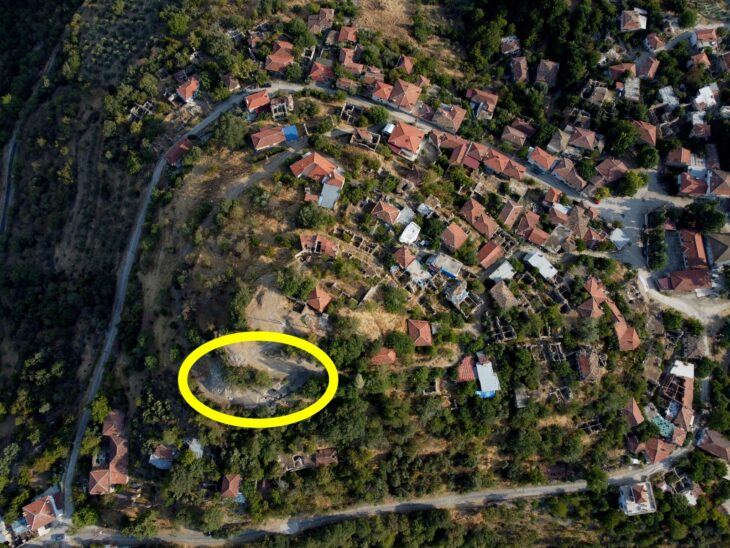
The 3,600-year-old fist-shaped drinking bowls found in excavations in Hattusa, the capital of the Hittite Civilization, which shaped the Anatolian civilization and has an important part in history, differents attract attention with their distinctive appearance.
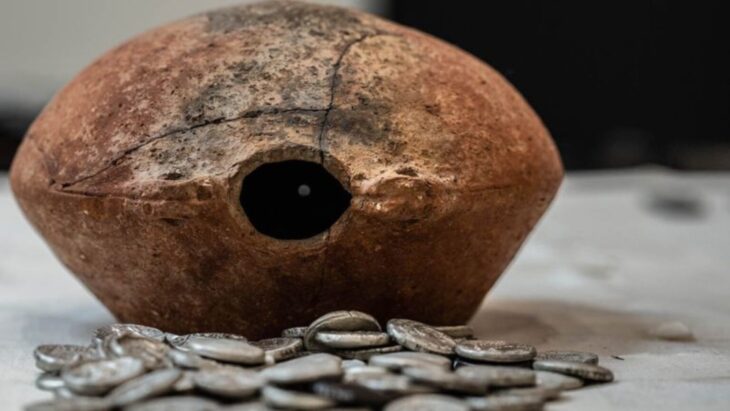
A 3,600-year-old fist-shaped drinking bowl, one of three ancient drinking bowls unearthed in past years in archaeological digs in Hattusha, the capital of the Hittite Civilization, is considered a “unique” work by the archaeology world.
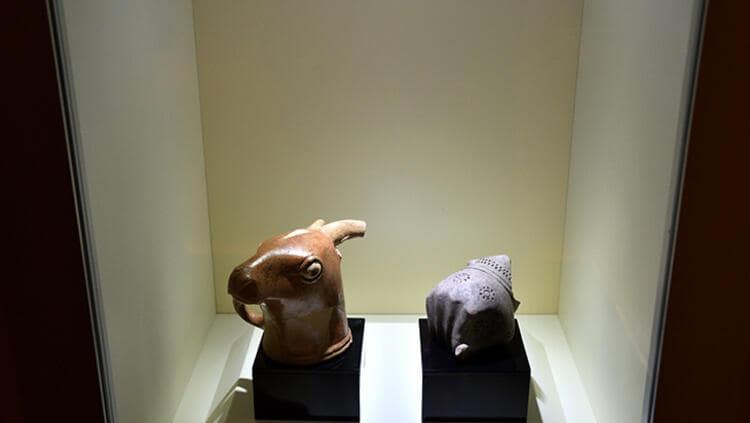
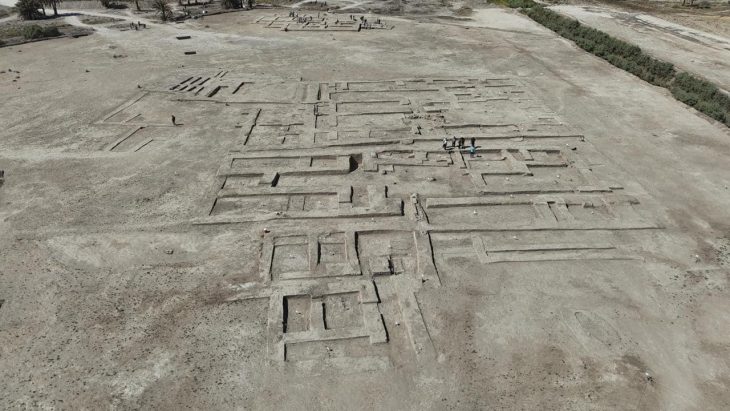
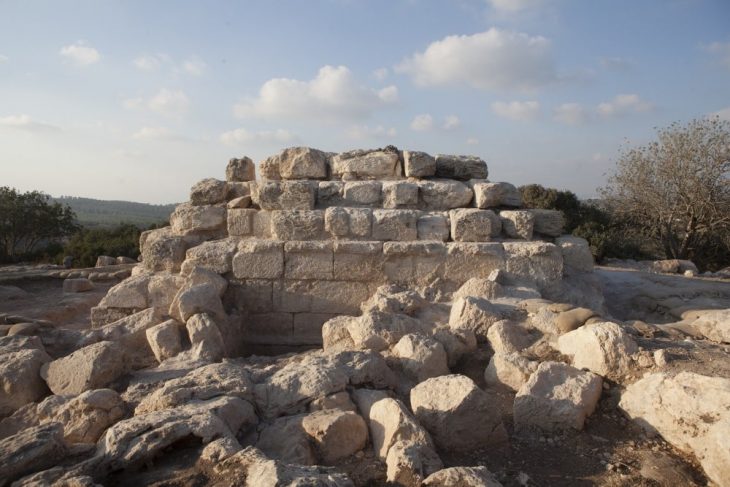
Drinking bowls (Rhyton) in the shapes of bulls, goats, and fists discovered during the German Archaeological Institute’s excavations at the Hattusa Ruins decorate the Boğazkale Museum in the Central Anatolian province of Çorum.
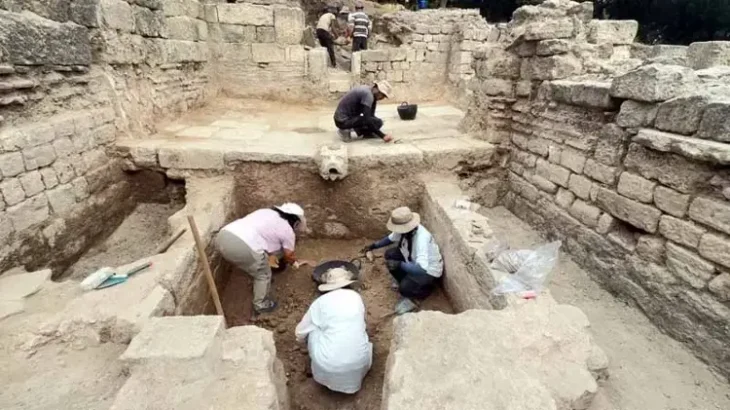
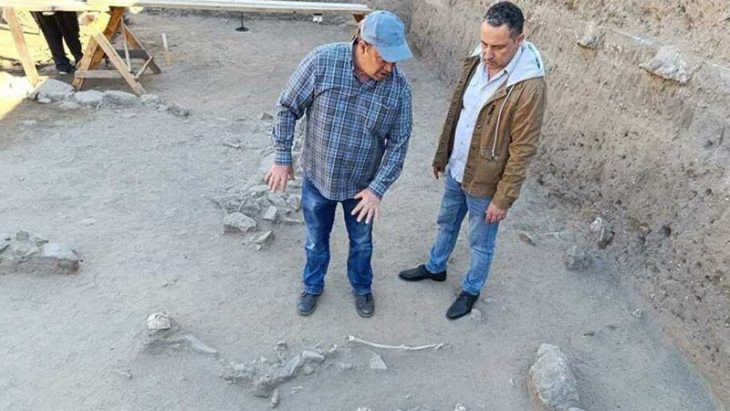
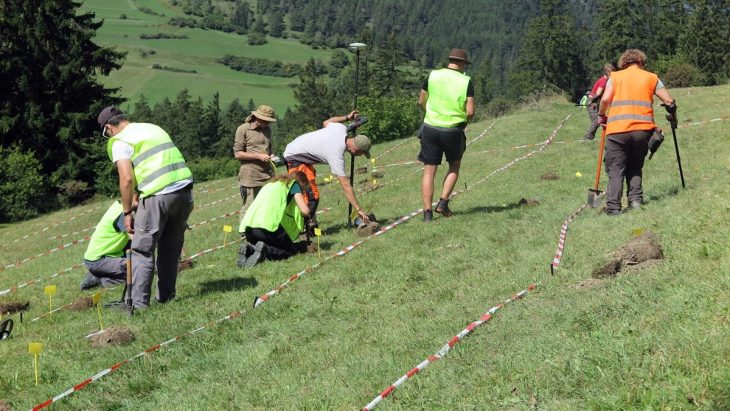
Professor Andreas Schachner, the leader of the Boğazköy Hattusha excavations, told the Anadolu Agency that they unearthed drinking bowls in the shapes of bulls, goats, and fists six years ago.
Boğazköy Hattusa Excavation Director Prof. Dr. Andreas Schachner: “During the excavations, we found three significant artifacts in the form of a bull, a goat, and a fist. The most interesting of these is the fist-shaped drinking bowl as the material from which it is made of is a very rare, gray ceramic,” he said.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
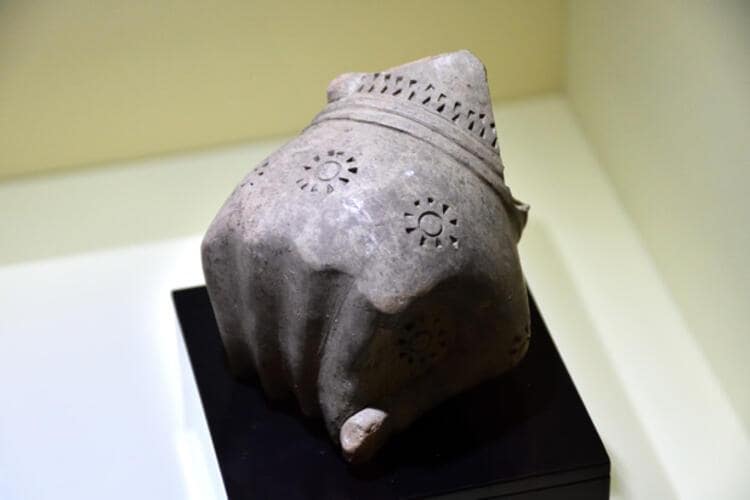

While all three drinking bowls are archaeologically significant, Schachner described the fist-shaped bowl in particular as a “unique relic” due to both the material used and its capacity to survive underground for thousands of years.
Schachner pointed out that a silver fist-shaped drinking bowl is on exhibit in a museum in the United States. Schachner said: “A drinking bowl in the shape of a human fist has yet to be found in legal excavations in Anatolia, except in Boğazkale. There is a similar one made of silver, which was smuggled abroad. It is not known where it was found exactly. It is currently exhibited in a museum in the U.S.”
“Thanks to this bowl we found in Boğazkale, we learned how these artifacts were used and where they were used, as the smuggled artifacts lose their environment and cannot reveal much. Therefore, the fist-shaped drinking bowl is a ‘unique’ artifact,” Schachner added.
Stating that the drinking bowl was found almost intact, Schachner added that the place where the drinking bowl was found was a place where ritual and cult activities were held.
“We think that it is an artifact used as a drinking bowl by the notables or high-level administrators of the Hittites during rituals, as the Hittites had a phrase called ‘drinking the god.’ This was something done in rituals. The elite of the Hittites, perhaps the priests, drank in such glasses,” he said.
Rhyton: Various ornate drinking vessels of ancient times, typically partially shaped into the shape of an animal or animal head. However, in the Hittite civilization and earlier periods, There are also examples shaped like feet and fists.