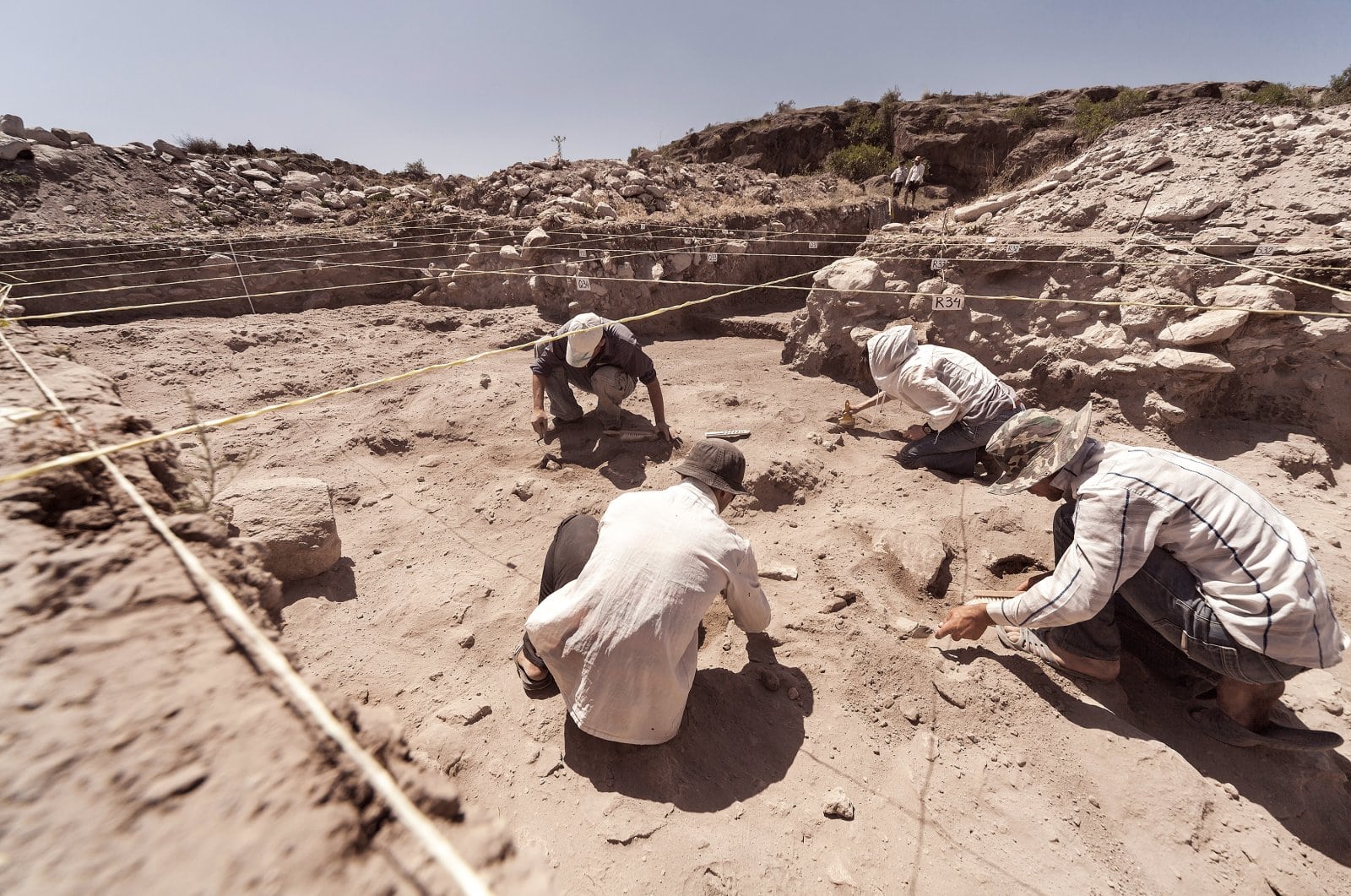
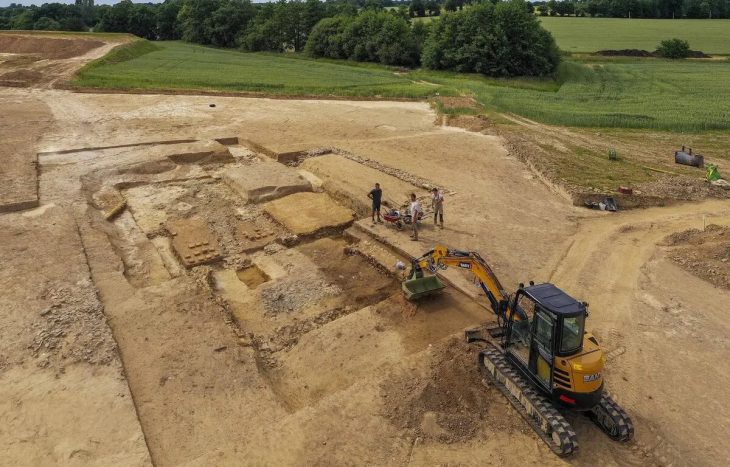
A multinational team of archaeologists announced the discovery of North Africa’s oldest Stone Age hand-ax manufacturing site, going back 1.3 million years, on Wednesday.
According to experts on the team, the discovery pushes back the founding date of the Acheulian stone tool industry linked with a crucial human progenitor, Homo erectus, by hundreds of thousands of years in North Africa.
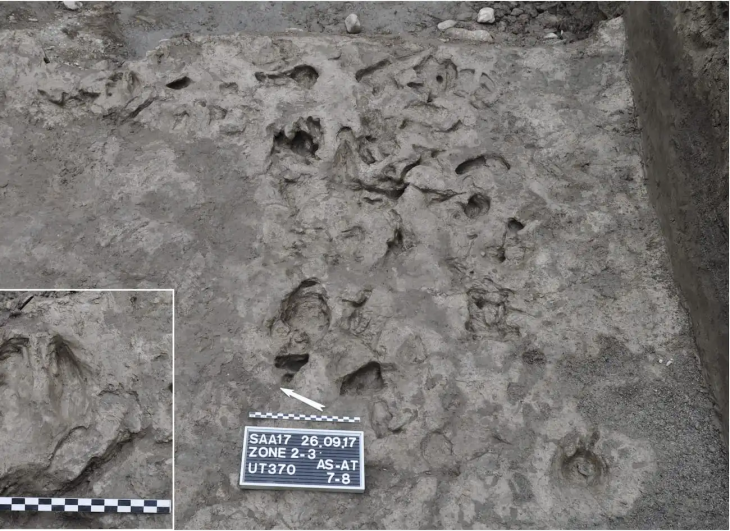
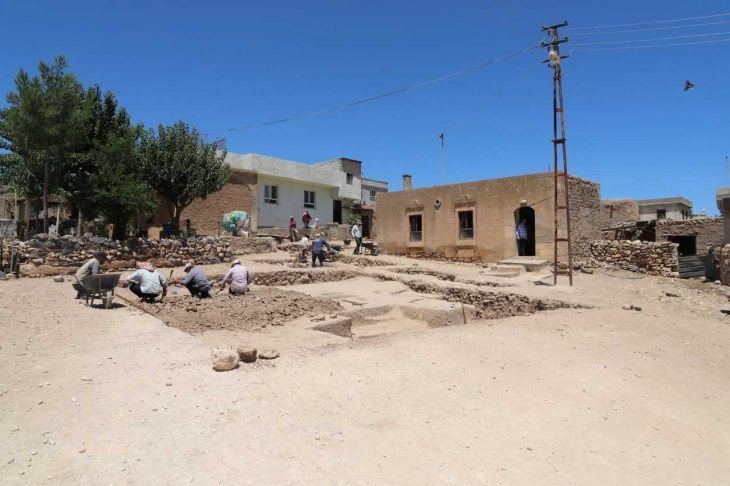
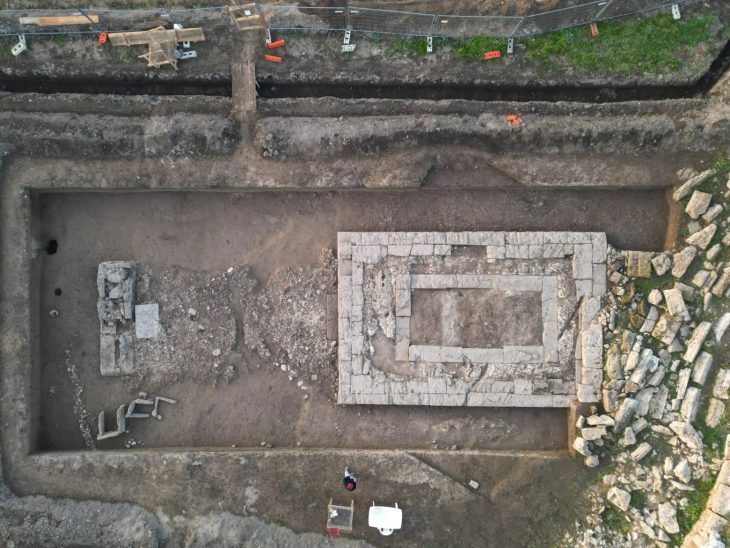
It was discovered during excavations in a quarry on the outskirts of Casablanca, Morocco’s economic hub.
Before the find, the presence in Morocco of the Acheulian stone tool industry was thought to date back 700,000 years.
This “major discovery … contributes to enriching the debate on the emergence of the Acheulian in Africa,” said Abderrahim Mohib, co-director of the Franco-Moroccan Prehistory of Casablanca program.
New discoveries at the Thomas Quarry I site, which became renowned in 1969 after a human half mandible was unearthed in a cave, indicate that the Acheulian there is nearly twice as ancient.
The 17-strong team behind the discovery comprised Moroccan, French, and Italian researchers, and their finding is based on the study of stone tools extracted from the site.
Moroccan archaeologist Abdelouahed Ben Ncer called the news a “chronological rebound.”
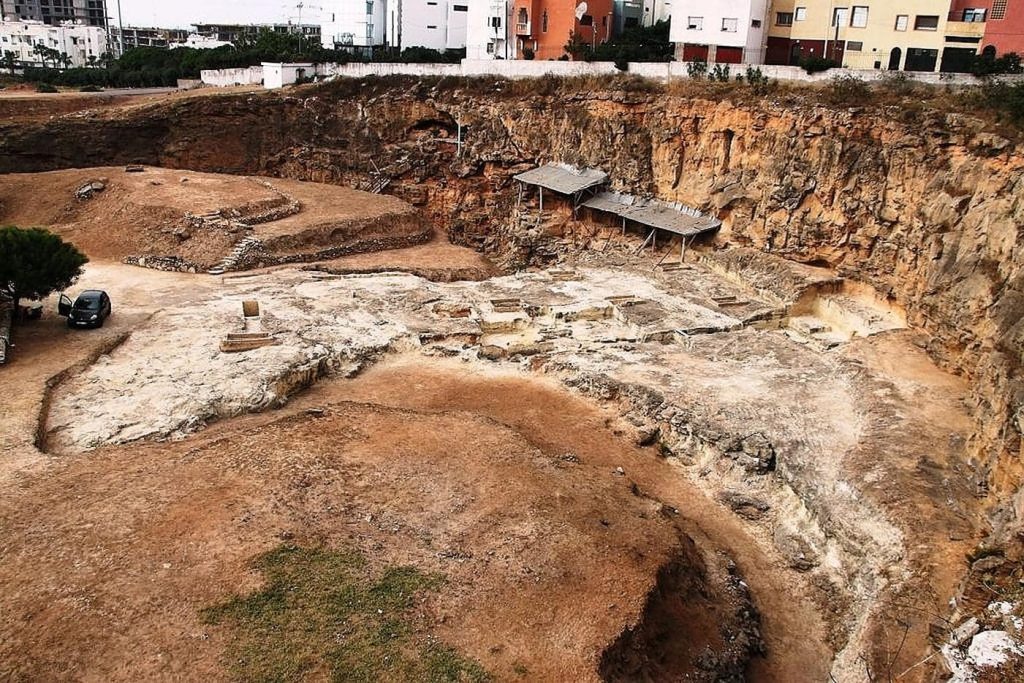

He said the beginning of the Acheulian in Morocco is now close to the South and East African start dates of 1.6 million and 1.8 million years ago respectively.
Earlier humans had made do with more primitive pebble tools, known as Oldowan after their East African type site.
Research at the Casablanca site has been carried out for decades, and has “delivered one of the richest Acheulian assemblages in Africa,” Mohib said.
“It is very important because we are talking about prehistoric time, a complex period for which little data exists.”
Mohib said the study also made it possible to attest to “the oldest presence in Morocco of humans” who were “variants of Homo erectus.”
Prehistoric man’s ability to “design the shape of the tool he wants”, such as the latest find, was a “very important technological advance,” he added.
In 2017, the discovery of five fossils at Jebel Irhoud in Morocco, estimated at 300,000 years old, overturned evolutionary science when they were designated Homo sapiens.
The Moroccan fossils were much older than some with similar facial characteristics excavated from Omo Kibish in Ethiopia, dating back around 195,000 years.
The “Prehistory of Casablanca” program is the result of collaboration between the Moroccan Institute of Archaeology (INSAP), Paul-Valery Montpellier 3 University in Montpellier, France, and the French foreign ministry.
French and Italian laboratories also took part in the project.
The Paleolithic age is the first and longest period of prehistory which began more than 3 million years ago and ended 12,000 years ago.
BY FRENCH PRESS AGENCY – AFP: Agence France-Presse is an international news agency with headquarters in Paris, France. It is the world’s oldest news agency, having been founded in 1835.