Professor Mark Munn of Pennsylvania State University has deciphered part of the inscription on the legendary Arslan Kaya Monument (also known as “Lion Rock”), a heavily damaged inscription that has been difficult to decipher for centuries.
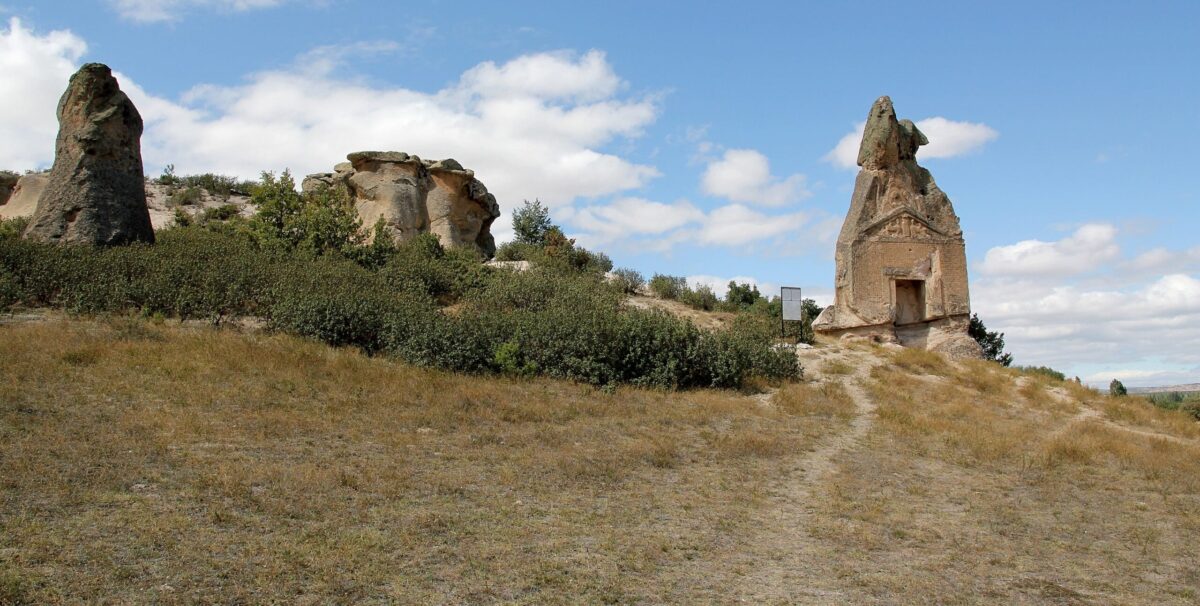
The Arslan Kaya monument is carved into a volcanic rock formation approximately 15 meters high in the Phrygian highlands in present-day western Türkiye, near Lake Emre Gölü. The 2,600-year-old monument, features figures of sphinxes, an image of the goddess flanked by lions, and a nearly erased inscription written in the Old Phrygian language.
Professor Mark Munn claims to have deciphered it, saying it spells out ‘ Materan,’ referring to a Mother goddess of the Phyrgians, whose worship flourished between 1200 and 600 BC.
This goddess, known to the Phrygians simply as “Matar Kubilea or Mother” was later revered by the Greeks as the “Mother of the Gods” and by the Romans as “Magna Mater” or “Great Mother.”
In April, Professor Mark Munn had a chance to photograph the previously indecipherable inscription on Arslan Kaya, in western Türkiye. After analyzing his imagery, Munn has published his conclusion that Arslan Kaya honors the Mother goddess Materan, the leader of the Phrygian pantheon.
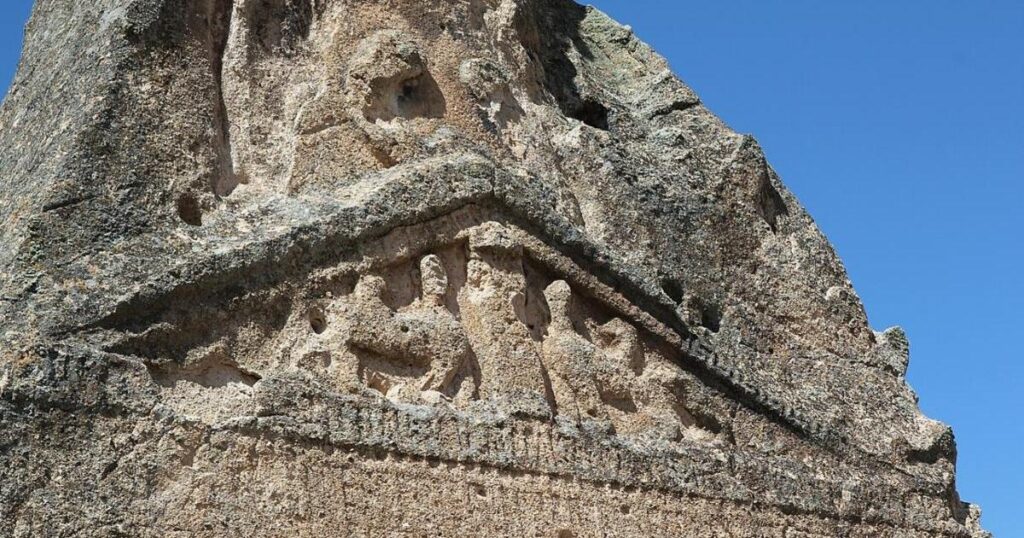

This finding confirms the mention of Materan —an ancient name of the Mother Goddess, or the Mother of the Gods— on the monument, suggesting a precise dating to the first half of the 6th century BCE.
The research has been published in the journal Kadmos, a platform for pre-Greek and Greek epigraphy.
Archaeologists have been fascinated and frustrated by the text at the base of the Arslan Kaya pediment since the 19th century. Nearly all evidence of this inscription has been lost due to rock erosion, looting, and vandalism. The surface has suffered natural wear from centuries of exposure to the elements, further aggravated in recent decades by treasure hunters using explosives, damaging the surface and fragmenting the goddess’s image in the niche Munn, however, used the mid-morning light, when shadows play on the last remnants, to photograph the inscription’s letters and compare them to earlier images dating back to the 19th century.
Famous archaeologist William Mitchel Ramsay discovered Arslan Kaya in 1884. He identified the site’s heritage based on the tall, narrow letters inscribed upon the base of its pediment, beneath two sphinxes. Throughout the next century, specialists visited Arslankaya to decipher its worn inscription, which was once a part of a much longer phrase that might have revealed the monument’s creator. French linguists Claude Brixhe and Michel Lejeune asserted in a frequently cited study 1984 that the inscription would never be read.
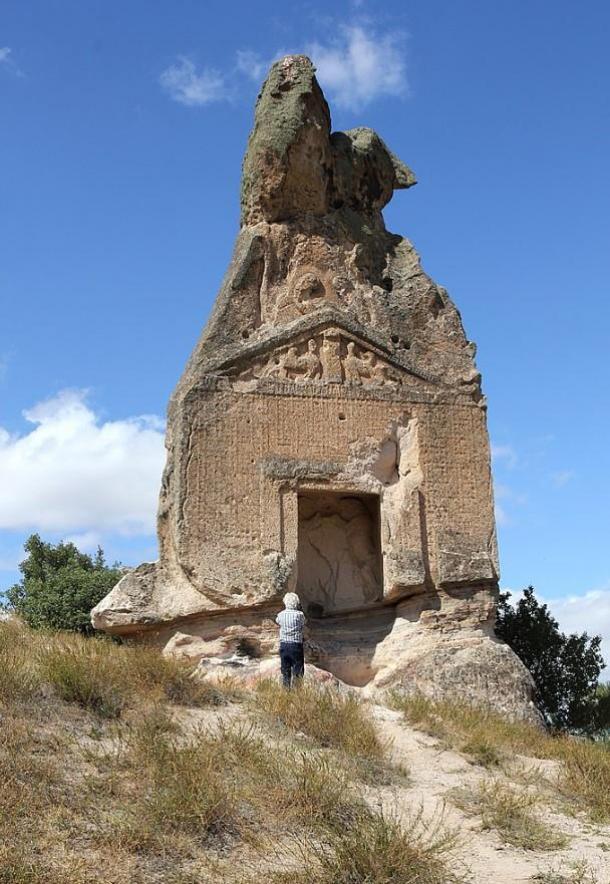

Professor Munn asserts that the key to comprehending the monument’s religious significance is the word Materan. This term is used in a number of Phrygian inscriptions to refer to the Mother Goddess, the central deity and protector of Phrygian cosmology who is also highly esteemed in Lydia, a nearby region.
Given that Materan would be the object of the inscribed phrase in this instance and appear in the accusative declension, it is possible that the monument was dedicated to the goddess, demonstrating her significance and veneration in this area. The name or title of the person who dedicated the monument or, alternatively, an invocation of protection to prevent damage to the structure—a common practice in ancient monuments—may have been included in the text, according to Munn’s analysis.
Munn’s research suggests that the Arslan Kaya monument may have been created at the height of the Lydian Empire, when Lydia, which also revered the Mother Goddess, dominated Phrygia.
Munn, Mark. The Phrygian inscription W-03 on the Arslan Kaya monument Kadmos, vol. 63, no. 1-2, 2024, pp. 79-92. doi.org/10.1515/kadmos-2024-0005
Cover Image Credit: Ingeborg Simon/CC BY-SA 3.0