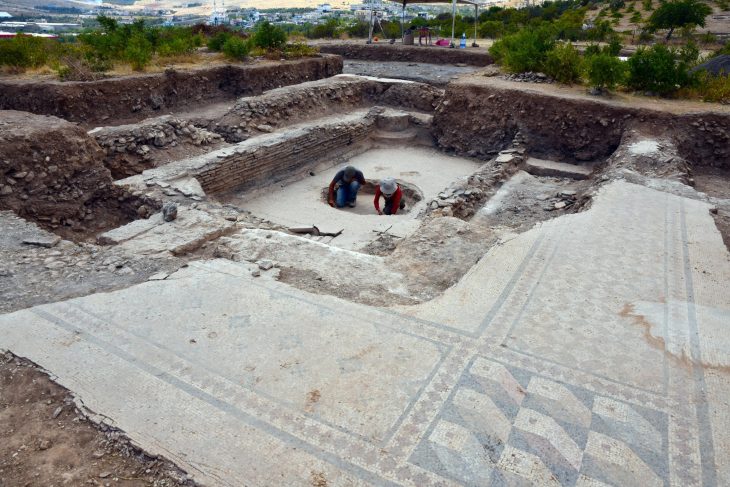
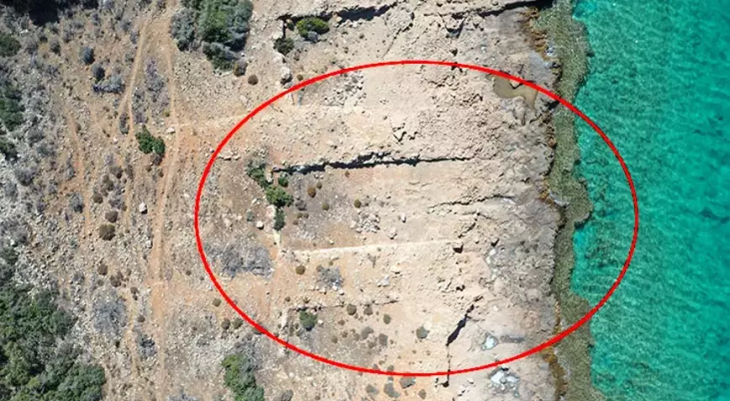
With the beginning of the Holocene period, many lakes have dried up and have become suitable for settlement. It is one of the lake floors in the Konya Plain that dried up in the Holocene period. There have many mounds in this area. One of the most important of these mounds is Çatalhöyük, which is undoubtedly located within the borders of Çumra province.
It probably owes its name to the fork-like shape of the two hills. Although there are two mounds, east and west, excavations continue in the west mound. Its inhabitants moved to the western mound when the river changed direction in the early chalcolithic period.
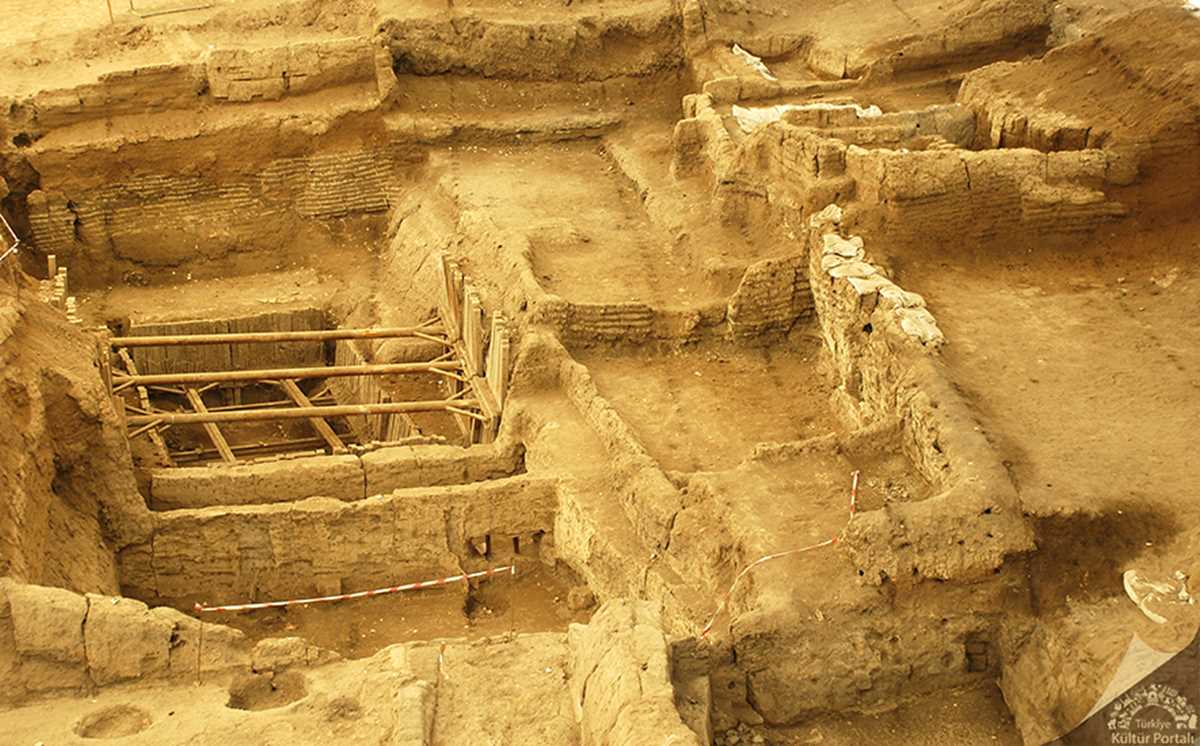
Çatalhöyük was discovered in 1958 by James Mellaart. Since 1993, excavations have been continued by Ian Hodder, a student of Mellaart, and if nowadays excavations are carried out by Assoc. Dr. Çiler Çilingiroğlu continues.
Eastern mound, BC. Eighteen layers of Neolithic settlements dating from 7400 to 6200 have been found. Layers 12 and 8 are dated to the first phase of the Early Neolithic (6500 – 6000 BC). After 6 layers it belongs to the second phase of early Neolithic.
The Chalcolithic Age layers in the western mound are dated between 6200 and 5200 BC.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

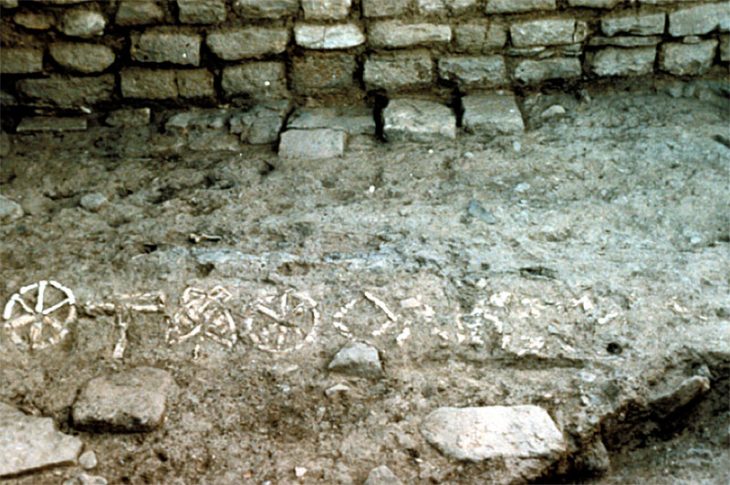
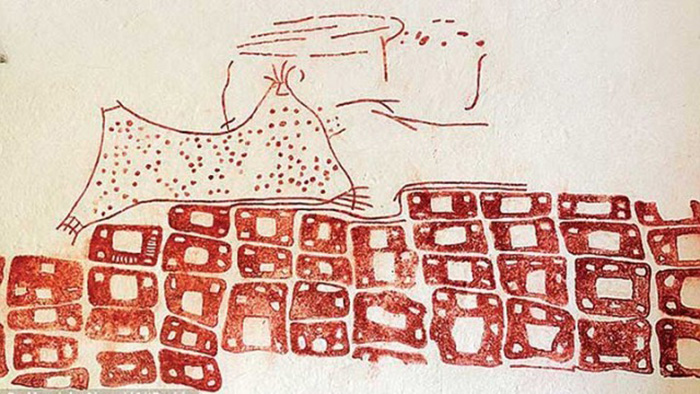
On the north and east walls of the building, a map that is thought to be the city plan of Çatalhöyük was unearthed during the 1963 excavations. This drawing, which is dated to 8200 years ago (age 6200 ± 97 BC as determined by radiocarbon dating method) is the first known map of the world. Approximately 3 meters long and 90 cm. has a height. It is still exhibited in Ankara Anatolian Civilizations Museum.
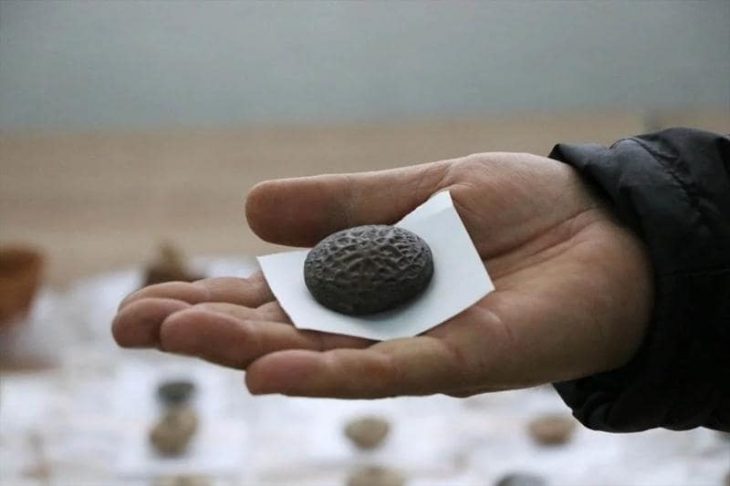
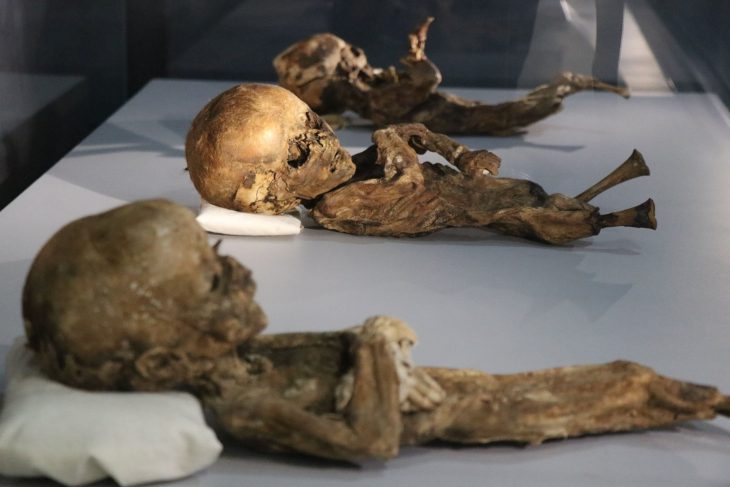
Çatalhöyük has its own characteristics. Conservation of art, symbolism, social structure, living of too many people, bull cult, the burial of people, skulls, ancestral cult and house shapes, an egalitarian lifestyle is seen.
Interestingly, although they know of pottery making, they did not show intensive use of up to 5 layers. This is just a preference of those who live there. Probably because they had developed in woodworking, they did not want to change their traditional structure.
The residences they use are intertwined. Since no traces of war and destruction were visible, this might mean that intimacy involves an intense bond of kinship relations. Houses were entered through roofs. Probably these roofs were used for socializing on hot days. It is thought that many jobs required for the home are here. These flat-roofed houses are now found in the South East.

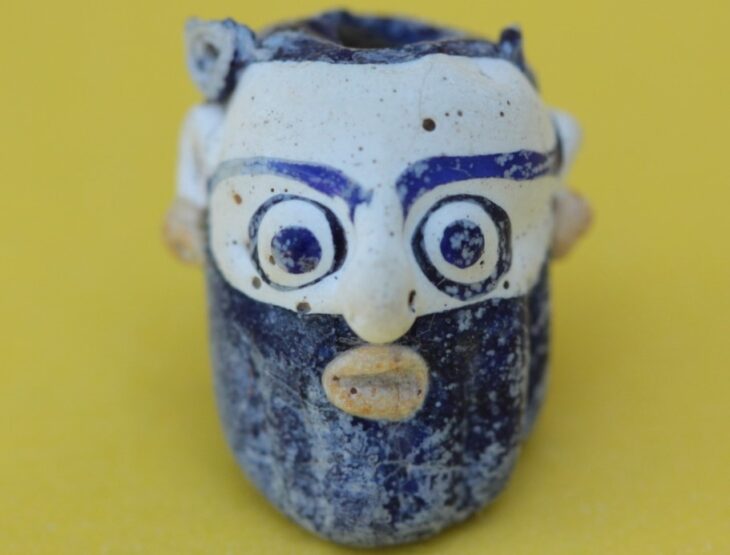
The pictures made on the walls in the settlement, where the understanding of art is very developed, is remarkable. The depictions on the walls of the housing are hunting and dance scenes, human and animal paintings. Animal pictures are animals such as vulture, leopard, various birds, deer, and lions. In addition, there are also motifs that can be called rug motifs dating back to 8800 years ago and are associated with today’s Anatolian rug motifs.
Bull horns and heads should be important to those living here. Many houses have reliefs made by plastering real bull heads with clay on the walls. The figurine finds are cattle, pigs, sheep, goats, bulls, dogs and single cattle horns.
There are Neolithic settlements older than Çatalhöyük in the Middle East. For example, Eriha is a Neolithic settlement a thousand years older than Çatalhöyük. Still, Çatalhöyük has different characteristics from older or contemporary settlements. One of the main differences is its population, which reaches ten thousand people.
According to Hodder, Çatalhöyük is “a center that carries the concept of village beyond logical dimensions”.
It was decided by UNESCO to be included in the World Heritage List in 2012.
SOURCE: Çatalhöyük Research Project, Çatalhöyük 2008 Report
YAZAR, M., 2008 “Anadolu’da Neolitik Dönem Sanatı ve Merkezleri”, Gazi Üniversitesi Sosyal Bilimler Enstitüsü Tarih Anabilim Dalı, Eskiçağ Tarihi Bilim Dalı Yüksek Lisans Tezi, Ankara