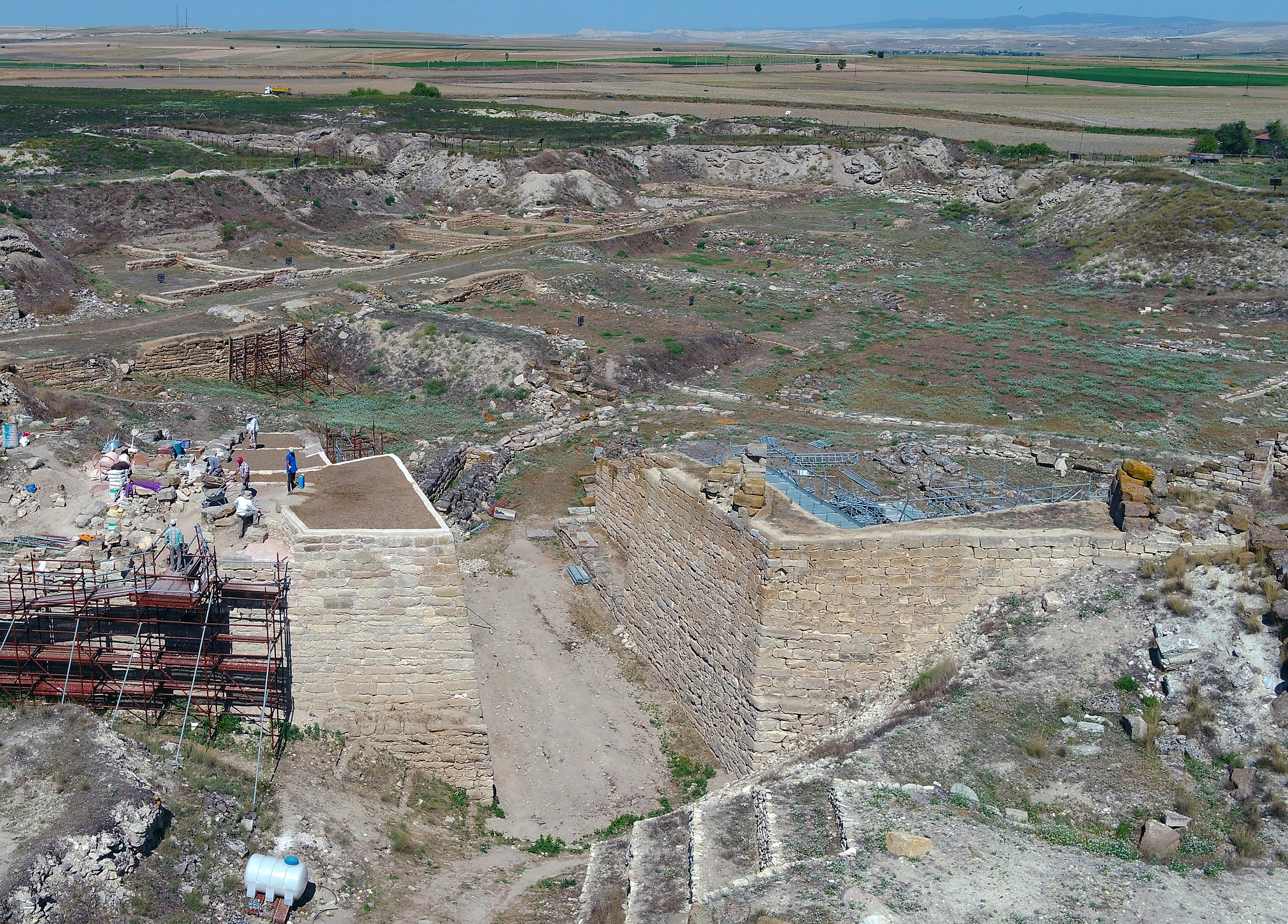
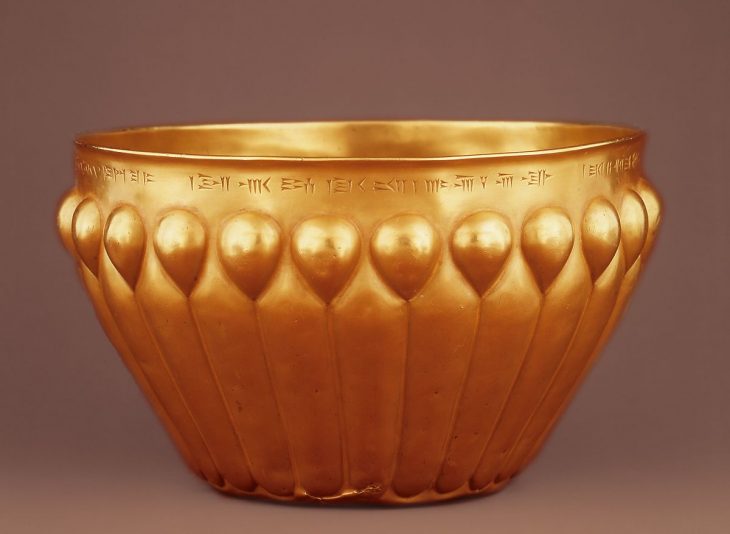
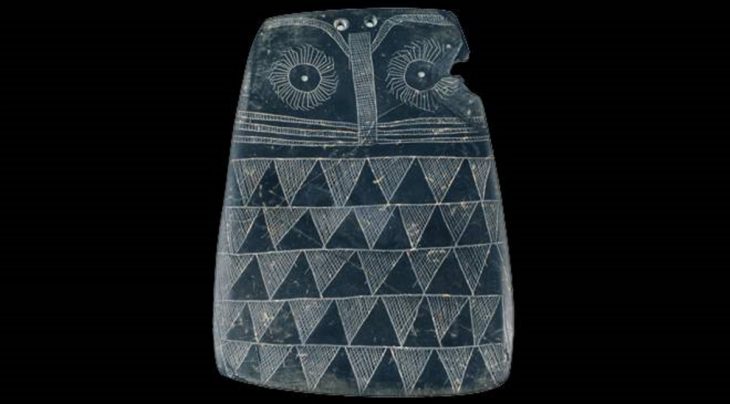
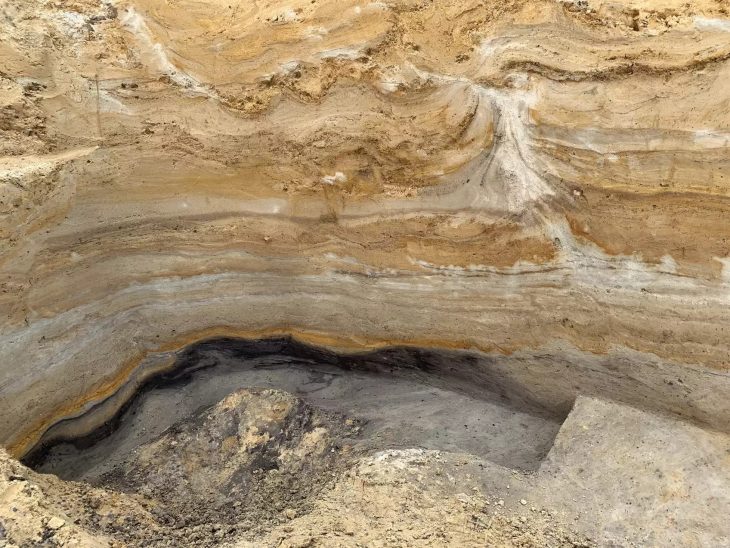
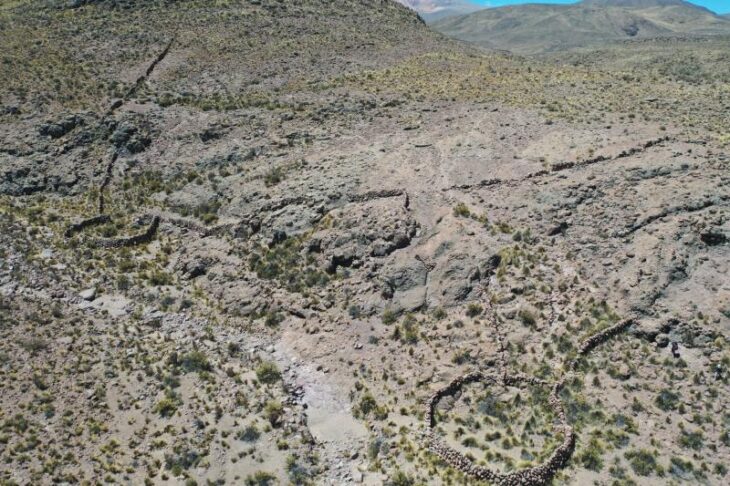
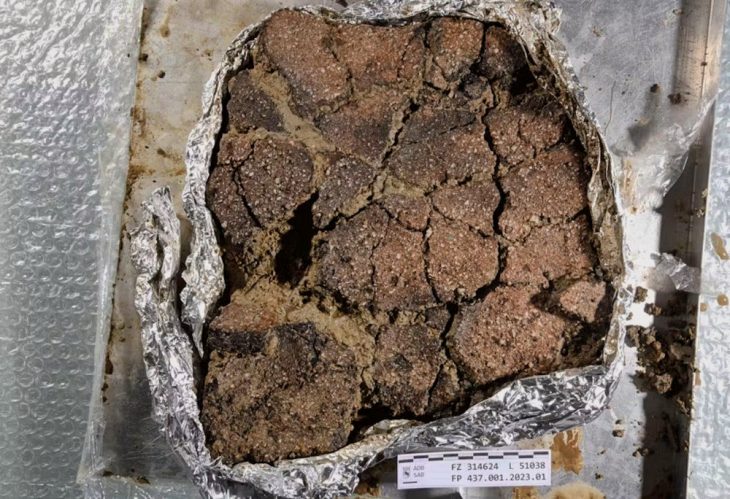
In a major archaeological breakthrough, Turkey’s Minister of Culture and Tourism, Mehmet Nuri Ersoy, announced the discovery of a wooden burial chamber in the ancient city of Gordion, believed to belong to a member of the Phrygian royal family. During a press briefing at the site, Ersoy confirmed the unearthing of 88 remarkably preserved metal artifacts, including large bronze cauldrons and vessels affixed with iron nails on the tomb’s walls.
“A wooden-constructed tomb chamber has been brought to light,” said Ersoy. “This group of artifacts is the most substantial since the earlier discoveries in the Midas Tumulus. Based on these finds, we estimate that the individual buried here may have belonged to the royal family associated with Gordios and Midas.”
This monumental discovery not only reaffirms Gordion’s royal heritage but also brings global attention to one of the world’s most important ancient cities, now a newly inscribed UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Gordion: Capital of the Phrygians and Cradle of Myths
Located near Yassıhöyük village in Ankara’s Polatlı district, Gordion served as the political and cultural heart of the Phrygian civilization—a kingdom closely linked to the legendary King Midas. Officially added to the UNESCO World Heritage List in 2023, Gordion is celebrated for its continuous settlement since 2500 BC and its pivotal role in early Anatolian history.
The Midas Mound Tumulus, one of the largest in Anatolia, is a centerpiece of the site and was originally constructed by King Midas for his father, possibly King Gordios. According to UNESCO, the intact wooden tomb beneath it “has no parallel anywhere in the world.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Ongoing Excavations Reveal Rich Royal Traditions
The latest find comes from Tumulus T26, excavated under the leadership of Professor Süleyman Yücel Şenyurt of Ankara Hacı Bayram Veli University. This 121-day project has brought new insights into Phrygian burial customs, daily life, and elite craftsmanship.
Plans are underway to exhibit the wooden chamber and its contents at the Gordion Museum by the end of 2025. So far, 47 artifacts have undergone restoration and were unveiled during the minister’s announcement.
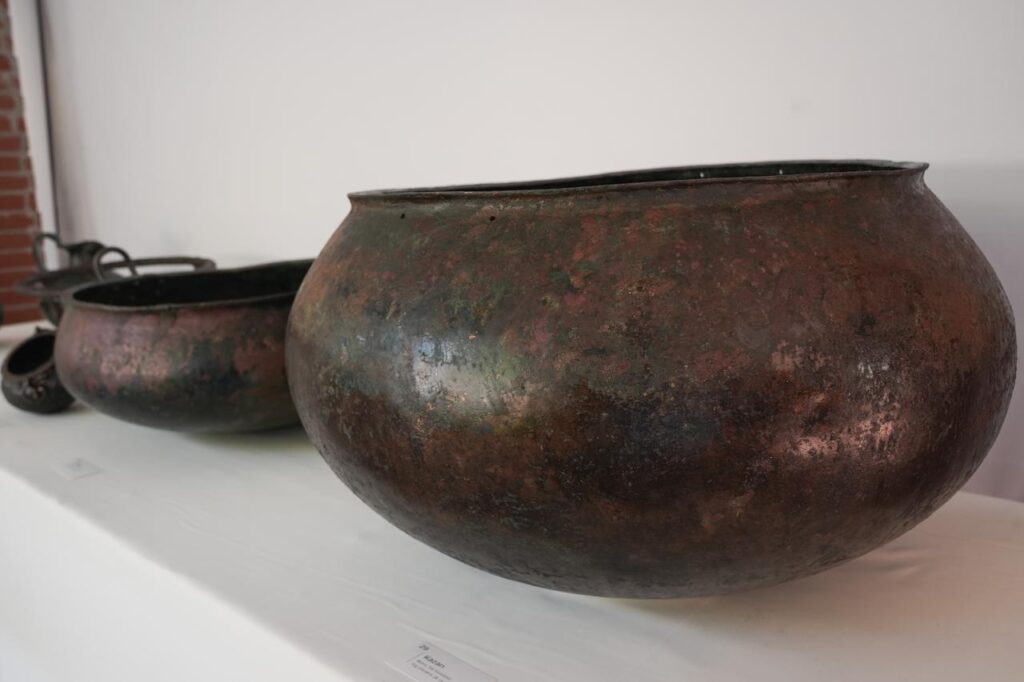

A City That Rivals Athens and Rome
Described by scholars as one of the most significant urban centers of the ancient world, Gordion stands alongside Athens, Rome, Babylon, and Hattusa. It was a hub of artistic, architectural, and technological innovation, offering some of the earliest examples of stone mosaics, expert-level carpentry, and textile craftsmanship.
According to Professor Brian Rose, head of excavations from the University of Pennsylvania, Gordion’s strategic position along key trade routes and fertile lands contributed to its long-standing influence.
The Legend of the Gordian Knot Lives On
No discussion of Gordion would be complete without mention of the Gordian Knot, the legendary puzzle said to guarantee dominion over Asia to whoever could untie it. In 334 B.C., Alexander the Great visited Gordion and allegedly sliced through the Gordian Knot—a prophetic puzzle promising rule over Asia to whoever could untie it. This legendary act gave birth to the expression “cutting the Gordian knot,” still used today to describe bold solutions to complex problems.
Recent excavations suggest the knot’s actual location may have been in Gordion’s Mosaic Building, where archaeologists recently found a gold-and-ivory sphinx, deepening the city’s mystical aura.
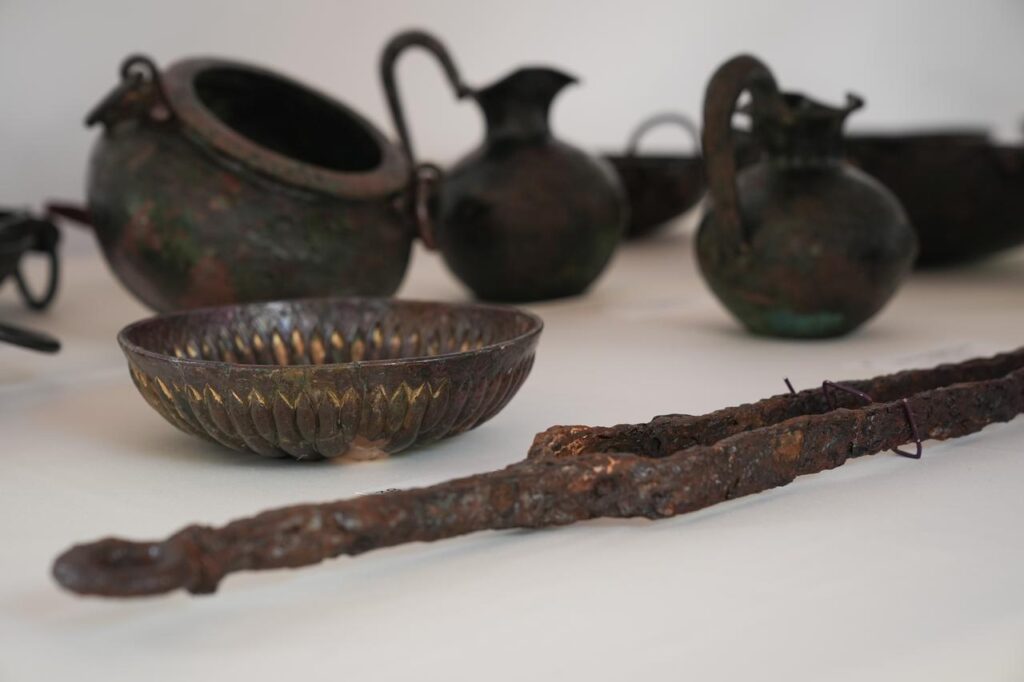

Preserving the Legacy of King Midas
While the legend of the “golden touch” remains symbolic, Professor Rose offers a historical explanation: elite garments of the Phrygian aristocracy may have appeared golden due to a pigment called goethite, possibly inspiring the myth.
Today, Gordion continues to reveal its secrets, offering invaluable insights into a civilization that once linked East and West, myth and reality.
Cover Image Credit: Public Domain