There are hundreds of things that are old in our world, one of them is people’s passion to win. Where there is a passion to win, cheating seems to be a natural phenomenon.
We are not surprised that we see the development of cheating develop with human existence. After all, the first thing to say in the speeches that motivate the contestants is that no one will remember to second… And man can do anything to win!
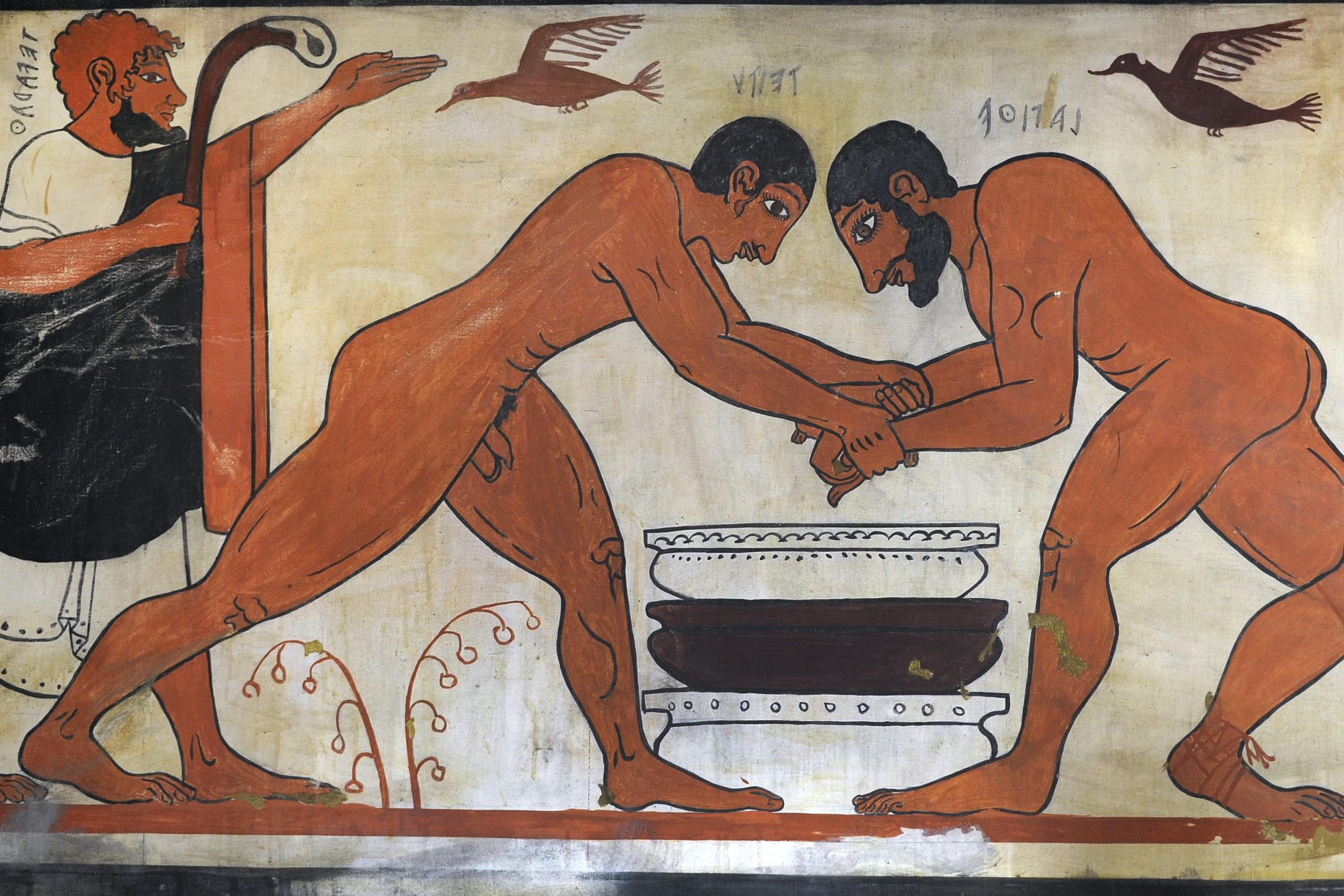
Researchers have deciphered a Greek document that shows an ancient wrestling match was fixed. The document, which was dated from the year 267, is a contract between two teenagers who had reached the final of a very prestigious tournament in Egypt. This is the first evidence of match fixing found in the ancient world.
In the contract, the father of a wrestler named Nicantinous agrees to pay a bribe to his son’s opponent, Demetrius, on the condition that he quits the match. The agreement stipulates that:
“…when competing in the competition for the boy [wrestlers], to fall three times and yield,” and in return would receive “three thousand eight hundred drachmas of silver of old coinage …”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

There were no complicated rules in ancient wrestling – you just had to throw your opponent to the ground three times and you won the game. Apparently, Demetrius was a pretty smart guy: the contract also includes a clause that he gets the money even if the referees somehow realize the match was fixed. There is also another clause that says that if Demetrius somehow wins the game, “you have to pay my [same] son as a penalty for committing a crime with three talents of silver from ancient coins without delay or inventive argument.”
The boys fought in the final wrestling match of the 138th Great Antinoea, an important series of regional games hosted with the religious festival in Antinopolis, Egypt. They were in the youth part. Interestingly, the Antinoeia were events in honor of Antinous, the young lover of Emperor Hadrian. Antinous drowned in the Nile, and the city of Antinopolis was founded in his honor – not only that but in a sense he was given god status, with his statues found throughout the Roman Empire. What can you say – apparently Hadrian loved him very much.
Researchers confirm that prominent nobles and even cities are ready to bribe to win in competitions. Because the first would have gained all the honor and reputation.
But the really interesting part of the contract is why sign a contract for a situation you know is illegal? Even if one of the parties did not fulfill their promise, it would be impossible for both parties to take this situation to court.
Bribery was widespread, especially in athletics competitions in ancient times. As games increased, financial rewards increased. Many cities did not hesitate to pay their earning citizens a pension until they died. They have tried every way to win. After all, races were a source of honor for every city.