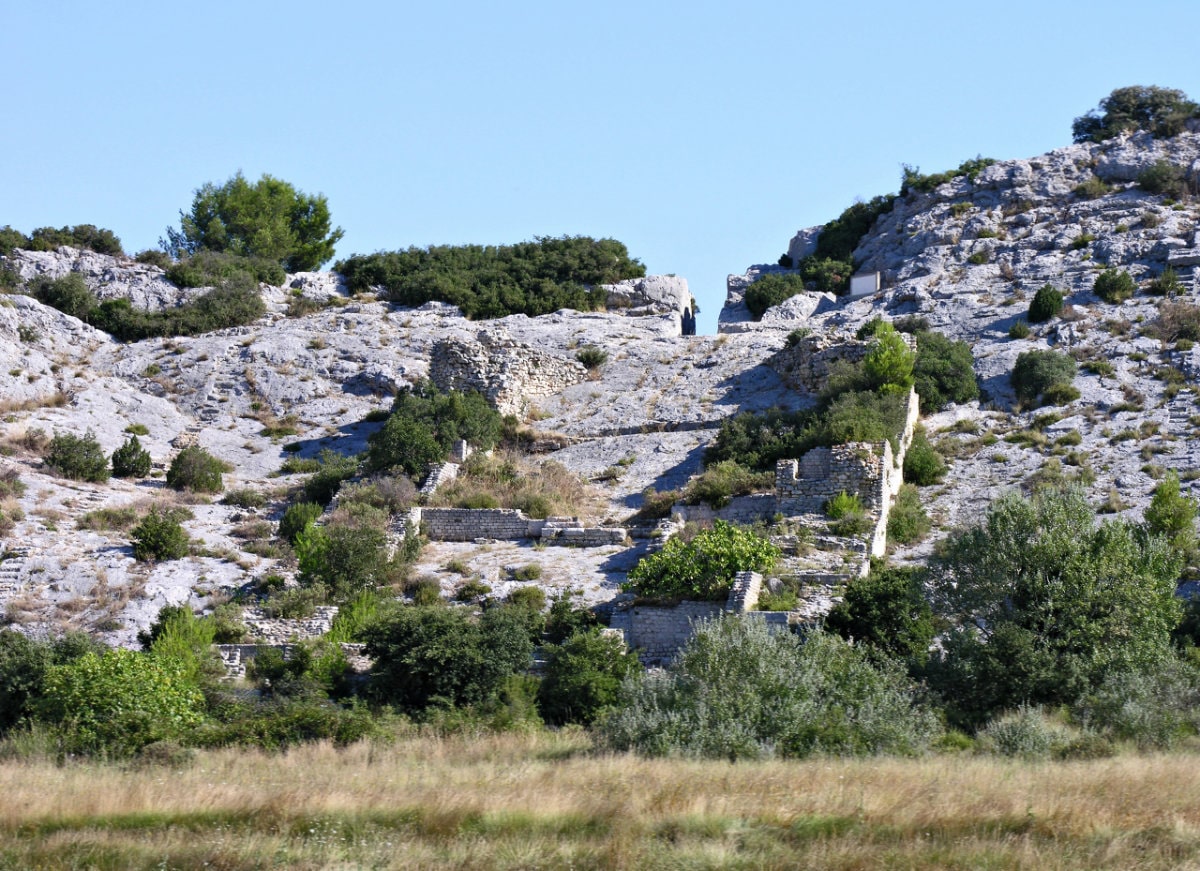
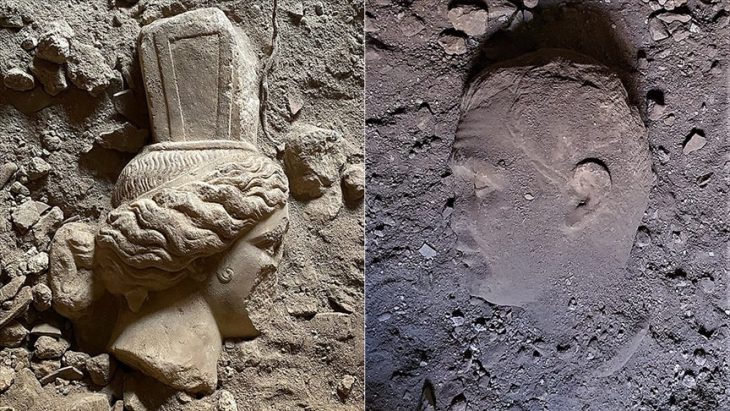
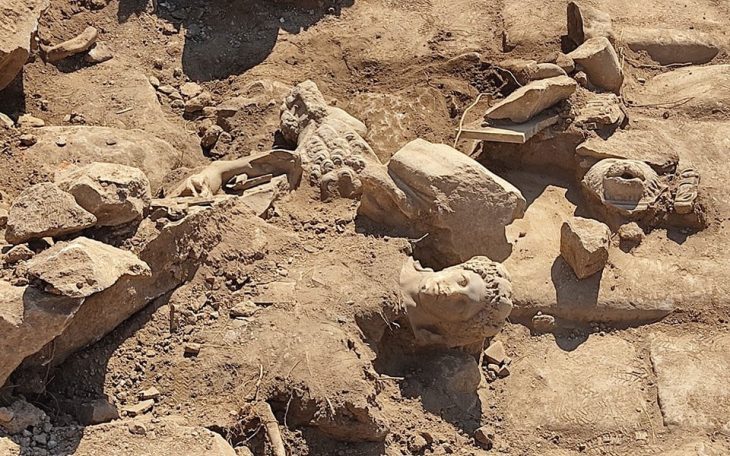
Archaeologists are faced with a difficult task: how can information be obtained about buildings or facilities of which – if at all – only ruins remain? The watermills in Barbegal in the south of France from the 2nd century AD were particularly tricky – a unique complex of 16 watermills, eight on the eastern side and eight on the western side, which were used from top to bottom as in a waterfall.
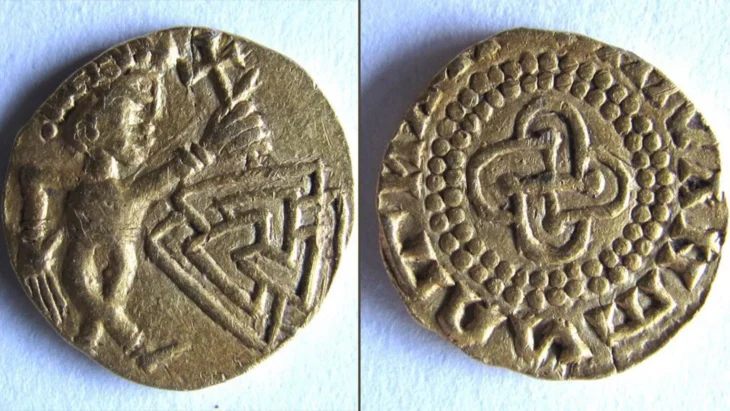
Until now, all that was known was what could be gleaned from the sparsely preserved ruins: The water mills were fed by an aqueduct from the surrounding hills. A coin of Trajan, found in a basin above the mills, and the construction features suggest that the mill was in use for around 100 years. However, the type of mill wheels and how they were used have remained a mystery until now.
Carbonates reveal exciting connections
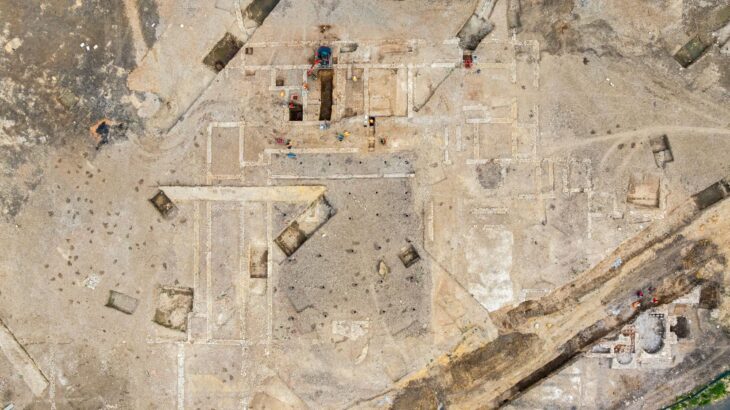
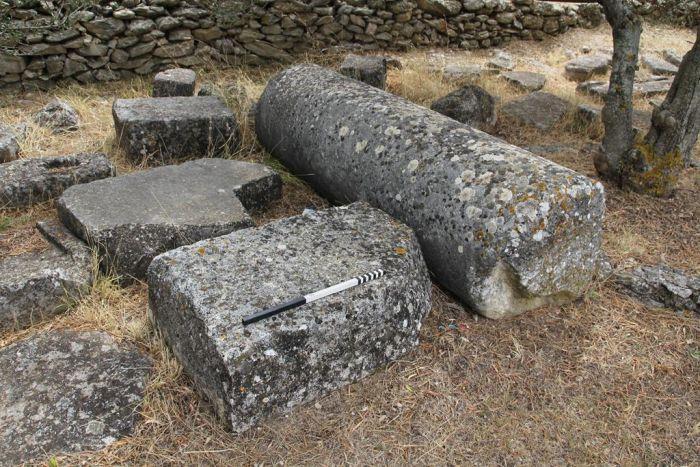
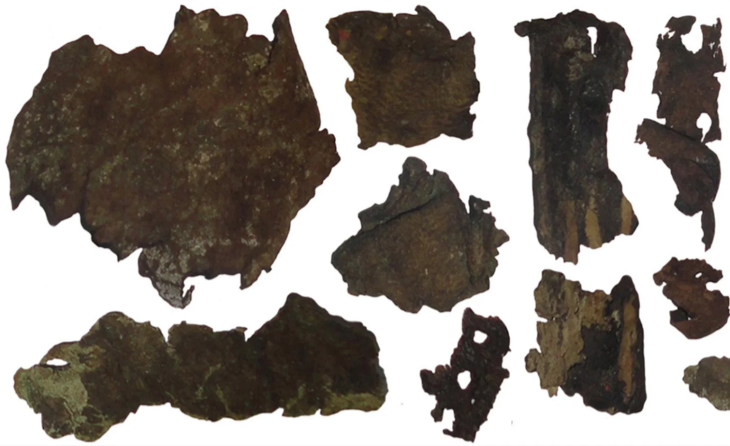
Professor Cees W. Passchier and Dr. Gül Sürmelihindi from Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU), together with colleagues from France and Austria, have now been able to unravel the history of the mill using pieces of carbonate stored in the Archaeological Museum in Arles. These deposits had formed towards the end of the roughly 100-year operational life of the Barbegal water mills on the sides and base of the wooden supply system that conveyed the water to the wheels.
“We show that it is possible to reconstruct to a large extent the history of a water mill on the basis of such carbonate deposits,” stated Passchier, head of the JGU team. First, the researchers had to fit some of the total of 140 stored pieces together like a jigsaw puzzle, then they analyzed the layers using various techniques, including mass spectrometry.
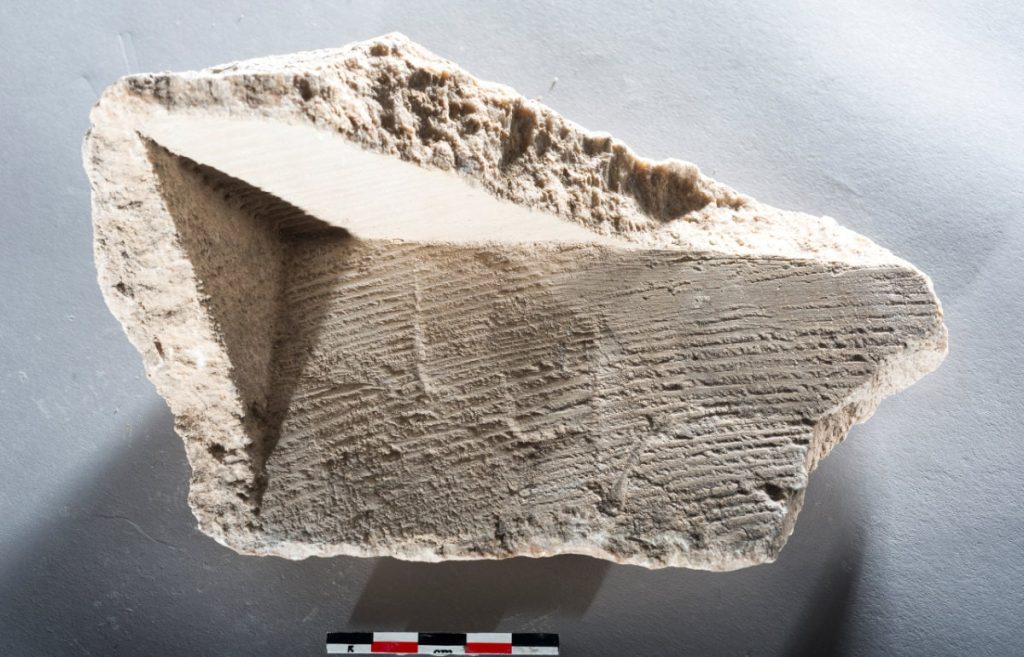

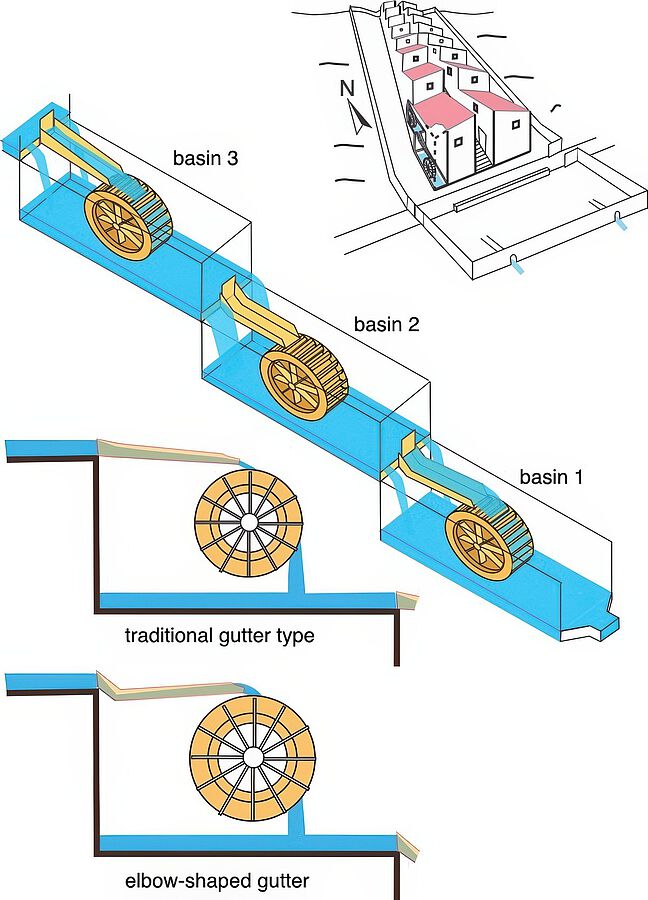
Wooden water wheels and gutters were replaced
The researchers have now published their results in Geoarchaeology. “We were able to show, for example, that wooden water wheels and water channels had to be replaced after three to eight years. In at least one case, an old water wheel was replaced by a larger one,” said Passchier.
The researchers drew this conclusion from the unusual shape of the carbonate deposits that had formed in the water channel. While the lower and earlier layers indicate that water levels must have originally been relatively low, upper and later carbonate layers indicate a higher water level. The possibility that there was originally less water flowing through the water channel which was subsequently increased was rejected by the researchers. They established that — for a gently sloping water channel and low water level — the amount of water provided would not have been sufficient to drive a mill wheel.
Therefore, the inclination of the water channel must have been altered, from what was at first a steeper angle with a low water level to a shallower slope transporting water at a correspondingly higher level. “The entire structure of this water mill must have been modified,” said Passchier. “If you uplift the water channel alone, the water tends to splatter, losing the power to drive the wheel efficiently. Thus, when you uplift the water channel, you also need a larger water wheel.”
In fact, a section of carbonate deposit formed on the water wheel corroborates this conclusion as it does not contain all the carbonate layers but only those of the latter years of operation.
Isotope analysis to classify the service life
Using isotope analysis of the carbonate layers, the researchers were even able to ascertain the operating periods before which parts of the mill required renewal. Carbonate contains oxygen and the relative ratios of oxygen isotopes differ depending on water temperature. Based on the isotope composition in the carbonate layers, the researchers were able to infer water temperatures and thus identify the seasons in which the layers were deposited.
They concluded that the carbonate from the samples in the Archaeological Museum in Arles had been deposited in the water channels over a period of seven to eight years. “The uppermost and thus youngest carbonate layer contains mollusk shells and fragments of wood, showing that the mill must have been abandoned by then and was disintegrating. The water continued to flow for a while so that carbonate deposits also continued to form, but maintenance of the water channels ceased,” said Passchier.
The researchers were able to answer yet another question. It was not previously known whether the mills had been run in combination by a single operator or whether the 16 water wheels had been used independently of each other. Judging from the layers of three investigated water channels, which are clearly different from each other, the mills were in operation separately — at least towards the end of their lifetime. Moreover, the western side of the complex was abandoned earlier than the eastern side. Finally, long pieces of carbonate from the water channels were later used as partition screens in a water basin for other industrial purposes after the mills had already been abandoned.
Johannes Gutenberg Universitaet Mainz
Cover Photo: View of the Barbegal plant in 2018. Photo: Robert Fabre
















