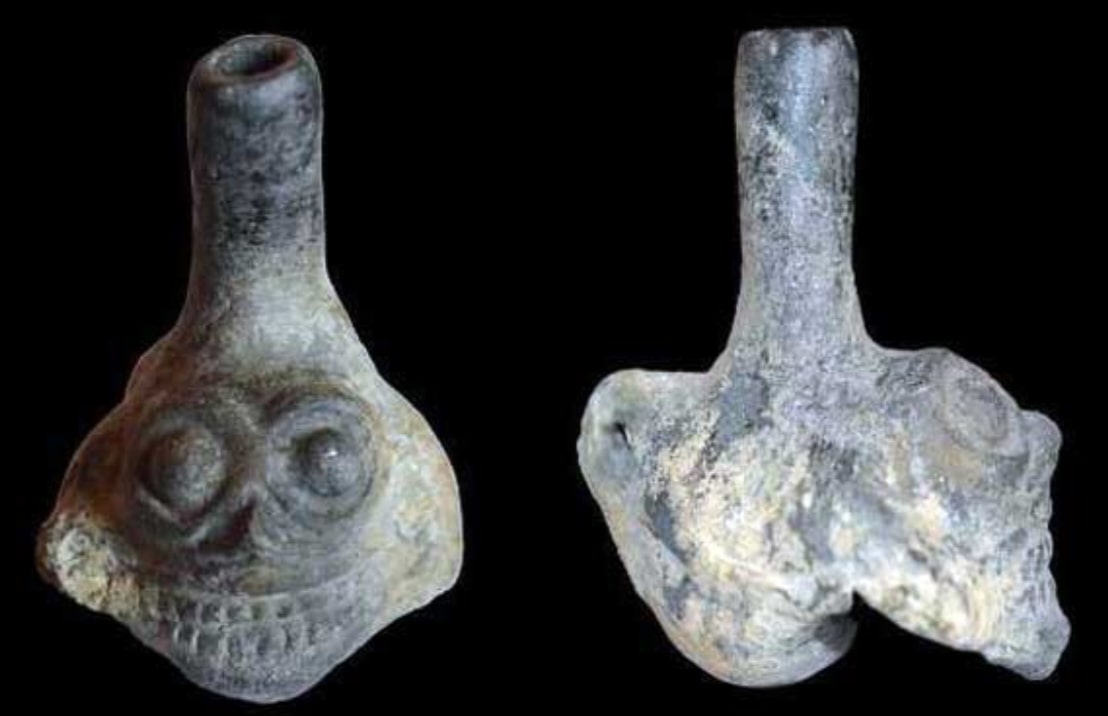
New research reveals that one of the Aztecs’ most chilling artefacts, clay death whistles, which resemble a human skull and produce a scream-like sound, not only frightened listeners in ancient times, but also had a profound effect on the human brain’s ability to increase states of alarm and fear.
The new study, published this month in the journal Communications Psychology, investigated the effect of these sounds on modern listeners, finding their ability to elicit negative emotional responses and increased neural activity in the auditory cortex.
For the first time, scientists investigated the effects of these disturbing whistles on the brains of modern European volunteers, conducting two separate experiments with different participant samples.
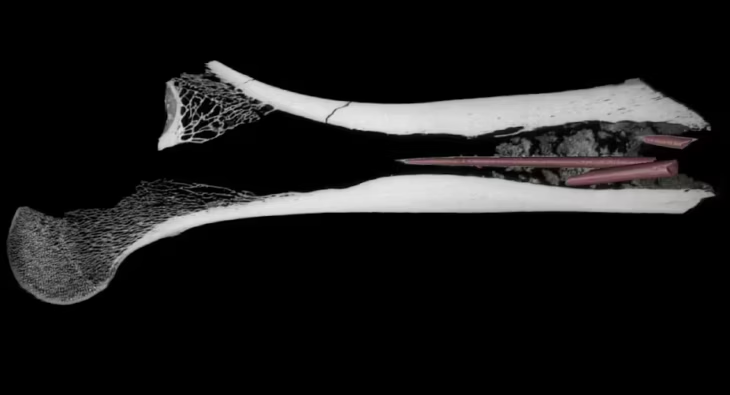
Aztec death whistles usually skull-shaped were designed to produce a high-pitched, penetrating sound similar to a scream, resulting from the collision of different air currents. Numerous examples have been found in graves dated between 1250 and 1521 CE.
Death whistles are thought to have been used by the ancient Aztecs to intimidate adversaries during battle. They are frequently found alongside the skeletons of sacrifice victims, fuelling suggestions that they might have had more of a ceremonial function. For example, according to some experts, the death whistles were designed to resemble the piercing winds of Mictlan, the Aztec underworld that was thought to receive sacrificed tributes. Some believe the sound was intended to symbolize the Aztec God of the Wind, Ehecatl, who formed humanity from the remains of the dead.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Researchers used volunteers from modern-day Europe to perform a number of psychoacoustic tests. When the researchers recorded the participants’ neural and psychological reactions to hearing the death scream, they found that the sound was perceived as “having a hybrid natural-artificial origin,” making it difficult for the brain to categorize.
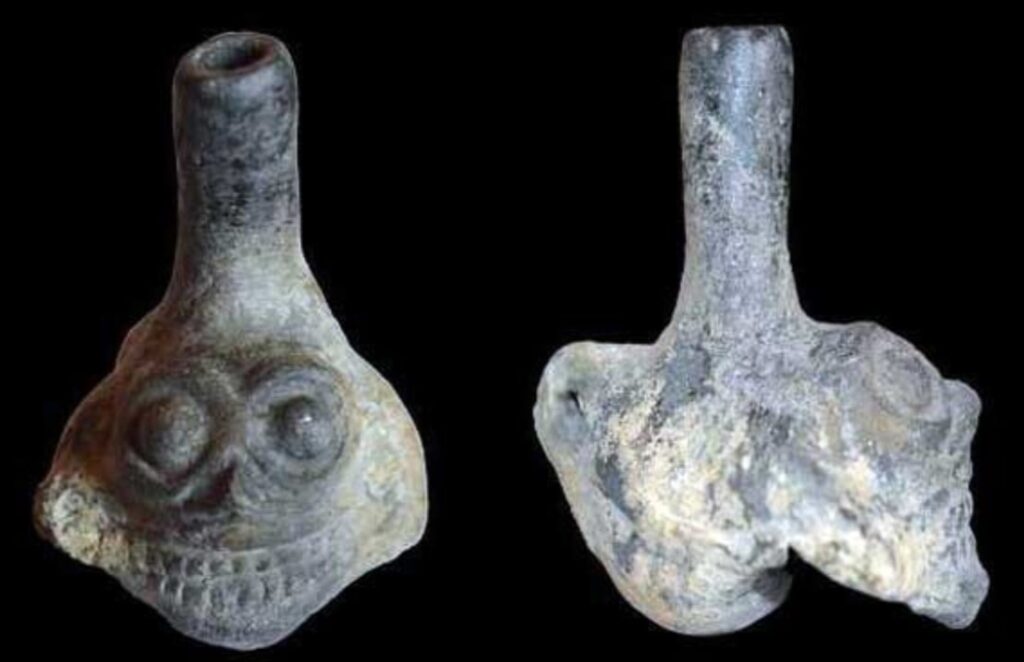
Research participants described the sounds as “scary” e “aversive”, matching the purpose of using whistles in Aztec rituals and wars.
The psychoacoustic experiments carried out in the study revealed that the brain perceives sound as both natural and artificial, creating a feeling of ambiguity that captures mental attention. This complex reaction involves lower-order auditory processing and higher-order cognitive systems, amplifying the emotional impact of sound.
Put another way, the death whistle’s terrifying ambiguity seems to spark the imagination as the brain tries to decipher the sound’s symbolic meaning. The researchers therefore conclude that the whistles’ “usage in ritual contexts seems very likely, especially in sacrificial rites and ceremonies related to the dead.”
These sounds may have been intended to instill fear in victims of sacrifices or admiration to those who attended the ceremonies.
As a result, the researchers suggest that it may have been deliberately used during Aztec ceremonies to evoke strong psychological responses.
Frühholz, S., Rodriguez, P., Bonard, M. et al. Psychoacoustic and Archeoacoustic nature of ancient Aztec skull whistles. Commun Psychol 2, 108 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44271-024-00157-7
Cover Image Credit: Wikipedia Commons