The largest-known fossilized flower encased in amber, dating back nearly 40 million years, was again discovered in the Baltic region of Northern Europe.
Researchers have reexamined the rare amber fossil, which was first identified as the property of a pharmacist by the name of Kowalewski in what is now the Russian city of Kaliningrad in 1872.
According to Eva-Maria Sadowski, a postdoctoral researcher at Berlin’s Museum für Naturkunde and author of the new study, the striking fossil had been languishing largely forgotten in the collection of the Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR).
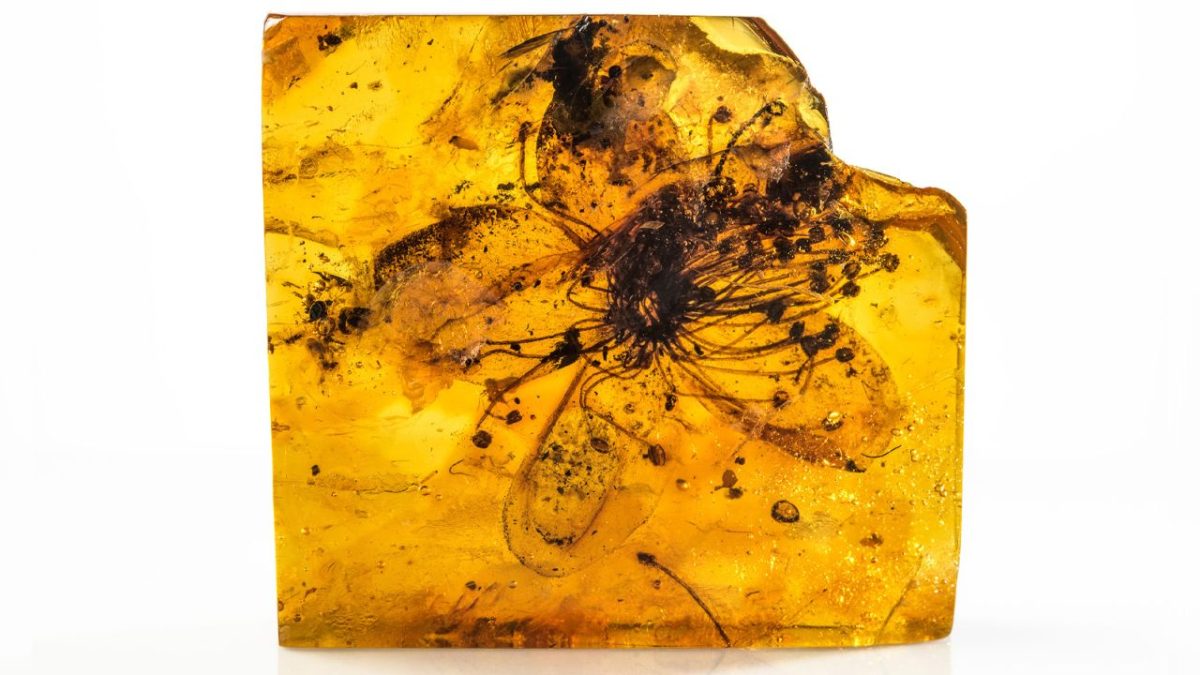
This tawny blossom, which looks like it was just plucked out of a bouquet, is the largest flower ever found in amber, the team reported on Thursday in a new study published in Scientific Reports. The blossom is so well preserved that the researchers were able to identify its floral descendants now residing a continent away.
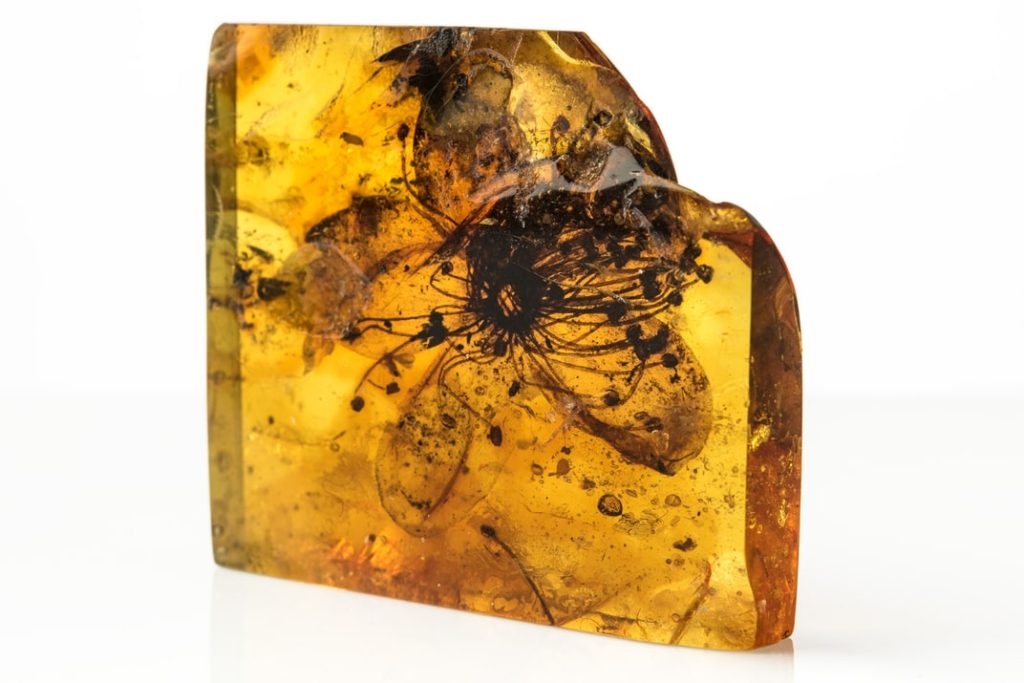

In 1872, scientists identified the flower fossil as an extinct evergreen plant named Stewartia Kowalewskii. Researchers have now reexamined the specimen and determined that it was a case of mistaken identity. They discovered that the flower came from a different genus entirely: Symplocos, a flowering species that grows in southeast China and Japan today. As such, they proposed a new name for the fossil—Symplocos Kowalewskii. The first record of an ancient Symplocos plant preserved in Baltic amber.
At 28 millimeters (1.1 inches) across, the fossilized flower may not sound particularly large. But it is about three times the size of most other amber-preserved flowers and larger than nearly half of all other Baltic amber pieces.
The specimen, which is kept at the Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources in Berlin, was found in an amber deposit in what is Kaliningrad, Russia, and was first described in the late 19th century. According to Dr. Sadowski, earlier research revealed that amber from this region dates to the late Eocene epoch, between approximately 33.9 million and 38 million years ago, which suggests that this specimen also comes from the late Eocene.
Fossils like the one described in the new study are key to reconstructing what ancient ecosystems were like, Dr. Sadowski said.