A piece of body armor was unearthed during excavations at a 17th-century colonial fort in Maryland, a Mid-Atlantic state of the United States.
While archaeologists continued their excavations in the City of St Mary’s, one of America’s premier historical sites, a project launched in 2021, they noticed a piece of metal sticking out of the dirt.
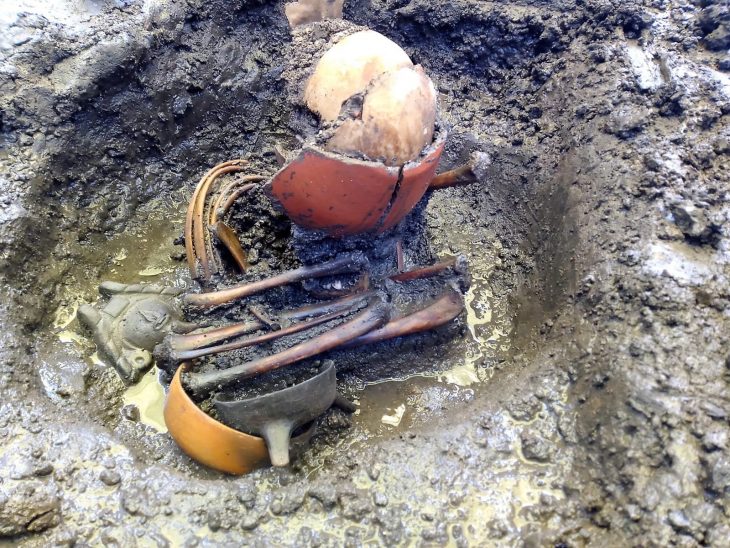
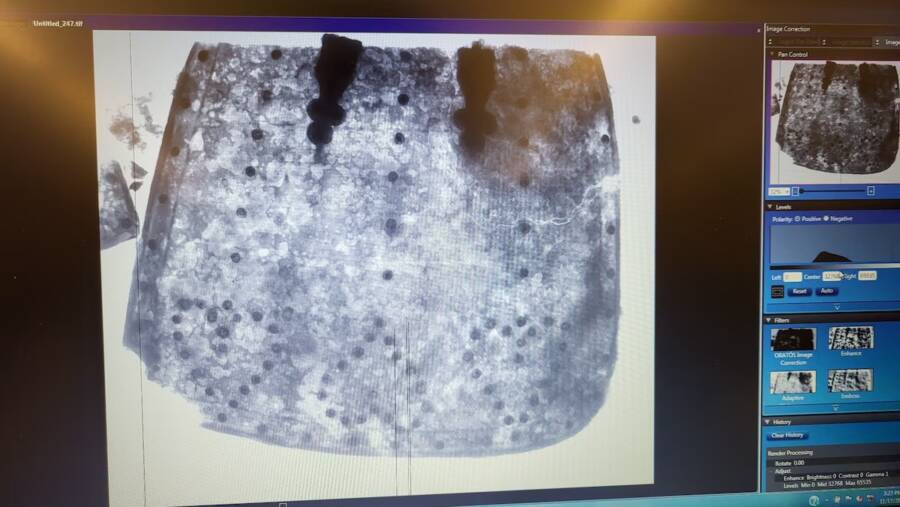
According to the Washington Post, the more they dug, the more they found until they came across a slab of metal the size of a cafeteria tray. Still caked with soil and corrosion materials, the plate was identified when an X-ray revealed its rivets forming the shape of three hearts.
What they found late last year was a rare piece of 17th-century armor called a tasset, which was designed to hang from a breastplate and protect one of the wearer’s thighs during battle. Originally, there would have been two — one for each leg.
“The X-ray really took our breath away,” Travis Parno, director of research and collections at Historic St. Mary’s City, told All That’s Interesting in an email. “Seeing the layers of steel, the individual rivets, the hearts(!). It was a good day.”
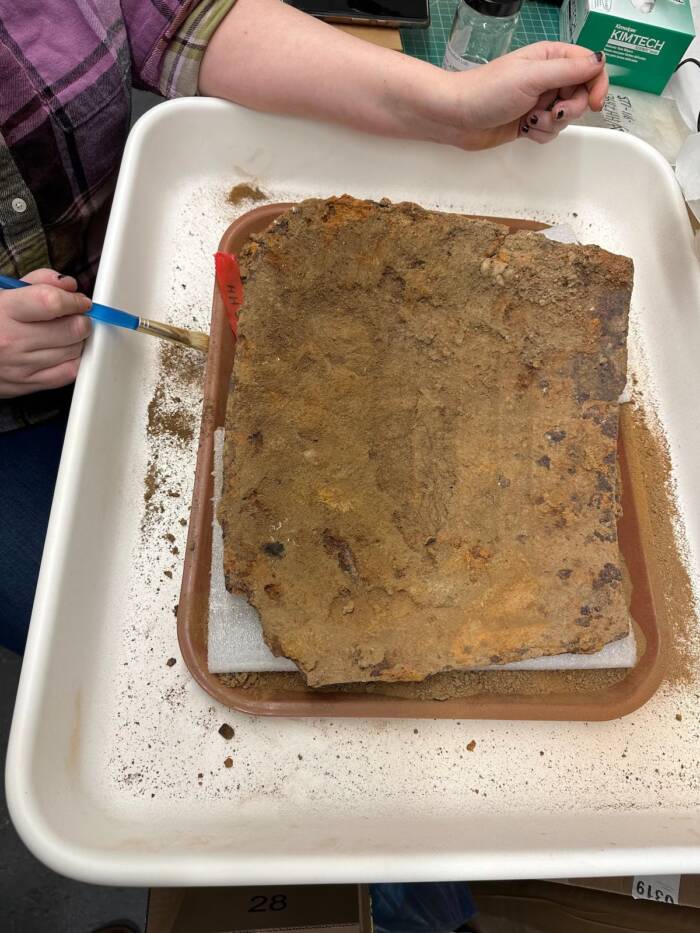

“This tasset is the second we’ve found at St. Mary’s City (the second was from a circa late-1640s context),” Parno said, “suggesting that colonists were actively making decisions about what was and wasn’t useful to be retained in their military accoutrements.”
Parno further noted that armor parts like this one are “not particularly common on 17th-century sites.” In Maryland’s hot, humid climate, the colonists most likely abandoned the tassets as suffocating and cumbersome.
The rare piece of armor called a tasset had been brought by the first European colonists who arrived in the mid-1600s to establish one of the earliest settlements in what would become the United States.
Historic St. Mary’s City, the site of the fourth permanent settlement in British North America, was Maryland’s first settlement. Founded in March 1634 on land acquired from the local Yaocomico people by newly arrived English settlers, it served as the colony of Maryland’s first capital for 60 years before being moved to Annapolis in 1694. St. Mary’s was abandoned after it was eclipsed by Annapolis and never built over, making it an undisturbed archaeological site.
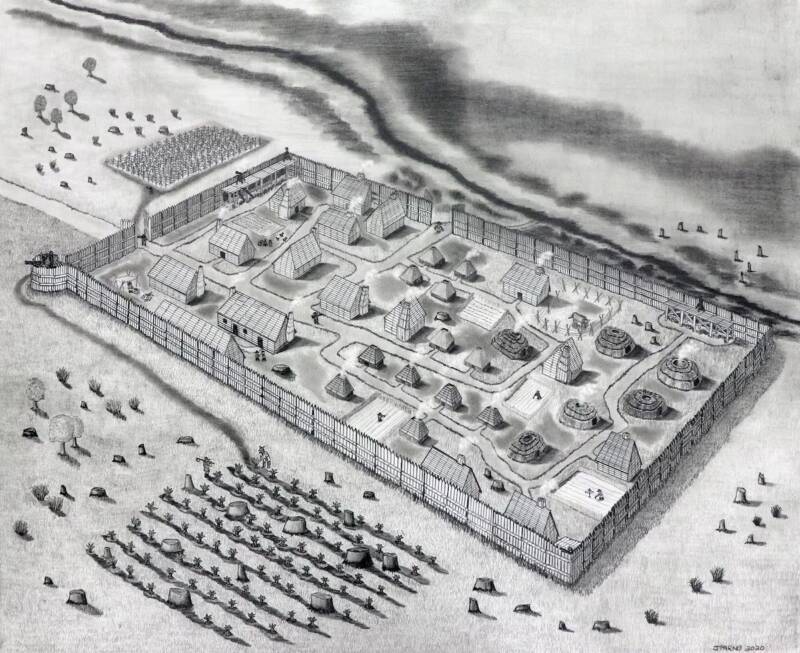
Colonists from Britain crossed the Atlantic on two ships called the Ark and the Dove. In 1634, they navigated up the St. Mary’s River and erected a fort — the earliest known colonial site in Maryland.
Finding evidence of the original fortified village has been one of the main objectives of archaeological research over the past fifty years. 17th-century documentation was ambiguous about the location, and references to the first fort vanished from the historical record in 1642.
Following a geophysical survey that revealed evidence of a palisade, an excavation in 2021 unearthed postholes, building outlines, coins, and artifacts from the 1620s and 1630s. The excavation of the original fort has continued, and late last year a large structure with an attached cellar was discovered. The structure was not a home, and artifacts discovered there — musket parts, lead shot, trade beads — suggest it was used as a storehouse. The tasset was found in the cellar.
Cover Photo: Historic St. Mary’s Commission