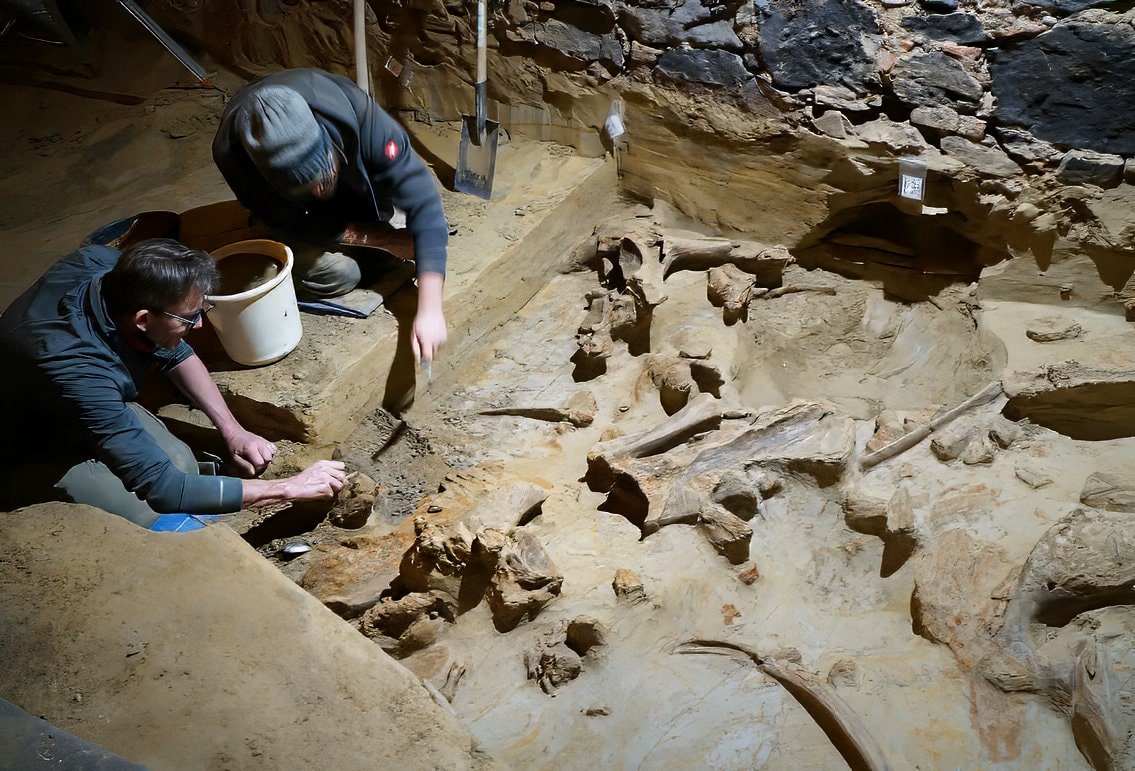
A winemaker has discovered mammoth bones up to 30,000 to 40,000 years old in a wine cellar in Lower Austria. It is the most important find of its kind in more than 100 years.
While renovating the wine cellar in Gobelsburg, a local winemaker in the Krems region of Lower Austria found around 300 mammoth bones, the likes of which haven’t been spotted in a century. Archaeologists now confirm that the cellar and surrounding area can be classified as “a significant bone site,” containing the remains of at least three mammoths after he reported the find in mid-May!
Andreas Pernerstorfer reported the discoveries to the Federal Monuments Office as soon as he discovered them. The Austrian Archaeological Institute of the Austrian Academy of Sciences (OeAW) was then tasked with conducting additional research on Pernerstorfer’s discovery.
Bones from three different mammoths
Since mid-May, archaeologists from the ÖAW have uncovered several layers of mammoth bones. The stone artifacts and charcoal finds discovered there indicate that the finds are between 30,000 and 40,000 years old, according to archaeologist Thomas Einwögerer and his colleague Hannah Parow-Souchon. They assume an “important bone site” that contains remains of at least three different mammoths.
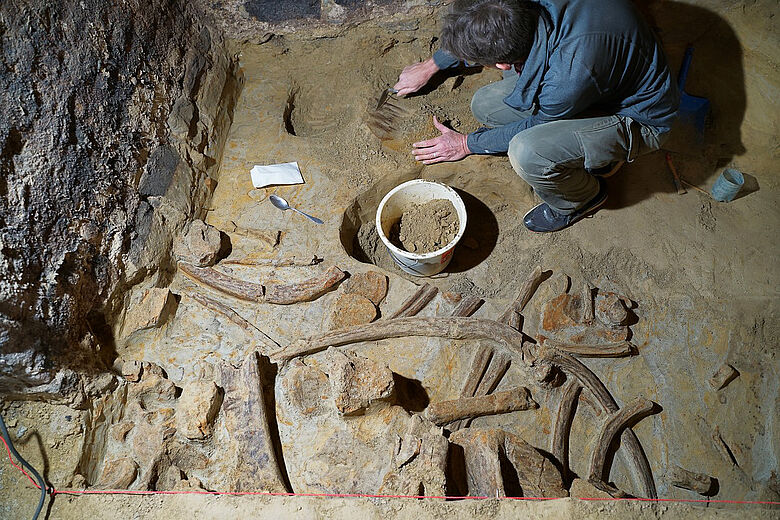

“Such a dense mammoth bone layer is rare,” says Hannah Parow-Souchon, who leads the excavation. “It’s the first time that we’ve been able to investigate something like this in Austria using modern means.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The last time comparable finds were made in Austria was 150 years ago, also in the district of Krems. At that time, a thick bone layer as well as cultural layers with flint artifacts, decorative fossils, and charcoal were discovered in an adjacent cellar in Gobelsburg.
“We think we have mostly the complete animals. They’re not in anatomical connection but we do probably have all parts,” Hannah Parow-Souchon said, adding that the recovered haul includes some rare finds, including a lingual (tongue) bone.”
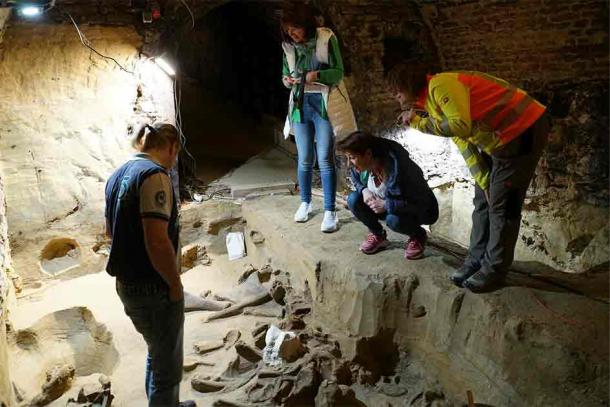

The find in Gobelsburg certainly raises many exciting questions, such as how Stone Age people were able to hunt these huge animals. “We know that humans hunted mammoths, but we still know very little about how they did it,” says OeAW researcher Parow-Souchon. Bones from three different mammoths were found: The place where they were found could be the place where the animals died. Humans could have chased them there and set a trap for them.
The find is currently being examined by the researchers and will subsequently be handed over to the Natural History Museum Vienna, where the bones will be restored. The excavations were funded by the Federal Monuments Office and the province of Lower Austria.
Cover Photo: © ÖAW-ÖAI/H. Parow-Souchon