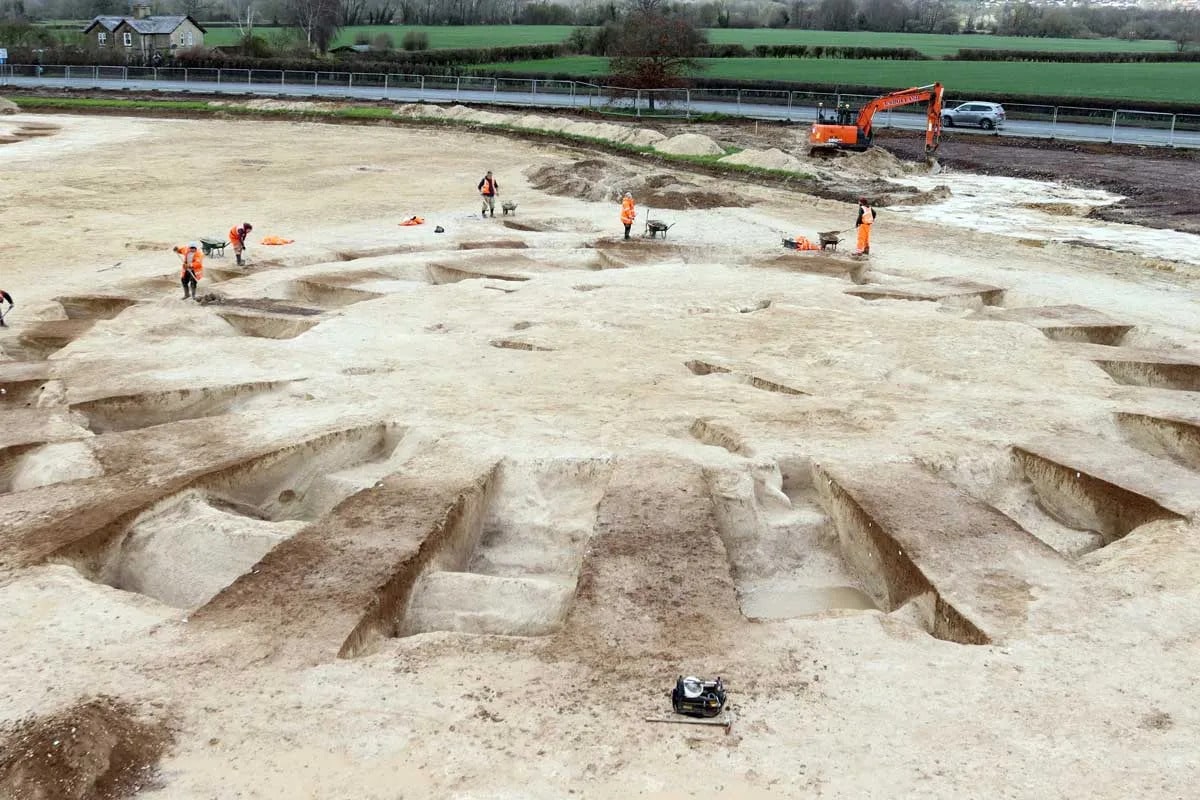
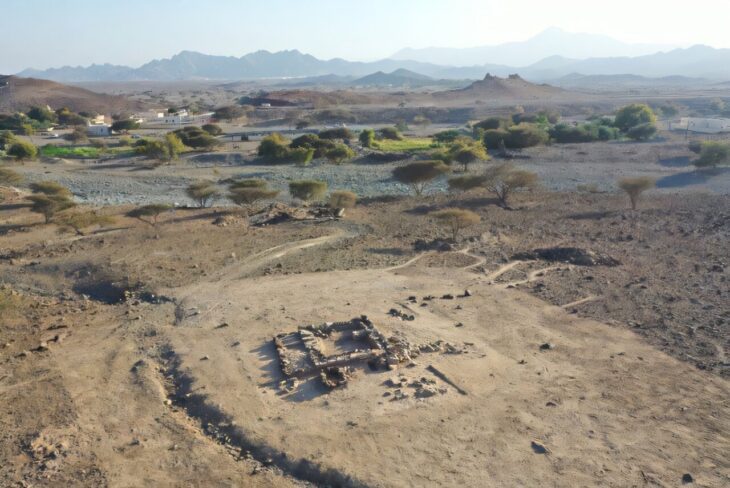
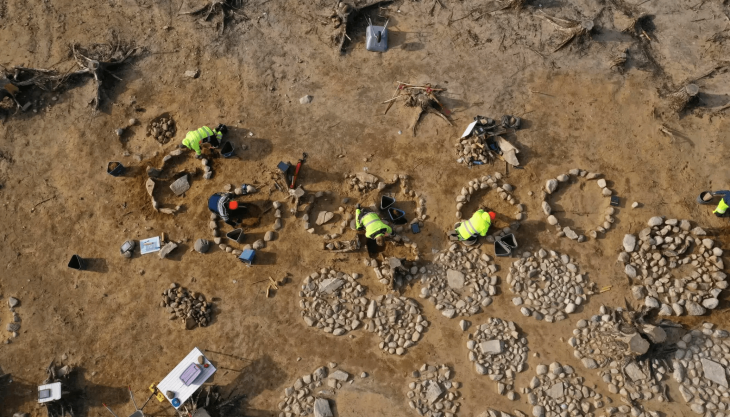
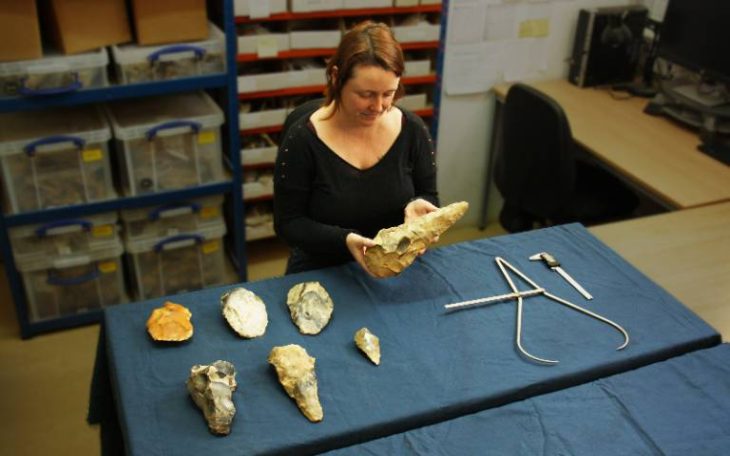
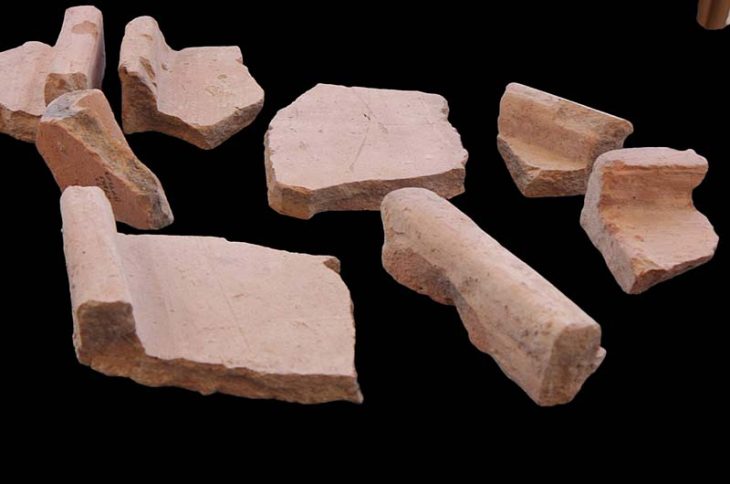
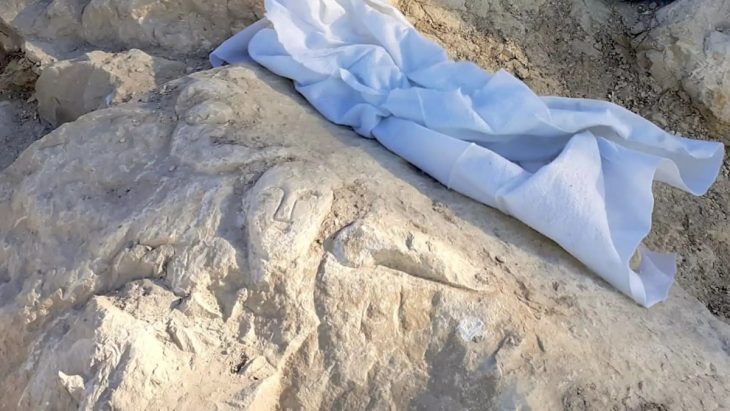
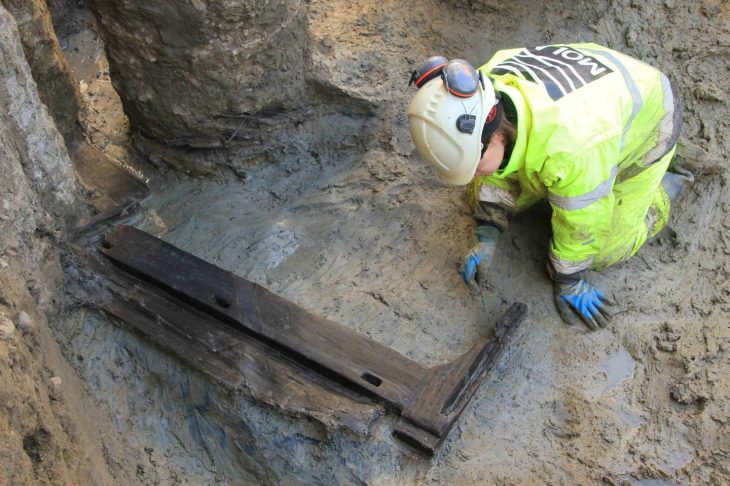
The Cotswold Archeology team excavating at the site of a planned housing development near Salisbury, England, has unearthed a giant barrow cemetery that could be between 3,500 and 4,000 years old.
Wiltshire is well known for its Bronze Age barrows, particularly those found within the World Heritage site of Stonehenge and on the chalklands of Cranborne Chase. In contrast, little is known about similar sites near the medieval city of Salisbury.
These barrows were installed 1,000 years or more after the monuments at Stonehenge were built on the Salisbury Plain just 10 miles (16 km) to the north. The archaeologists discovered enough evidence to conclude that these barrows had been made during the latter period.
However, Vistry’s construction of a new residential housing development on the outskirts of Harnham, a southern Salisbury suburb, has provided the opportunity to unearth some of the remains of a major round barrow cemetery and its landscape setting.
Round barrows were first constructed in the Neolithic period, although most were built during the Beaker and Early Bronze Age (2400 – 1500 BC), and usually consist of a central burial, a mound, and an enclosing ditch.
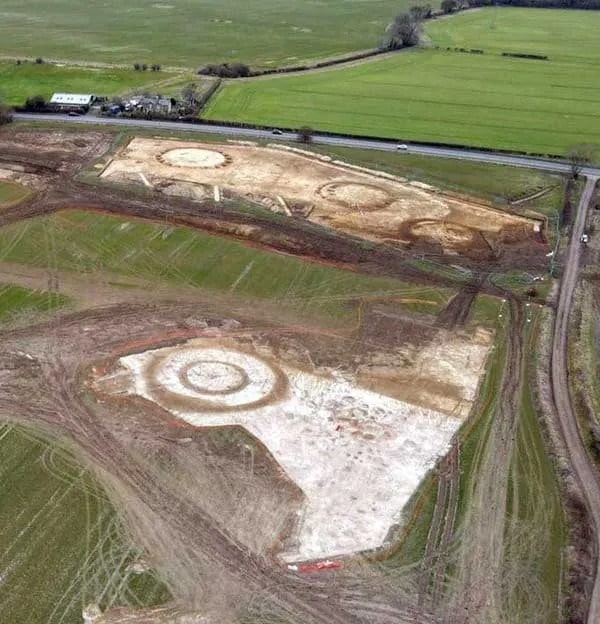

The size of round barrows can range from under 10 meters in diameter to up to 50 meters, although the majority tend to average between 20 and 30 meters. Additionally, the earthworks associated with barrows can vary.
Some have large central mounds (‘bell barrows’), others small central mounds and outer banks (‘disc barrows’), and some have central hollows (‘pond barrows’).
Their ditches would have provided material for the barrow mound, which would have been constructed of chalk, topsoil, and turf. Barrows are typically associated with burials; some contain only a single individual, while others contain a series of burials and, on rare occasions, multiple burials.
“Our cemetery is made up of about twenty or more barrows that spread from the very edge of Harnham on the Nadder valley floor, up and across the adjacent chalk hillside on what is the northern edge of the landscape of Cranborne Chase,” the Netherhampton site discoverers wrote in a Cotswold Archaeology press release. “The cemetery is arranged in small clusters of barrows—either pairs or groups of six or so—and we’ve so far excavated just five.”
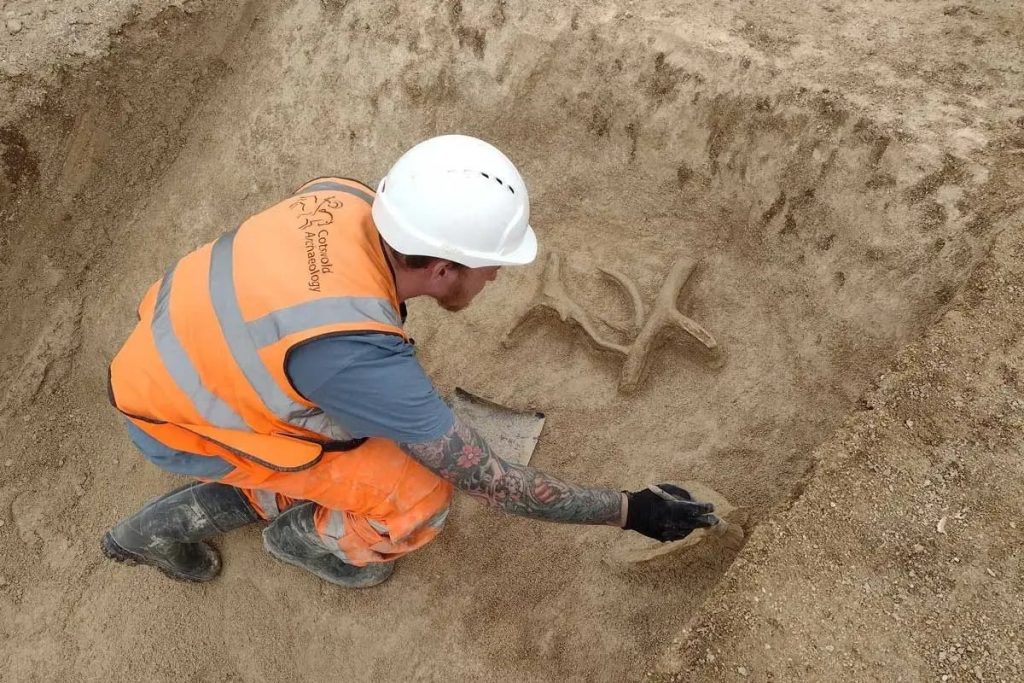

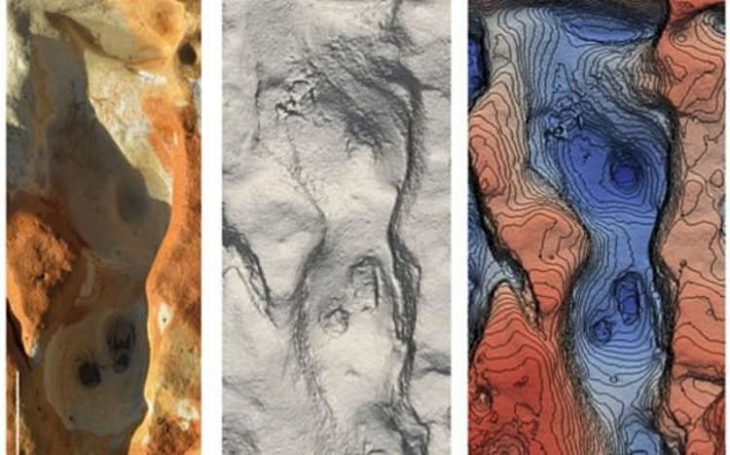
The Cotswold archaeologists have discovered 10 burials as well as three piles of buried cremation ash inside the five ditches they have already excavated. A further indication of how well-liked this burial ground must have been with the people who lived in the area around Salisbury 4,000 years ago and beyond are the signs that two of the site’s barrows have undergone significant expansion at some point.
Excavations also uncovered Saxon remains, including a possible sunken-featured building, preserved timbers, iron knife blades, and ceramics, as well as a cultivation terrace (‘lynchet’) of probable late Iron Age date and Bronze and Iron Age pits.
Cover Photo: The central ring ditch in Area 1, under excavation by CA’s Andover team. Cotswold Archaeology