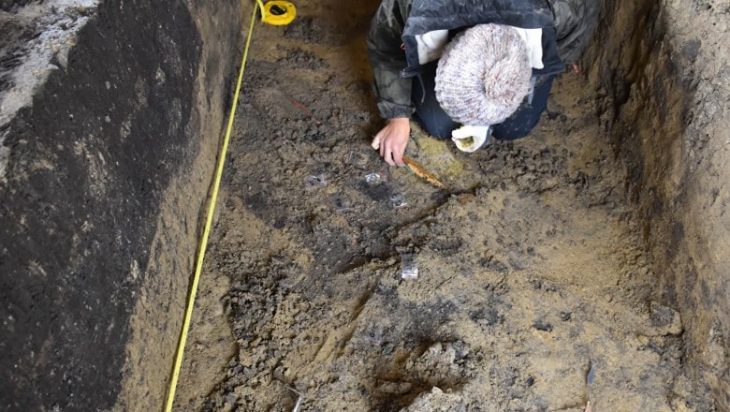
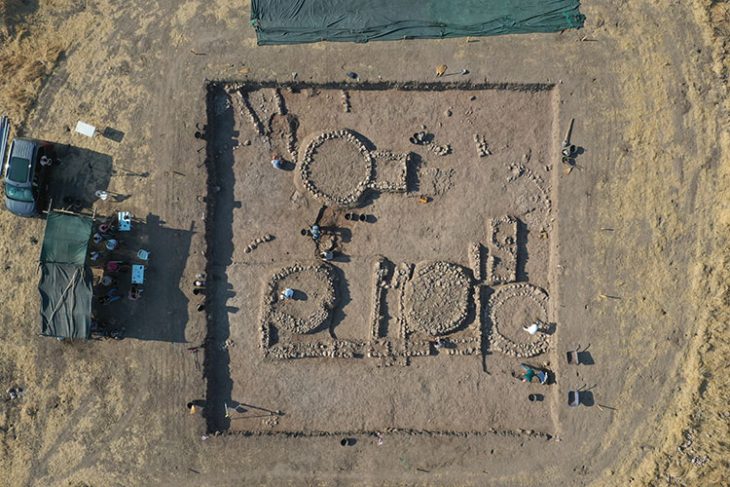Village women take part in the renovation works of the largest synagogue in the ancient world, located in the ancient city of Sardis (also Sardes, Sart in Turkish), the city of King Croesus with its legendary wealth.
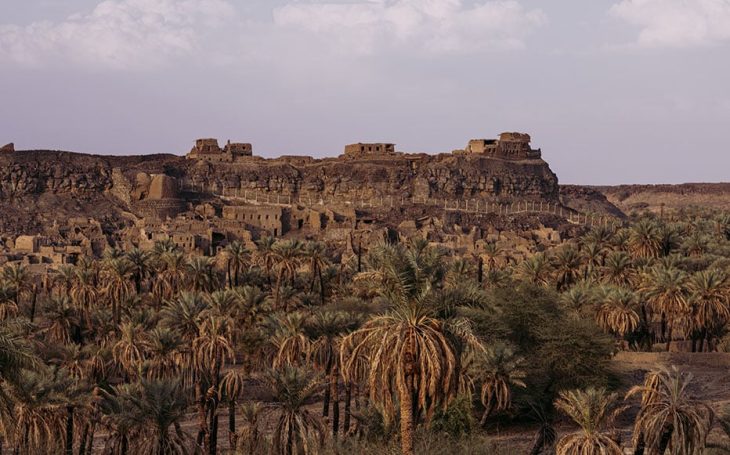
The ancient city, located in the Sart district of the Salihli district in the western province of Manisa, was the capital of the Lydian Kingdom.
Sardis has a long history that goes back as far as 1200 BCE. It was established near the Pactolus River (present Sart Çayı), which carried specks of gold that washed down from the nearby mountains.
Sardis was the major city and capital of Lydians, an Anatolian people. The kings of Lydia Gyges, Alyattes, and Croesus were fabulously rich and created a powerful empire in the 7th and 6th centuries BCE.
After the defeat of Croesus, Sardis was incorporated into the Persian Empire as one of its most important cities and the seat of a Persian satrap. It was conquered by Alexander the Great and after his death, it became the seat of a Seleucid satrap. Sardis was incorporated into the Roman Empire in 133 BCE and became the administrative center of the Roman province of Lydia and the seat of a Roman proconsul.
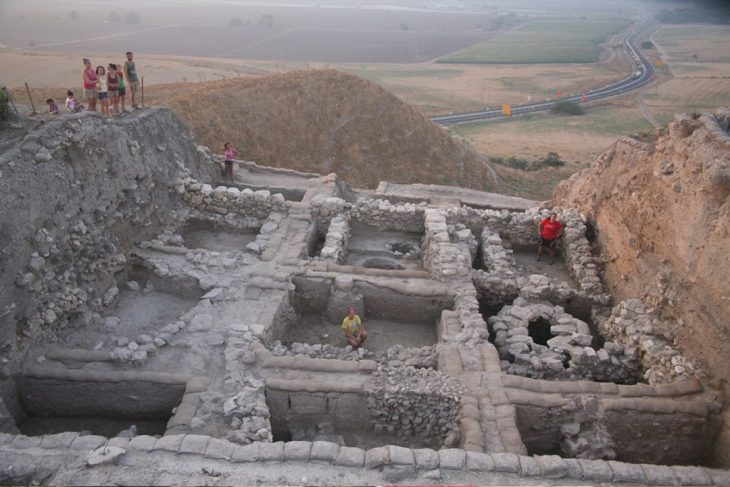
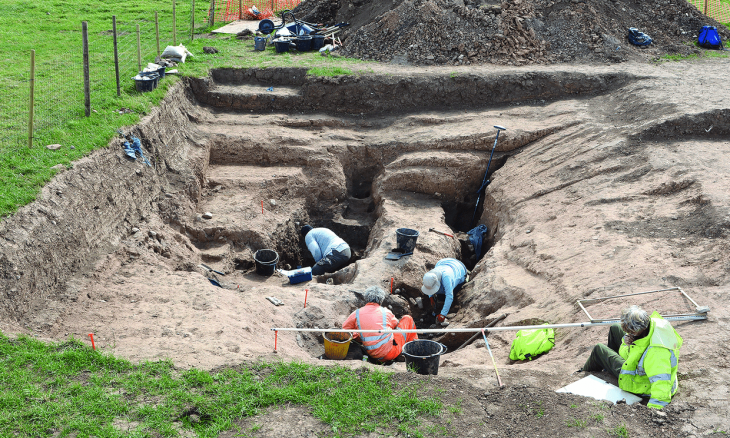
The monumental synagogue was the center of Jewish religious life at Sardis during the Late Roman period. Discovered in 1962, the building and its decorations have been partly restored.
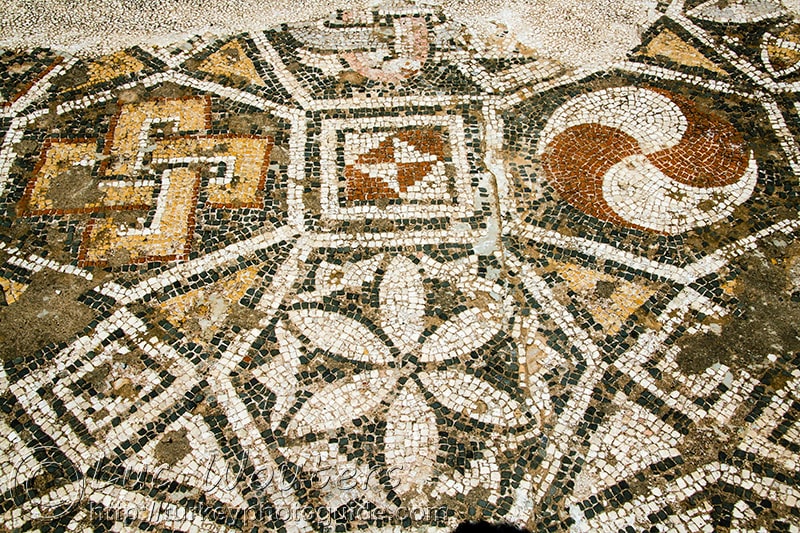
The synagogue, an important venue for faith tourism, is now open to tourists, and its mosaic stones on the floor were laid by women in accordance with the original.
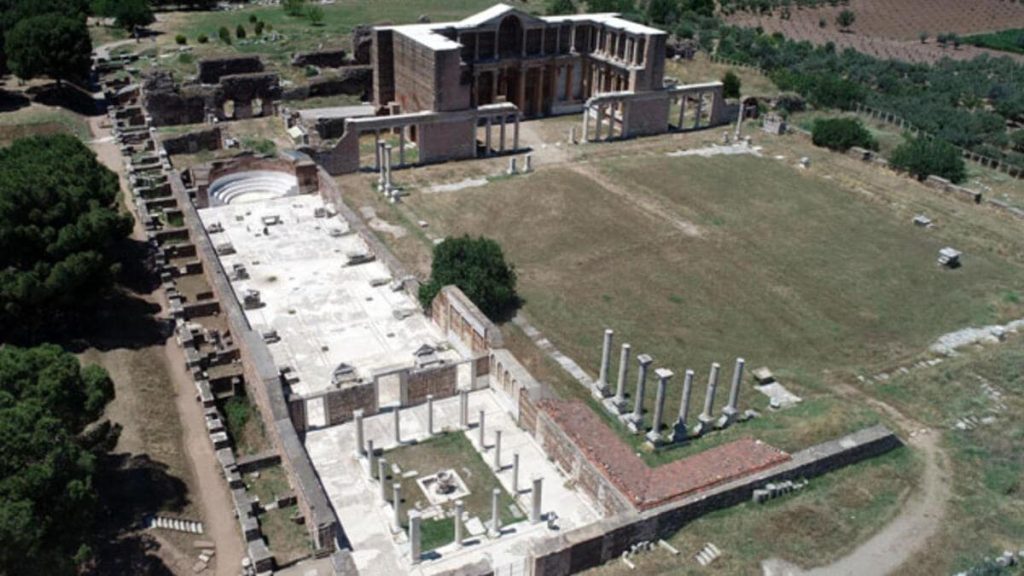

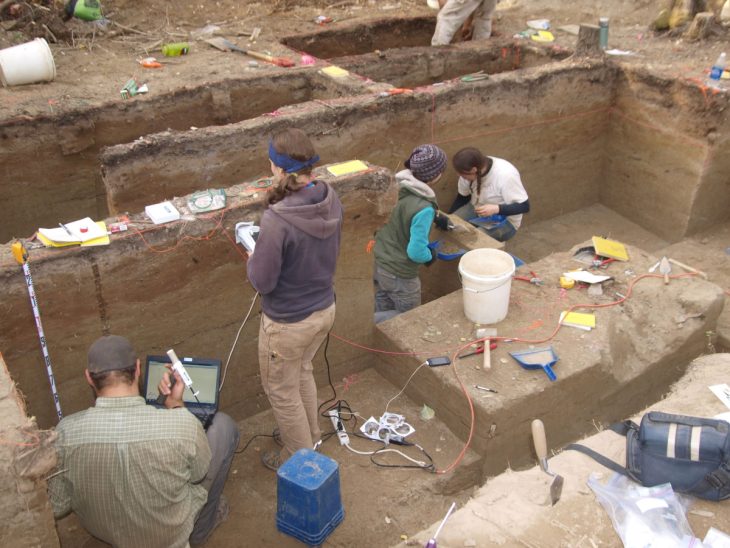
Archaeological excavations started 159 years ago in the ancient city of Sardis and still continue. Many structures and artifacts from Lydian, Persian, Hellenistic, Roman, Byzantine, and other cultures have been unearthed during the excavations in the ancient city, which was the home of various settlements and many civilizations for over 5,000 years. It is also home to the largest synagogue of the ancient ages.
Sardis, which played an important role in the spread of Christianity to the West in the revelation part of the Bible, also has special importance in terms of religion. The synagogue, which has traces of the Jewish community’s life, still preserves its splendor.
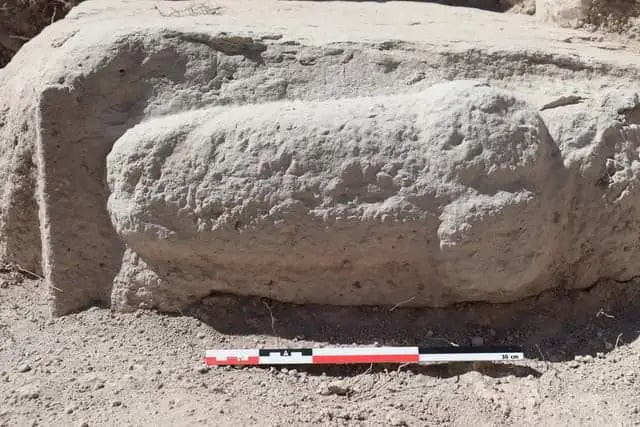
The mosaic stones on the floor of the Sardis Synagogue, which was covered with an iron roof two years ago and where renovation works started on the floor last year, are being repaired with great care by nine village women. White mosaic stones of the floor are brought from the tumuli of Bintepe and black mosaic stones are brought from Antakya.
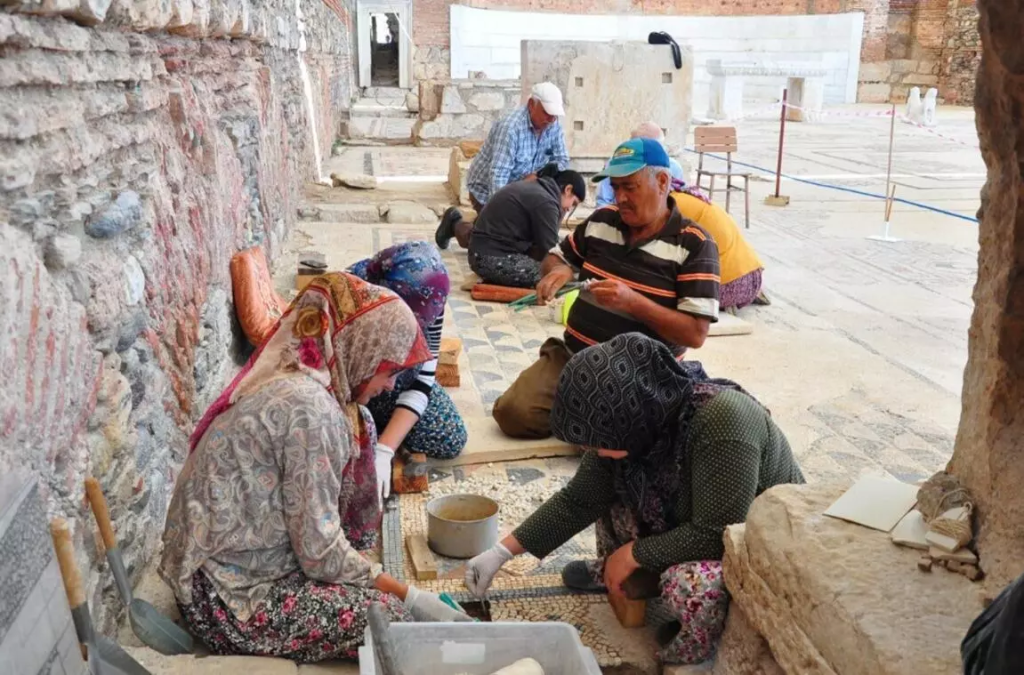

Speaking about the works carried out in the ancient city, the head of the excavations, Professor Nicholas Cahill, said that the works continue this year in many different parts of the city.
“The synagogue was unearthed in 1963. The mosaics on the floor of the synagogue have been removed and replaced with modern iron panels. But because of the diggings, there are many gaps. Together with the women, we repair those gaps on the floor and restore the gaps with mosaic stones in accordance with their original form,” Cahill said.
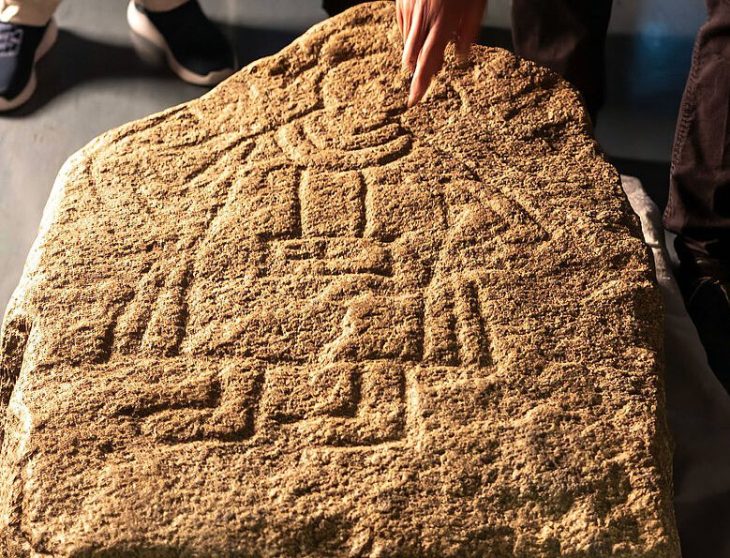
Speaking of the structure of the synagogue, Cahill stated: “It is an interesting structure, the largest synagogue in the ancient world and a very luxurious one. Its floor is covered with mosaic and its walls are covered with colored marble. The names of those, who paid for the construction of the structure, are written on the wall, and the inscription on the wall writes in Greek who paid for its construction.”
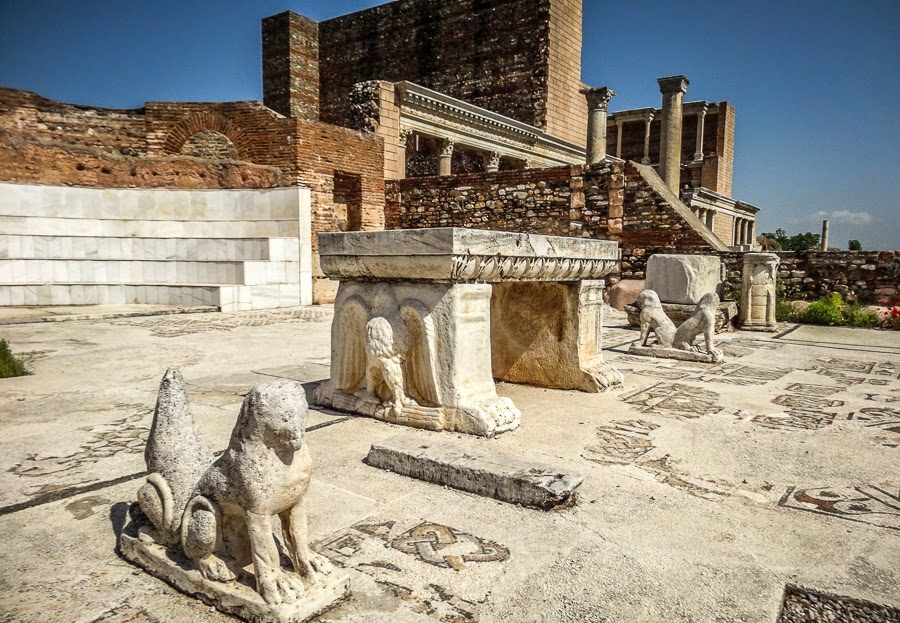

“Sardis was one of the largest cities in the 6th century B.C. and also the capital of a great empire. With the findings we obtained during the excavations, we reach much earlier periods. We are working to learn the history of the city better,” Professor Cahill added.
The Sardis synagogue was entered through a colonnaded forecourt from the east. The forecourt was roofed around the sides but open to the sky in the center. Beyond that is the main assembly hall, which is over 50 meters long and can hold nearly a thousand people. Massive stone piers supported the roof of the main hall at a height of about 14 m above the floor.
The synagogue occupied the corner of the Roman bath-gymnasium, converting part of this public building into a Jewish house of worship. The mosaic floors, furnishings, and marble wall decorations were installed at different times; most of those which remain are from the 4th and 5th centuries. The synagogue was abandoned after an earthquake along with much of the rest of the city in the early seventh.