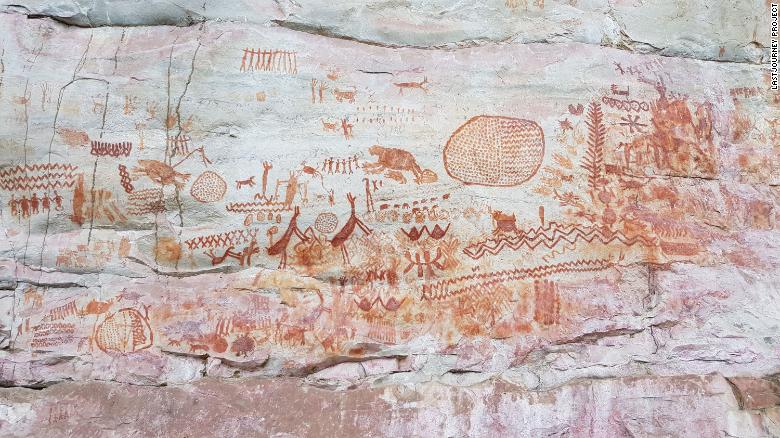
South America was filled with ice age animals more than 12,000 years ago, including car-sized ground sloths, elephantine herbivores, and a deer-like species with an extended snout. However, there is much more we do not know and still to learn about what kinds of beings walked on Earth 12,000 years ago.
According to the study published in the journal Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B. “the La Lindosa rocky outcrop in the Colombian Amazon rainforest contains thousands of paintings which, along with the ones reported for Chiribiquete National Park, represent one of the richest rock art.
Many of the images in the Serranía de la Lindosa depict hunting and ritual scenes showing humans interacting with plants, forests, and savanna animals.
Among this rich pictorial variety of animals, there are some intriguing images that appear to represent extinct mega fauna including a giant ground sloth, gomphothere, camelids, horses, and three-toed ungulates with trunks that bear some resemblance to some extinct megafauna such as Xenorhinotherium or Macrauchenia.”
According to Jose Iriarte, the author of the study and professor in the Department of Archaeology at the University of Exeter, UK the rock paintings have the whole diversity of Amazonia. Turtles and fishes to jaguars, monkeys and porcupines.
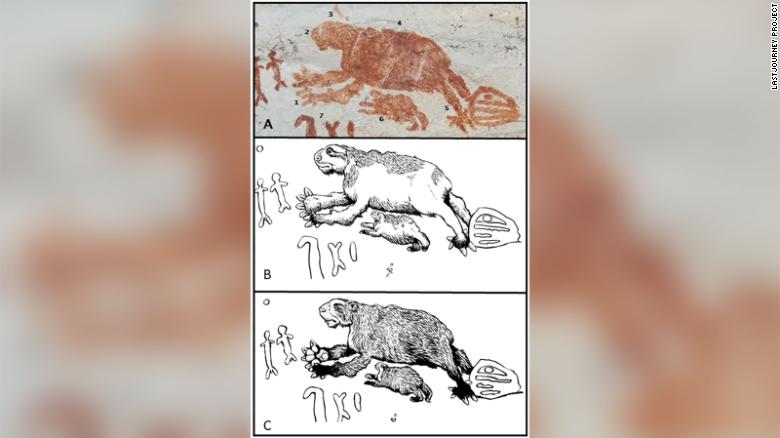

“Iriarte calls the frieze, which likely would have been painted over centuries, if not millennia, “the last journey,” as he said it represents the arrival of humans in South America — the last region to be colonized by Homo sapiens as they spread around the world from Africa, their place of origin. These pioneers from the north would have faced unknown animals in an unfamiliar landscape.
“They encountered these large-bodied mammals and they likely painted them. And while we don’t have the last word, these paintings are very naturalistic and we’re able to see morphological features of the animals,” he said.
But the discovery of what scientists term “extinct megafauna” among the dazzlingly detailed paintings is controversial and contested.
Other archaeologists say the exceptional preservation of the paintings suggest a much more recent origin and that there are other plausible candidates for the creatures depicted. For example, the giant ground sloth identified by Iriarte and his colleagues could in fact be a capybara — a giant rodent common today across the region,” CNN reports.
Opinions of the nature and timeline of the La Lindosa rock art vary among scientists and more research must be carried out to determine what kind of animals our ancestors encountered and immortalized on the wall.
Iriarte said he and his team have identified five of the animals painted by the Ice Age people. These animals are a giant ground sloth with massive claws, a gomphothere (an elephantlike creature with a domed head, flared ears and a trunk), an extinct lineage of horse with a thick neck, a camelid like a camel or llama, and a three-toed ungulate, or hoofed mammal, with a trunk.

In addition to this, the researcher also said there are fossilized skeletons that will help paleontologists reconstruct what the extinct animals looked like.
As reported by CNN, “while the red pigments use to make the rock art have not yet been directly dated, Iriarte said that ocher fragments found in layers of sediment during excavations of the ground beneath the painted vertical rock faces dated to 12,600 years ago.
The hope is to directly date the red pigment used to paint the miles of rock, but dating rock art and cave paintings is notoriously tricky. Ocher, an inorganic mineral pigment that contains no carbon, can’t be dated using radiocarbon dating techniques. The archaeologists are hoping the ancient artists mixed the ocher with some kind of binding agent that will allow them to get an accurate date. The results of this investigation are expected possibly later this year.
Further study of the paintings could shed light on why these giant animals went extinct. Iriarte said no bones of the extinct creatures were found during archaeological digs in the immediate area — suggesting perhaps they weren’t a source of food for the people who created the art.”
Iriarte acknowledges the new study is not the final word in this debate, he is confident that they have found evidence of early human encounters with some of the vanished giants of the past.
Unlike the Upper Palaeolithic artists of Europe who chose to paint in deep dark caves, these early Amazonians painted in open rock shelters. Preservation of the paintings is highly variable, with images extremely faded or lost where exposed to the elements, whereas panels protected from prevailing wind and rain retain their vibrancy. The vertical rock walls reach up to 10 meters high.
Cover Photo: Las Dantas panel at Cerro Azul, La Lindosa. The Royal Society