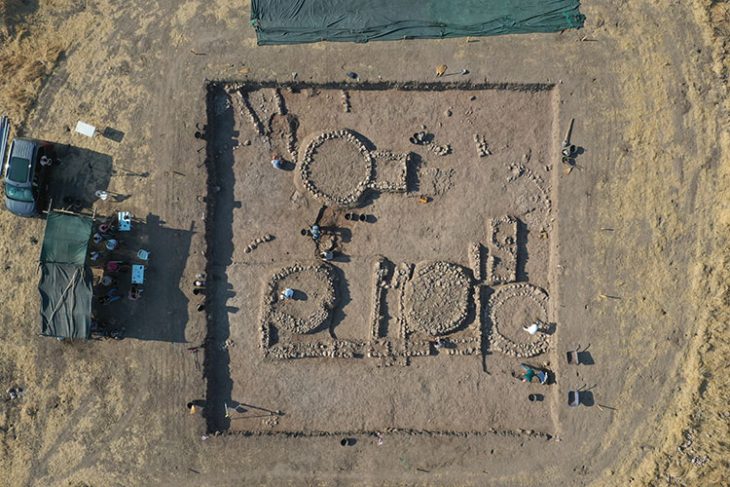Mustatils—stone monuments from the Late Neolithic period thought to have been used for ritual purposes—have been the subject of new research following a thorough analysis of an archaeological site in Saudi Arabia.
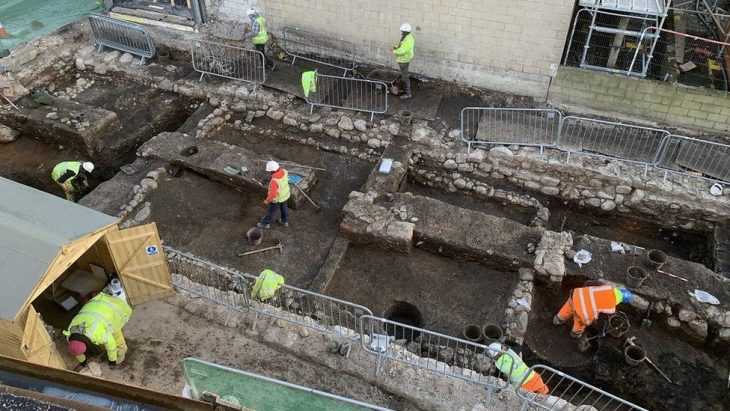
A team of archaeologists has now published the findings of extensive excavations of one of these massive structures near AlUla, revealing previously unknown evidence of ceremonial customs in Saudi Arabia thousands of years ago.
Melissa Kennedy of the University of Western Australia, Perth, and colleagues, in conjunction with The Royal Commission for AlUla present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on March 15, 2023.
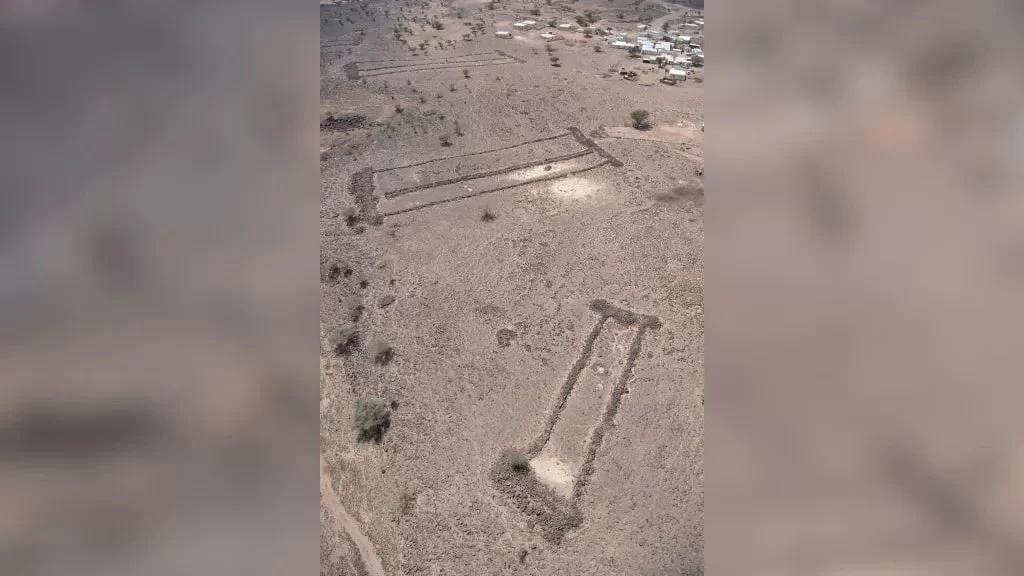
Mustatils are rectangular, low-walled stone structures that range in length from 20 to 600 meters and were built around 7,000 years ago. Researchers first discovered mustatils in the 1970s, and over 1,600 have now been discovered, primarily in northern Saudi Arabia.
These structures have long been associated with ritualistic activities like animal sacrifices and fertility and rain-related ceremonies. Similar to the square platforms of ancient Mesoamerica, some researchers have hypothesized that they might have been utilized for astronomical observations and the creation of calendars.
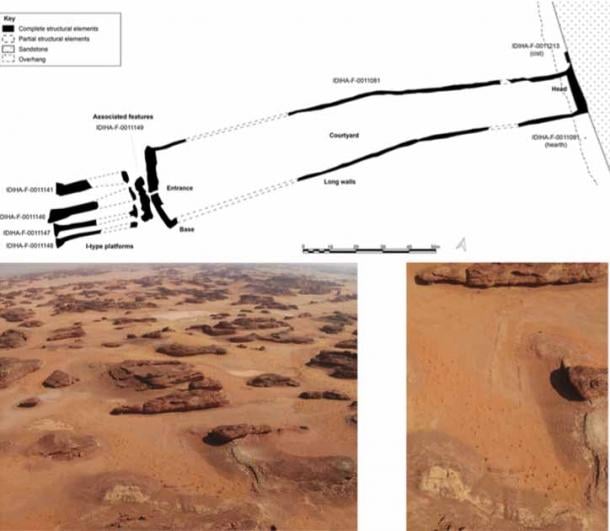
The new study is based on a thorough excavation at a sandstone-built mustatil that is 140 meters (451 feet) long and 88.5 kilometers (55 miles) east of AlUla.
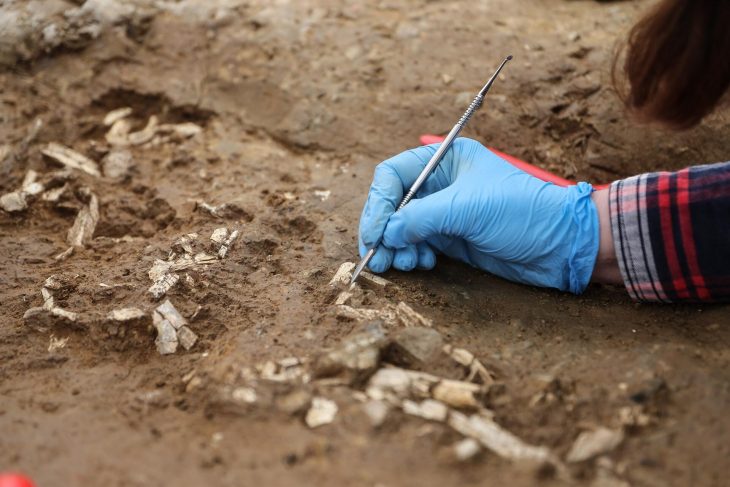
Recent excavations in the city of AlUla suggest that mustatils were used for ritualistic purposes involving placement of animal offerings. Now, Kennedy and colleagues have conducted an extensive excavation at a mustatil located 55 east of AlUla. This mustatil is 140 meters long and is constructed from local sandstone.
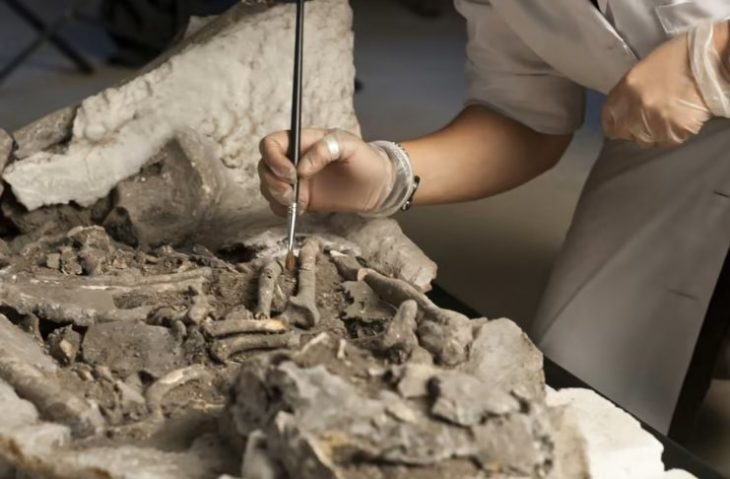
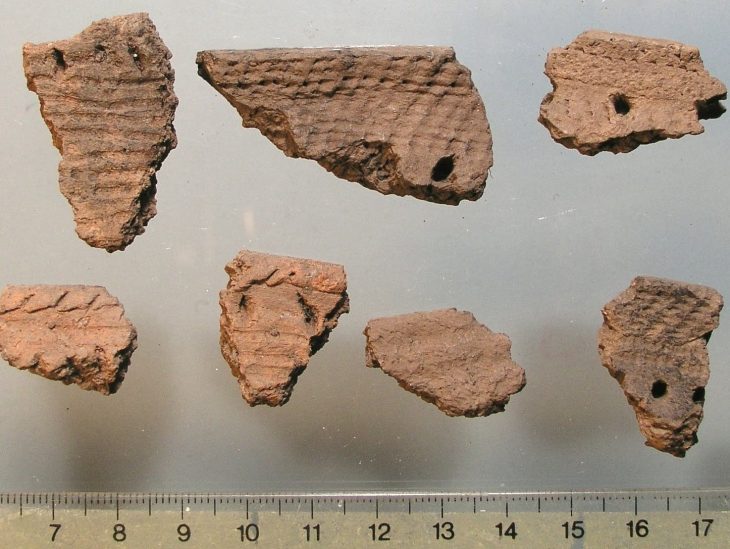
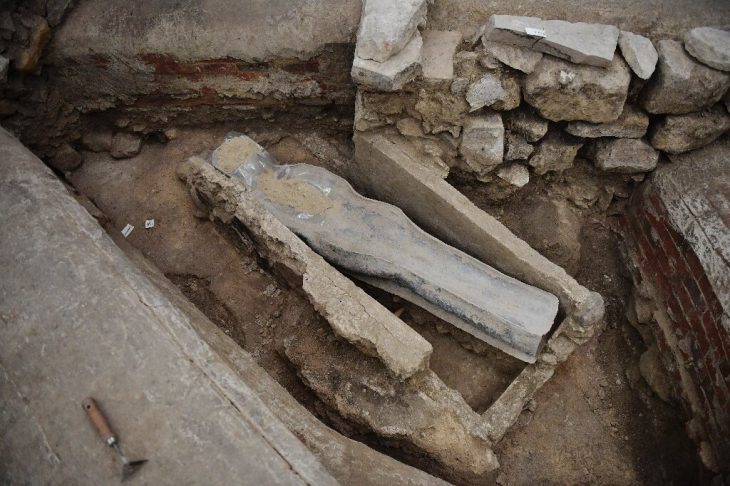
The researchers’ analysis included identification of 260 fragments of animal skulls and horns, primarily from domestic cattle, as well as from domestic goats, gazelle, and small ruminants. Nearly all of these remains were clustered around a large upright stone interpreted to be a betyl.
Radiocarbon dating suggested that the betyl is one of the oldest identified in the Arabian Peninsula, and the bones provide some of the earliest evidence for domestication of cattle in the northern Arabia.
This study also uncovered evidence for several phases of offerings at the mustatil, as well as interment of an adult male human, suggesting that the site may have been the destination of repeated pilgrimages.
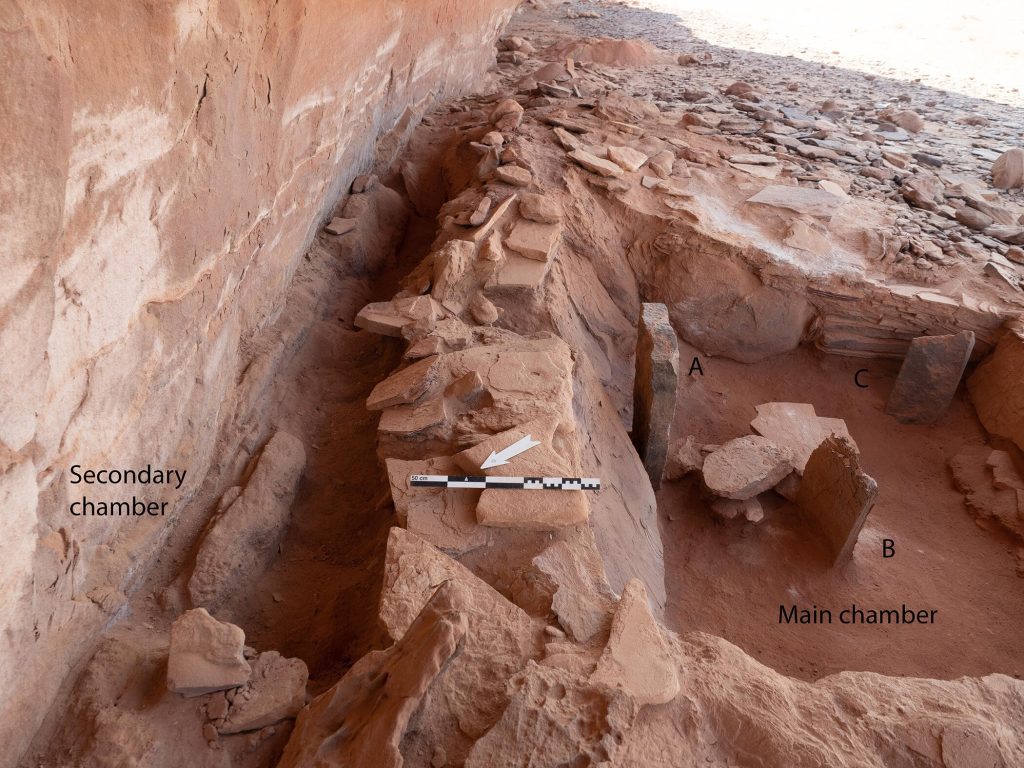

Taking all the new data into consideration, the researchers suggest that ritualistic belief and economic factors were more closely intertwined for Neolithic people in northwest Arabia than previously thought, and that this entanglement was shared over a broad geographic area.
The authors concluded that the ritual interment of animal horns and upper craniums discovered within the mustatil suggest “a profound intersection of belief and economic life-ways in the Late Neolithic of Northern Arabia,” over a vast geographic distance.
According to the researchers, this indicates far more, “The incorporation of these two facets suggests a deeply rooted ideological entanglement, one which was shared over a vast geographic distance, indicating a far more interconnected landscape and culture than had previously been supposed for the Neolithic period in north-west Arabia.”