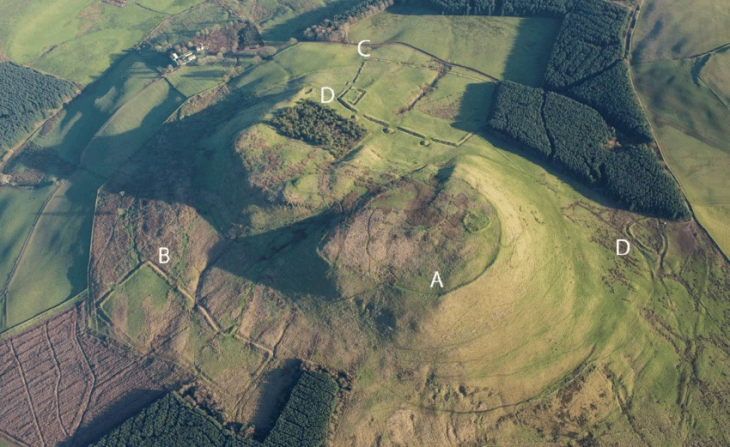
A recent archaeological mission has unveiled groundbreaking findings at the Ramesseum, the grand mortuary temple of Pharaoh Ramesses II, located on the West Bank of Luxor. This joint effort by Egyptian and French experts has not only shed light on the temple’s historical significance but has also provided a deeper understanding of the educational and economic structures of ancient Egyptian society.
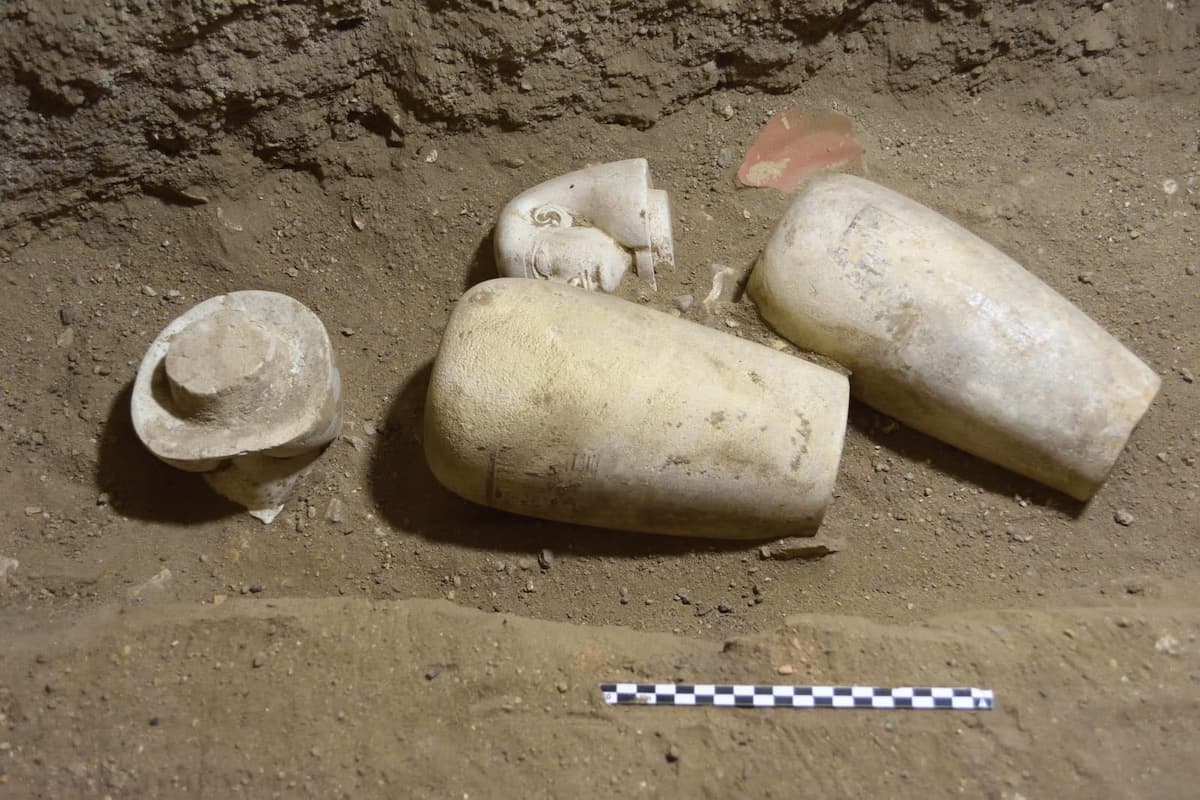
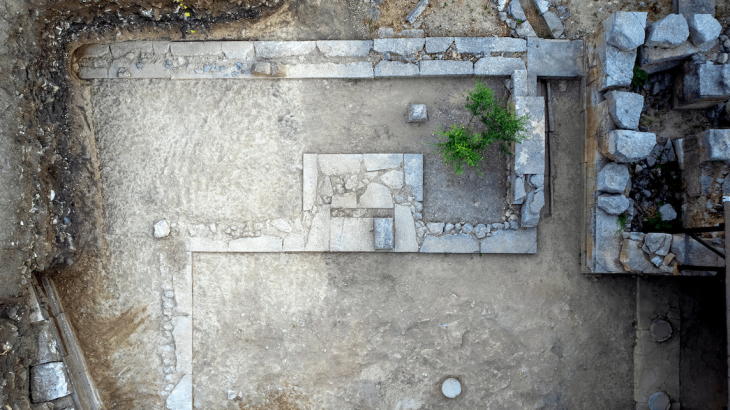
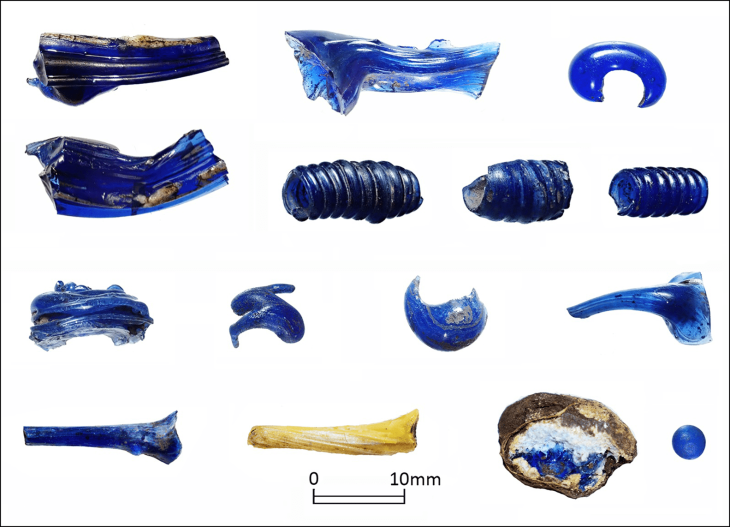
Among the most remarkable discoveries is the identification of a “House of Life,” a temple-school that serves as the first physical evidence of an educational institution within the Ramesseum. This center of learning, long theorized by Egyptologists, has yielded a treasure trove of artifacts, including students’ drawings, fragments of educational toys, and ancient learning tools. These findings suggest that the Ramesseum was not merely a religious site but also a vibrant hub of education, where knowledge was imparted and preserved.
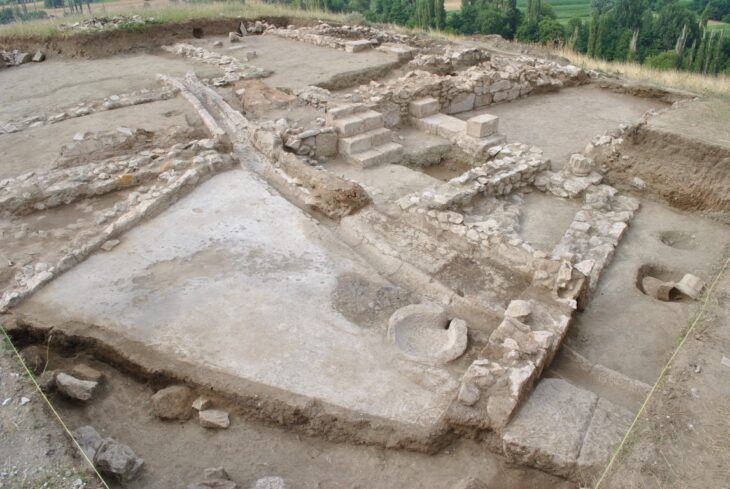
The implications of this discovery extend beyond education. The excavation has revealed extensive economic infrastructure, including storerooms and cellars that housed olive oil, honey, and wine. The presence of wine jar labels indicates that the temple functioned as an active wine cellar, while the discovery of textile and stone workshops, kitchens, and bakeries paints a picture of a self-sufficient complex that catered not only to temple staff but also to the surrounding community.
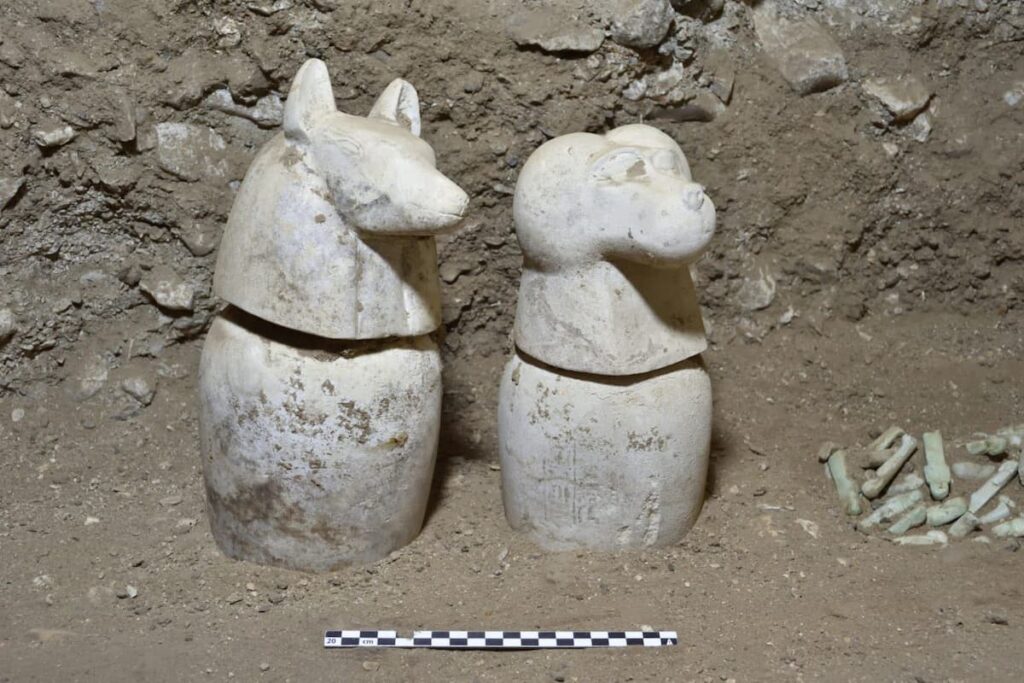

In addition to the educational and economic aspects, the mission has uncovered administrative offices within the temple’s eastern sector. These structures suggest a sophisticated hierarchy of civil servants responsible for managing the production and distribution of goods, further emphasizing the temple’s role as a center of governance and community support.
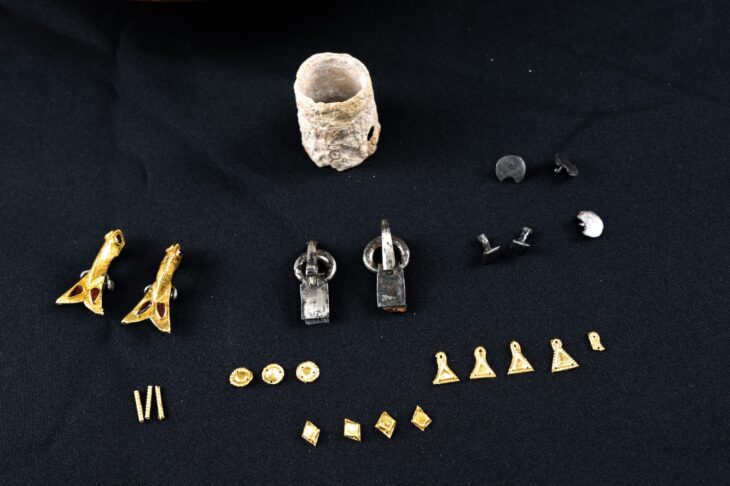
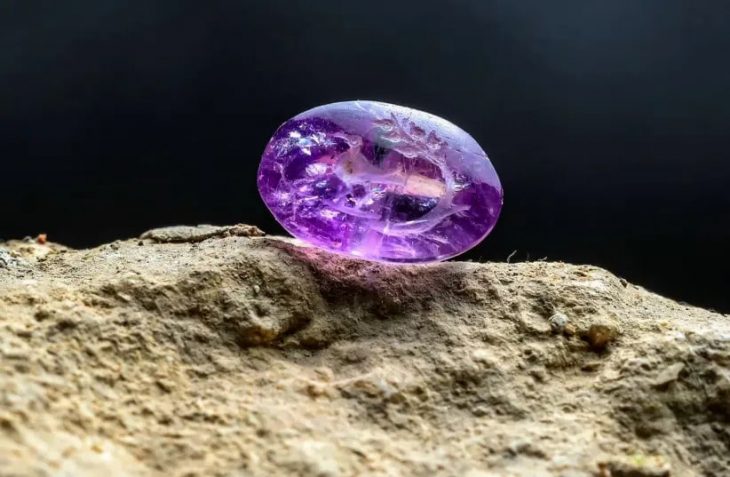
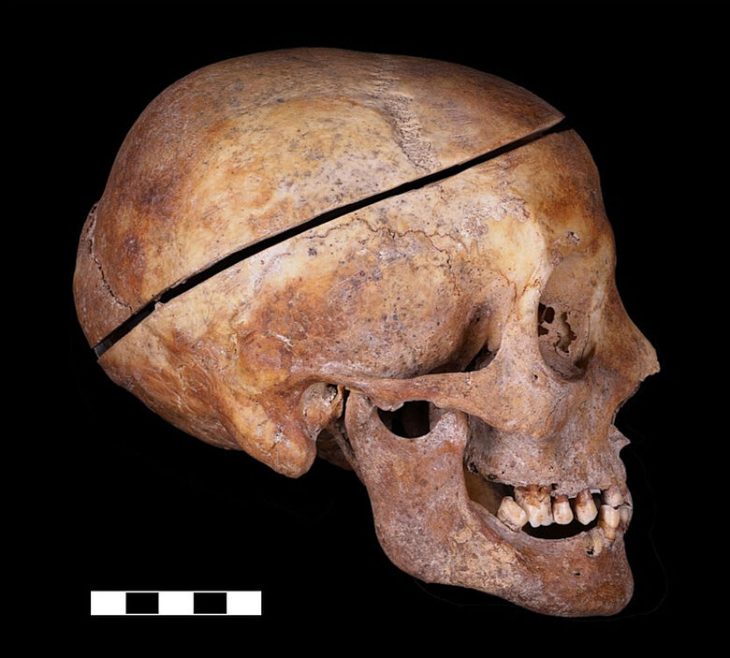
The findings also include a series of tombs from the Third Intermediate Period, which contain well-preserved funerary artifacts and human remains, confirming the site’s continued use as a necropolis. Notably, the re-excavation of the Middle Kingdom burial of Sehetep-ib-Re adds another layer to the temple’s rich history, showcasing the continuity of burial practices over centuries.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The restoration efforts have also been significant, with the reconstruction of colossi of Ramesses II and his mother, Queen Tuya, as well as the royal palace adjacent to the temple. These restorations not only enhance the site’s historical integrity but also provide insights into the architectural grandeur of the period.
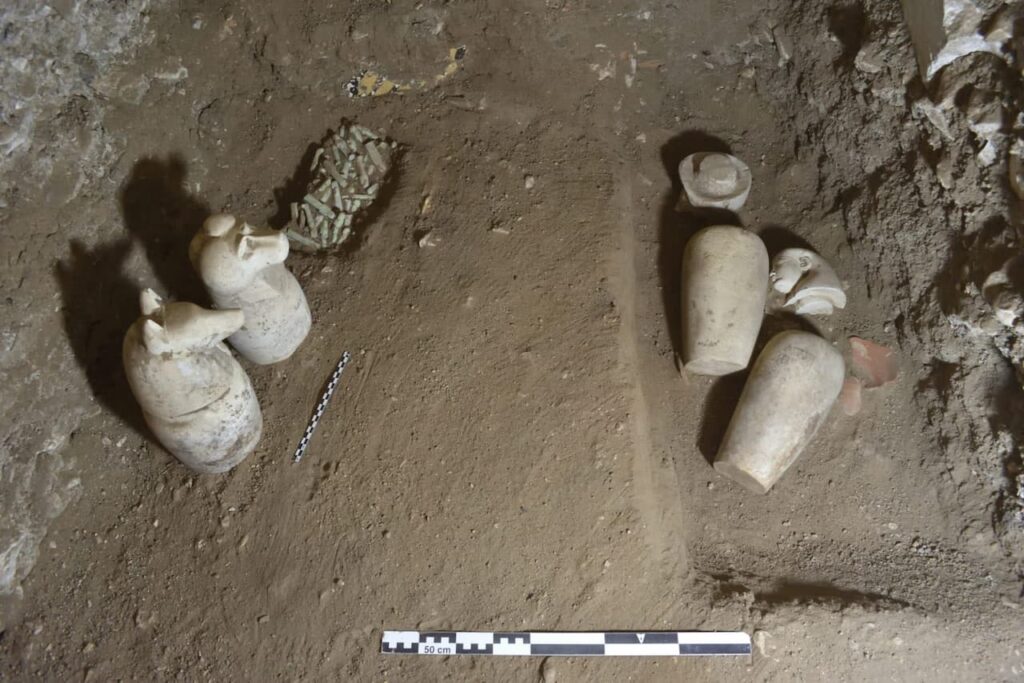

As the mission continues to uncover the multifaceted nature of the Ramesseum, it becomes increasingly clear that this site was a microcosm of ancient Egyptian life, intertwining education, economy, and administration in a way that has reshaped our understanding of this iconic civilization. The discoveries at the Ramesseum not only honor the legacy of Ramesses II but also illuminate the complexities of the society that thrived under his reign.
Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities of Egypt
Cover Image Credir: Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities of Egypt