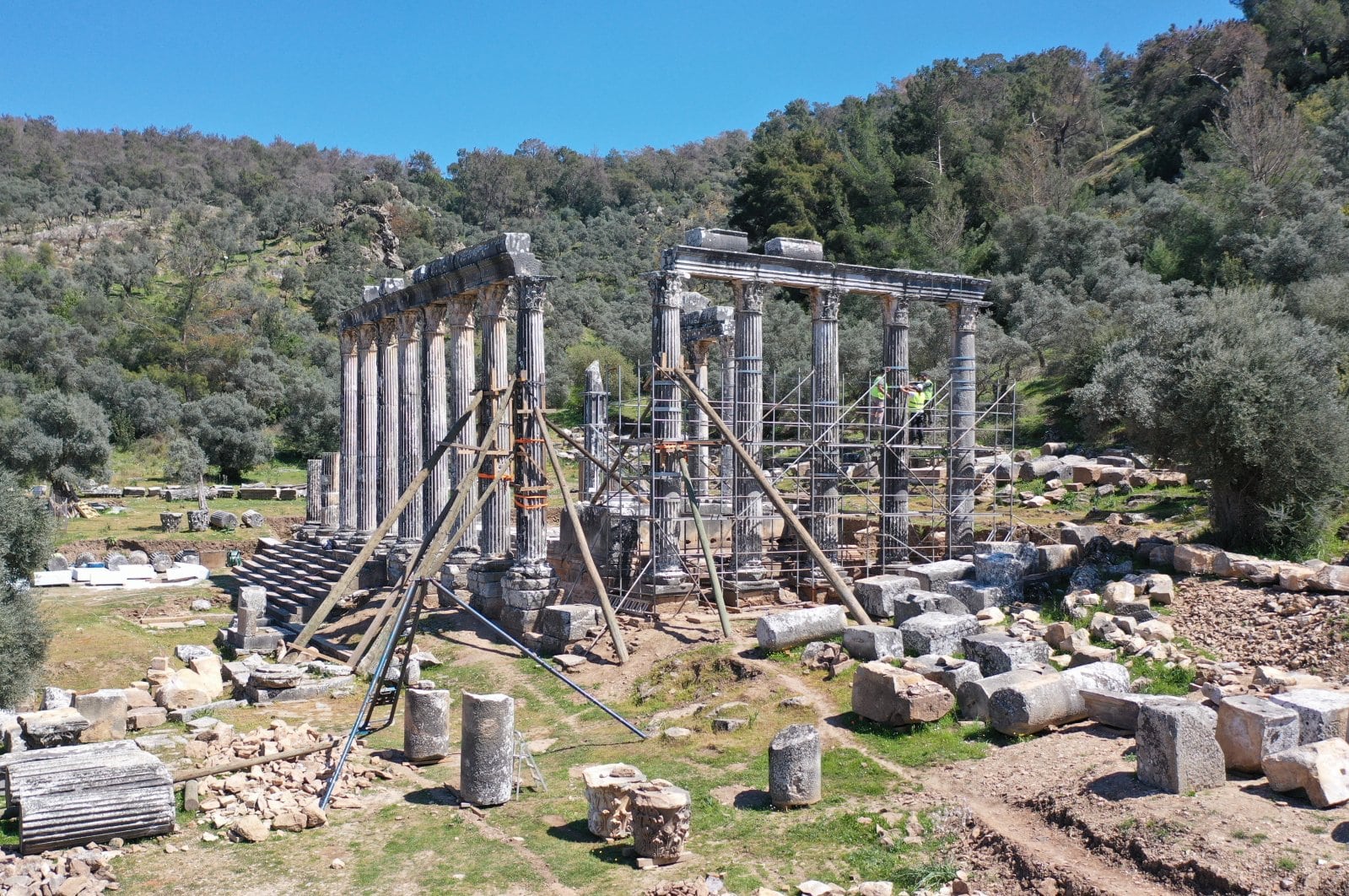
The temple of Zeus in the ancient city of Euromos in southwestern Turkey regains its original splendor with the revitalization of its columns with original materials and architectural methods. The Zeus Lepsynos Temple is one of the best-preserved temples in Anatolia.
Euromos is one of the important cities of Caria – the ancient name for the southwestern portion of Anatolia’s Aegean shores. It was the most important city in the region after Mylasa in ancient times.
Euromos is about 12 km from Milas located in the province of Mugla. The city was named “Eurome” by Roman author Plinius. The name of the city was Kyramos or Hyramos in the 5th century BC. However, as a result of the Hellenization policy of Mausolos in Caria, the name Euromos, which means strong in Greek, began to be used.
The first excavation and restoration work was carried out by Ümit Serdaroğlu between 1969-75. After nearly 40 years of interruption, a team led by Assist. Assoc. Dr. Abuzer Kızıl (Muğla Sıtkı Koçman University) was re-started in 2011 and the work is still ongoing.

The restoration of the Temple of Zeus Lepsynos has also been carried out meticulously in the ancient city, and the repair and strengthening works continue.
Stating that they used 90% of the original architectural elements in the restoration of the temple, the classification works of which were completed, Kızıl said: “There were column drums, column capitals, architrave blocks, friezes, and cornice blocks that we could use on every facade. We documented all of these materials and recorded them. And we are using these original materials in restorations.”
Kızıl also said that they used practices of the ancient period as a basis for their studies. “We made the combinations of the materials by using iron, bronze and lead. As I have previously mentioned, most of the architectural structures we used in the restoration consist of original materials. In this framework, we first installed the lower drums of six columns in their original places. After that, we carried out the removal and disposal of the previously used concrete blocks. In the meantime, the cracks, wear and spalling in standing columns of the temple were also tried to be strengthened.”
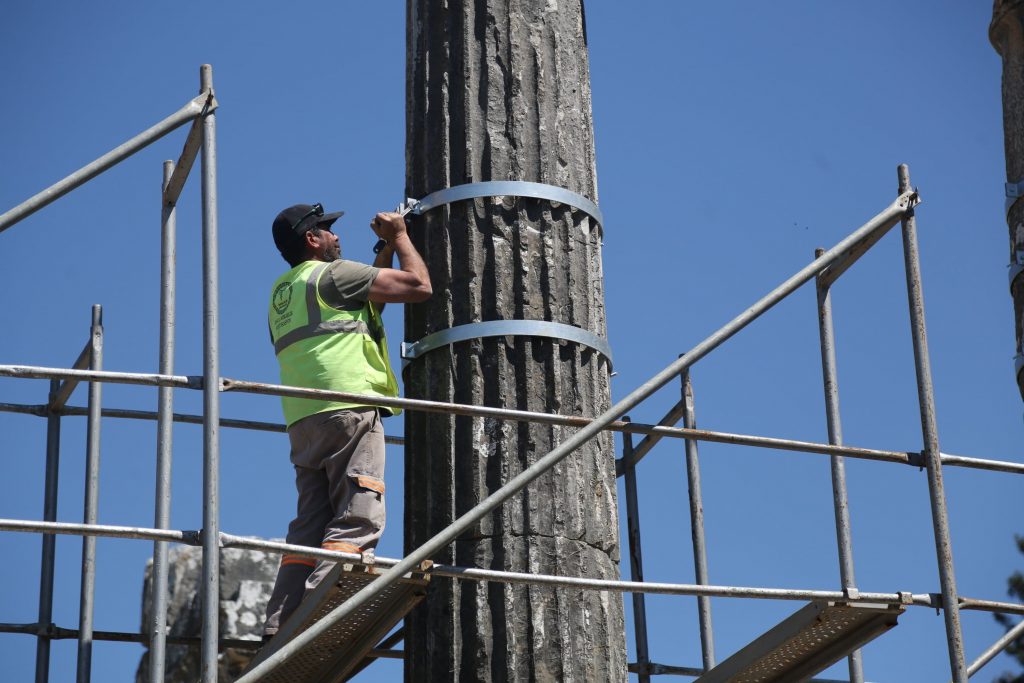

According to the excavation head, they want to show the original state of the temple to visitors coming to the ancient city.
Explaining that they prepared a small number of missing architectural pieces with marble by using the original versions as examples to complete the restoration of the columns, Kızıl said: “All the stone needs of the ancient city of Euromos are supplied from the marble quarries on the mountain rising from the bottom of the temple. Visitors can easily observe how stones are quarried, how they are roughly processed, how they are brought to the temple, and how the last works are done in the temple.”
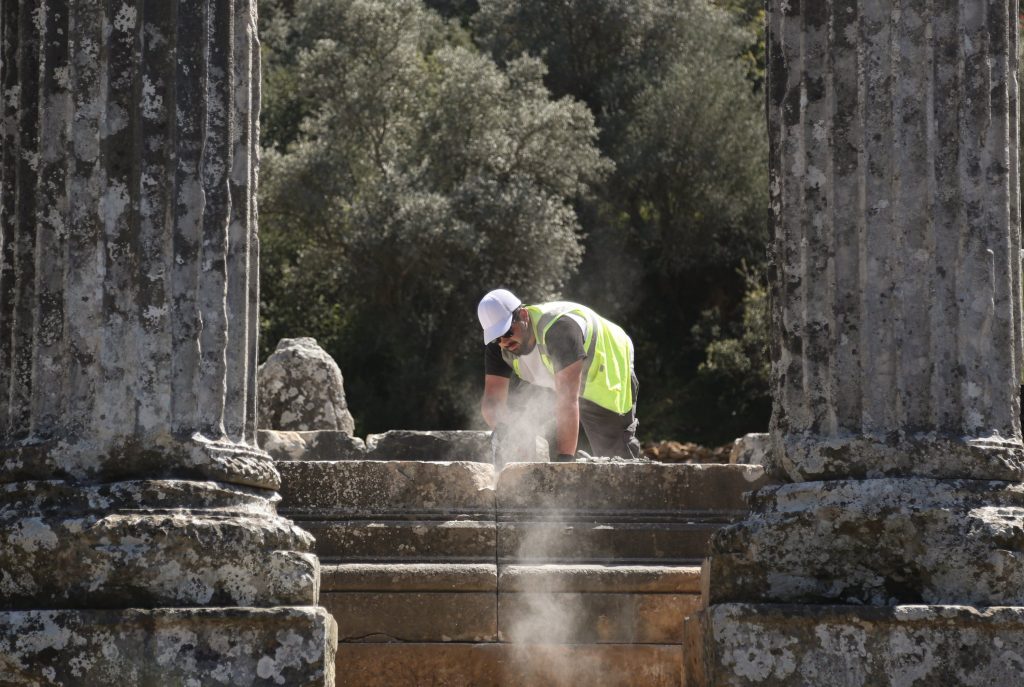

The Temple of Zeus Lepsynos was built in the 2nd century, during the reign of Roman Emperor Hadrian, at the foot of the hill called Kızılbayır outside the city. Since 16 of the 17 columns, together with their upper beams, have survived to the present day intact, the people called it Footed. Known that 5 of the columns were made by the physicist and public official Menekrates and his daughter Tryphania, and 7 of them were made by another public official named Leo Quintos.
Work on the ancient city continues with the support of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism, the Turkish Historical Society (TTK), the General Directorate of Cultural Heritage and Museums, the Provinces of Mugla, Milas, and the Sıtkı Koçman University in Mugla.