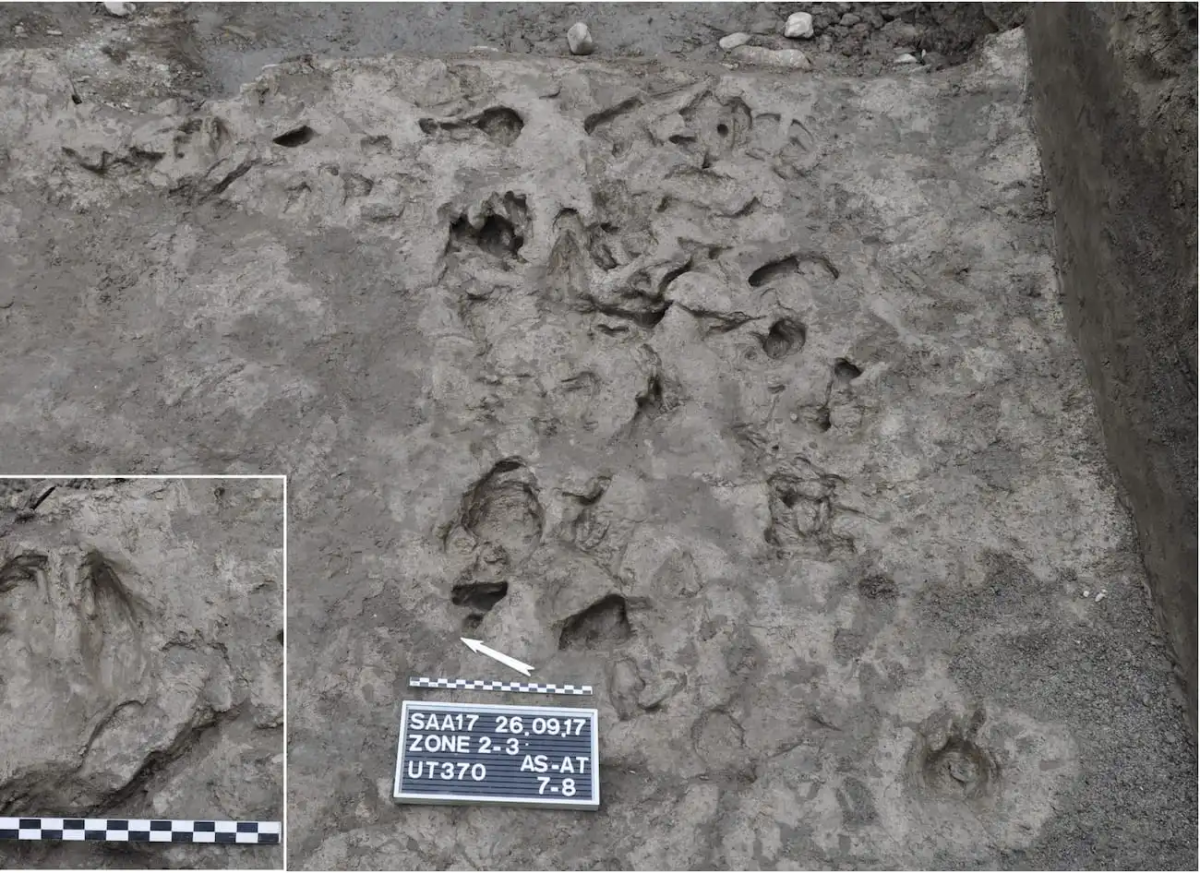
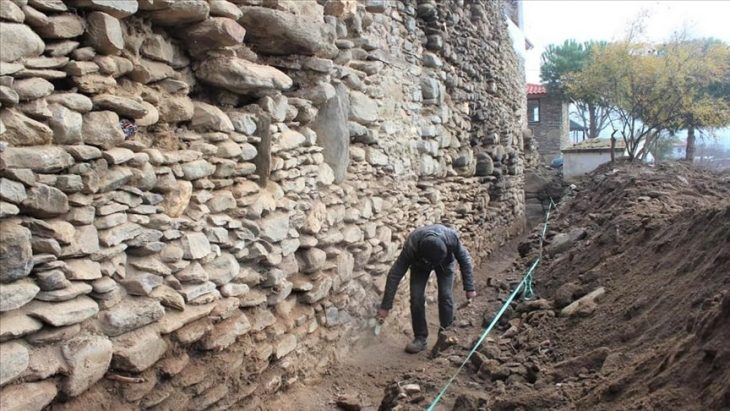
Excavations at the Anciens Arsenaux site in Sion, Switzerland, researchers revealed evidence that Neolithic farmers used animal traction to pull plows between 5,100 and 4,700 years ago. This discovery is nearly a millennium older than the previous oldest known plow marks.
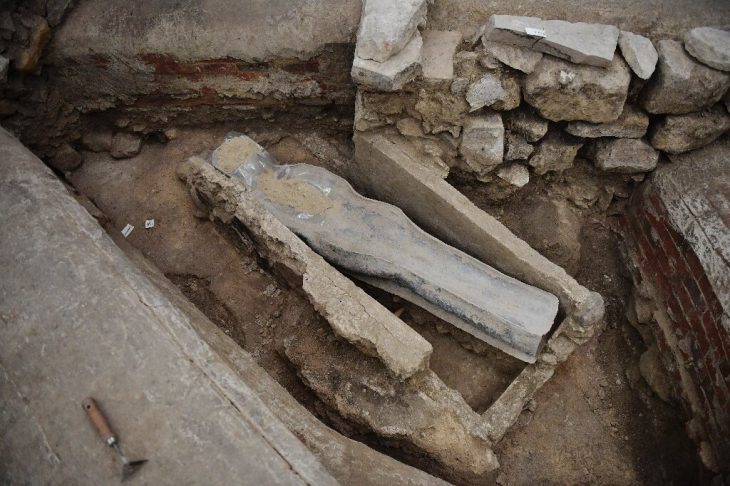
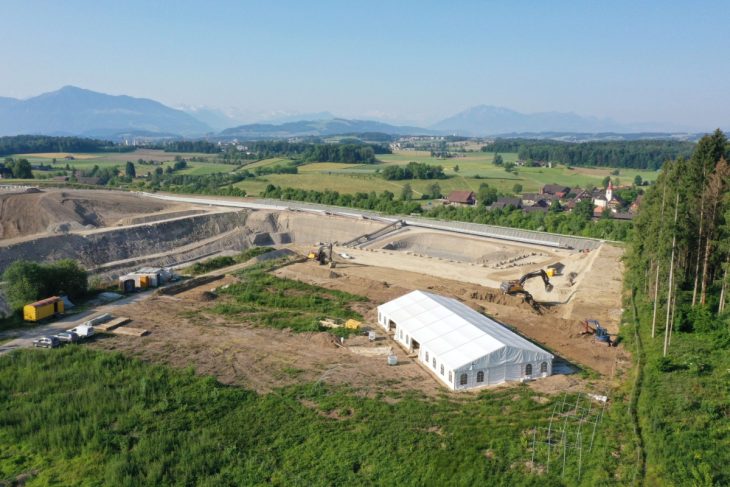
The Anciens Arsenaux site is located in Sion (Canton of Valais, Switzerland), on the alluvial cone of the Sionne, an Alpine torrent that runs through the town and into the Rhône. Excavating the 800-square-meter site for the Valais Cantonal Archives in 2017 revealed alternating human occupation levels and ten-meter-thick alluvial deposits.
Researchers have revealed that settlement levels span much of the Neolithic period, covering approximately between 5200 and 3500 BCE, in their documentation studies.
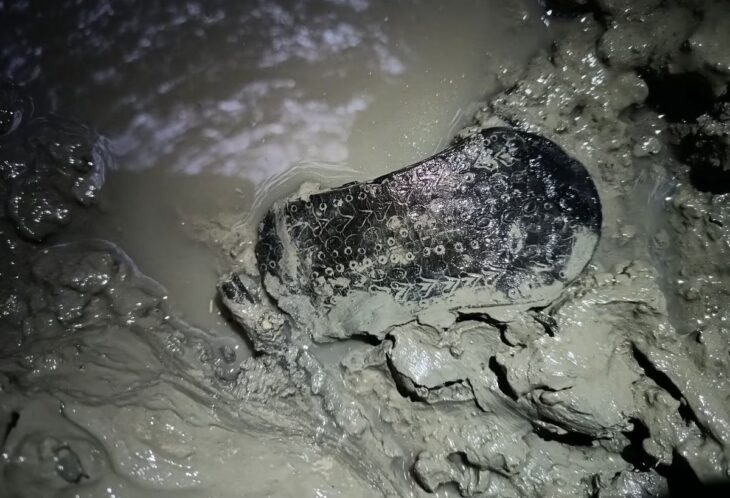
The presence of these alluvial deposits was undoubtedly the most important factor that made the discovery possible. Because ancient plow marks are easily erased by erosion or subsequent agriculture, their discovery is extremely rare. The only reason the furrows in Sion survived is because the surrounding stream’s sediments swiftly covered them, preserving the impressions of the furrows in the soil layers.
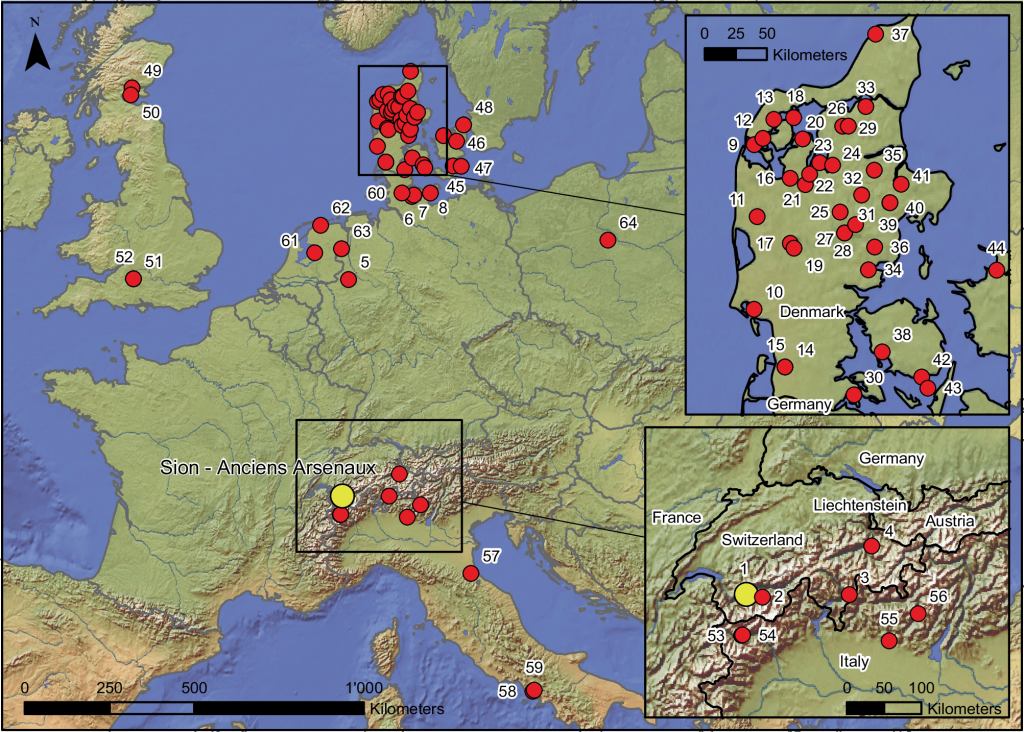
The strongest evidence of animals pulling plow-like tools in European agriculture before this discovery came from sites in northern Germany and Denmark that date back approximately 3,700 years.
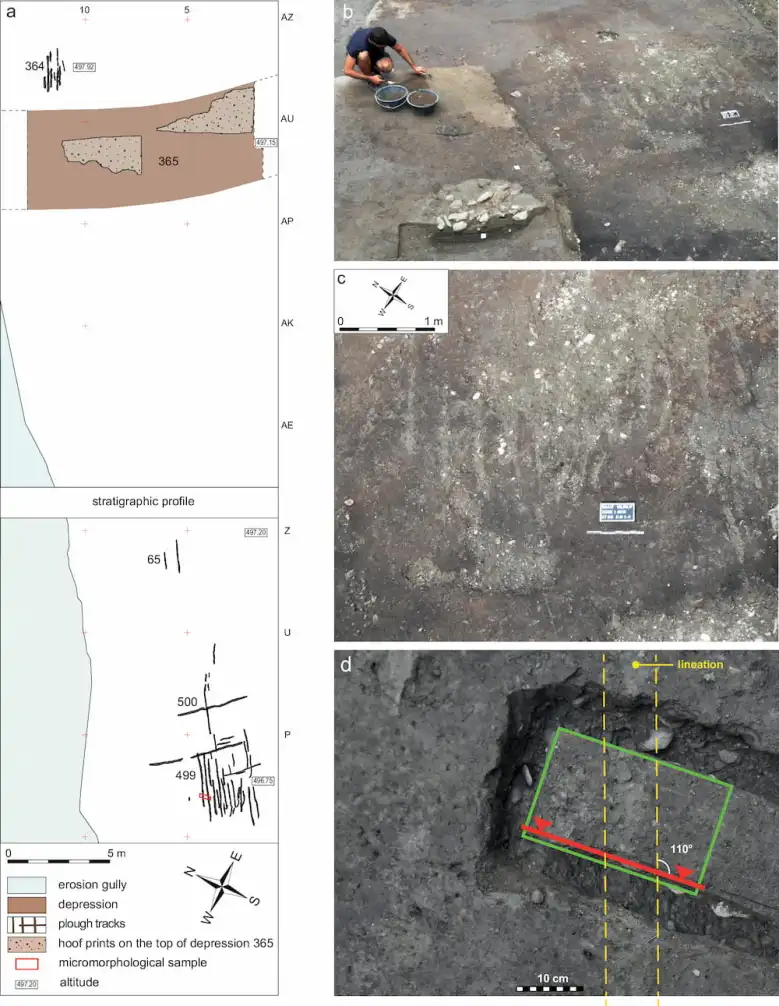
The Sion site contains parallel furrows and impressions in the ground consistent with being made by a plow dragged through the soil, as well as hoofprints indicating that the pulling force came from domesticated cattle or oxen.
In the past, there has been evidence from animal bones that people in areas like Anatolia and the Balkans have occasionally used cattle or oxen for traction since the seventh millennium BCE. On the other hand, this is the first concrete proof of widespread plow agriculture found in prehistoric archaeology.
Researchers were able to conclusively date these pieces of evidence to the early Neolithic period by conducting detailed radiocarbon dating on organic materials found above and below these soil disturbances.
These new findings show that animal traction in agriculture appeared very early after agriculture itself emerged in the alpine region of Europe, explain the researchers. It wasn’t a later adaptation but likely an integral part of the early processes of continent-wide neolithization.
Compared to agriculture which relies only on human labor and hand tools, using animal power to pull plows represents a significant technological innovation that increases agricultural productivity and surplus and enables the cultivation of much larger areas. In many early agricultural societies, economic stratification and social complexity are thought to have been fueled by this excess production.
The dating of the plow marks in Sion suggests that we need to reevaluate long-standing theories about the pace of agricultural intensification and its impact on society during the expansion of agriculture across Neolithic Europe, the authors of the study said.
The ability to work larger fields with animal traction may have emerged from the outset rather than being a later revolutionary development.
Researchers note that the site’s location in a significant alpine valley may have been an ideal environment to quickly adopt and preserve evidence of plow use. Any early analog traces across the vast European plains where Neolithic agriculture first settled may have been erased by increasing erosion and intense agricultural development that followed.
Therefore, the archaeological team intends to conduct additional excavations in similar alpine environments throughout Switzerland and Italy to continue investigating the origins of animal traction in agriculture.
The research was published in Nature.
doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-02837-5
Cover Photo: ARIA SA / s. van Willigen et al. / Humanities and Social Sciences Communications