In the annals of history, few figures are as intriguing as Alexander of Abonoteichus, the self-proclaimed prophet who captivated the hearts and minds of many during the Roman Empire. His story is one of ambition, deception, and the relentless pursuit of power, set against the backdrop of a society teetering on the edge of change.
Alexander of Abonoteichus, also known as Alexander the Paphlagonian was a Greek mystic and oracle who lived approximately between 105 and 170 CE. Alexander of Abonoteichus was born in the ancient city of Abonoteichus (İnebolu-Kastamonu), located in the region of Paphlagonia, in what is now modern-day Türkiye. He is best remembered as the founder of the Glycon cult, which briefly gained widespread popularity throughout the Roman Empire.
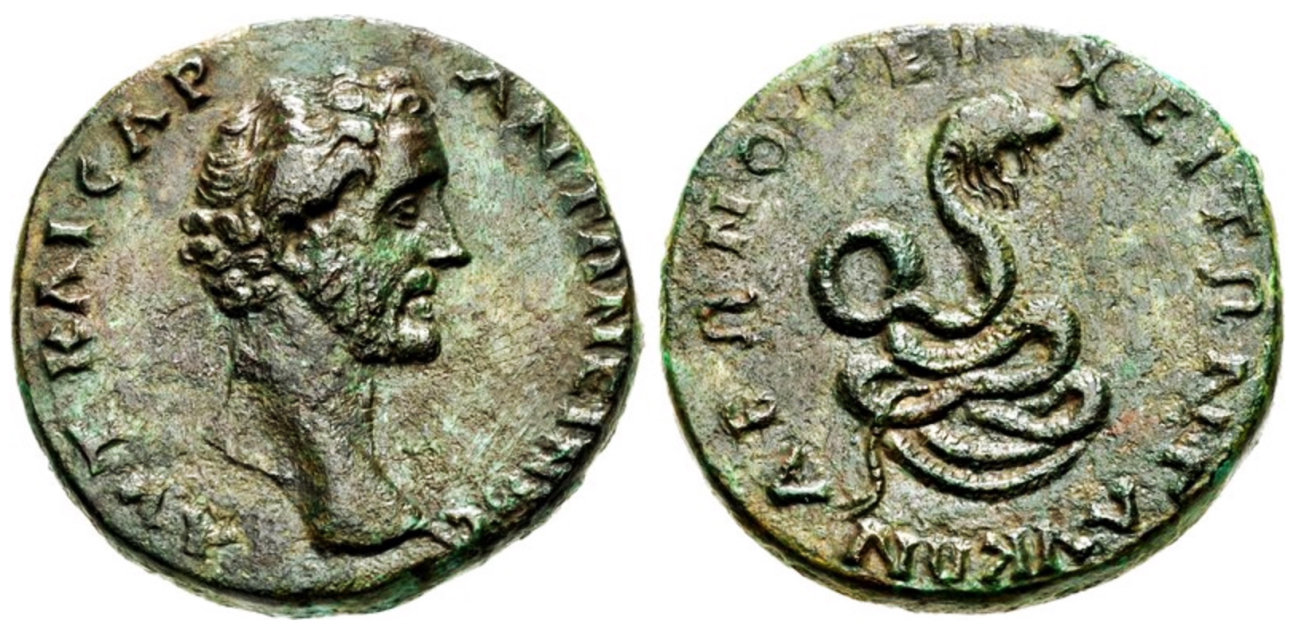
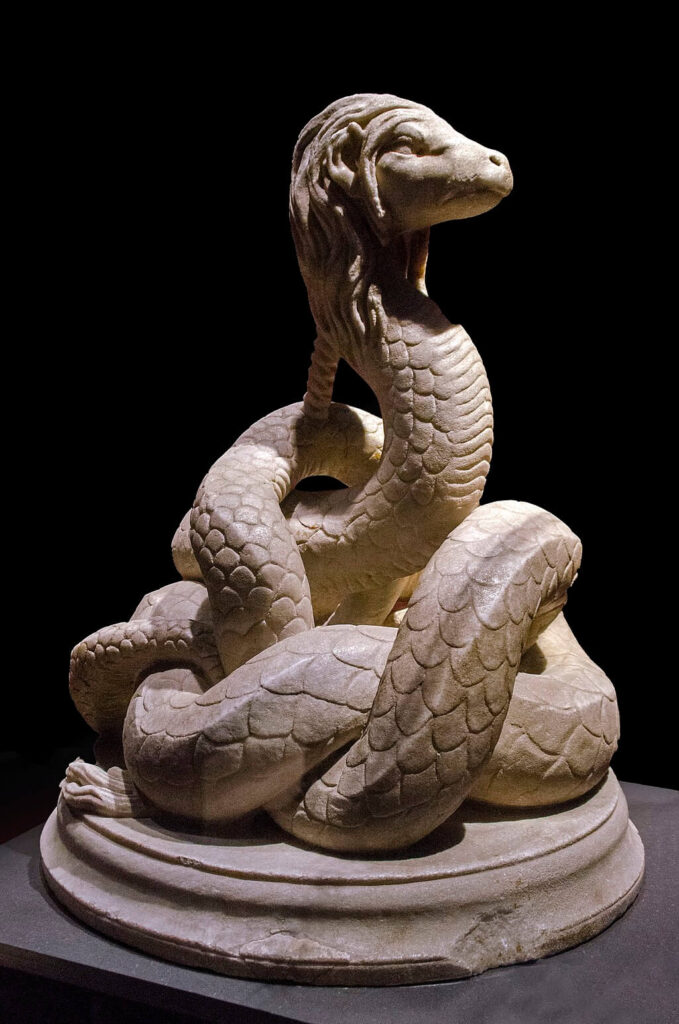
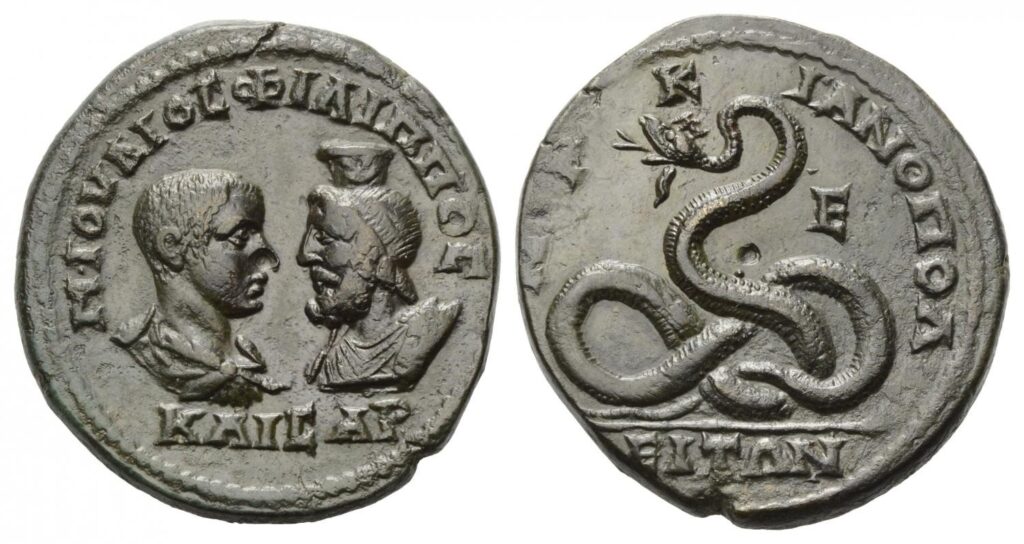
The Glycon cult emerged in the 2nd century CE, during a time when the Roman Empire was experiencing a surge in various religious movements and mystery cults. Alexander claimed to have received divine revelations from a serpent deity named Glycon, who he presented as a manifestation of the god Asclepius, the god of healing and medicine. Glycon was depicted as a snake or a serpent with a human head, symbolizing both wisdom and healing.
The legend of Alexander and the snakes is an important tale that highlights his mystical and divine attributes. According to the story, Alexander encounters a group of snakes during his travels. In the tale, Alexander walks among the snakes and, rather than harming them, he manages to communicate with them. The snakes, in turn, impart secret knowledge and teach him the ability to foresee the future. This event contributes to his perception as a divine figure and strengthens the faith of his followers in him.
The Rise of Alexander
Born into obscurity, Alexander emerged in the tumultuous period of the late Roman Republic, a time marked by political strife and social upheaval. As the Republic faced internal conflicts and external threats, many sought solace in spiritual leaders who promised guidance and salvation. It was in this fertile ground that Alexander began to cultivate his persona as a prophet.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
With a charismatic presence and a silver tongue, he traveled from town to town, weaving tales of divine visions and celestial messages. His followers, drawn by the promise of hope and the allure of his prophecies, grew in number. Alexander claimed to possess the ability to communicate with the gods, offering insights into the future and solutions to the pressing problems of the day. His proclamations resonated with the disillusioned masses, who were eager for a savior in a time of uncertainty.

The Allure of Prophecy
What made Alexander particularly compelling was his ability to tap into the fears and desires of the people. He spoke of impending doom, but also of a glorious future, painting vivid pictures of a world transformed by divine intervention. His prophecies often mirrored the anxieties of the time, addressing issues such as famine, war, and political corruption. This uncanny ability to predict the zeitgeist endeared him to many, as they believed he was a conduit for divine wisdom.
As his influence grew, so did the complexity of his prophecies. Alexander began to intertwine his messages with political aspirations, positioning himself as not just a prophet, but a potential leader. He promised to guide his followers to a new era of prosperity, one that would be achieved through their unwavering faith in him. This dangerous blend of spirituality and ambition set the stage for a dramatic confrontation with the established order.
Lucian of Samosata, a contemporary satirist, paints a scathing portrait of Alexander, accusing him of swindling countless individuals and employing his followers in various forms of thuggery. Lucian’s sharp criticism is largely fueled by Alexander’s disdain for the Epicureans, a philosophical school that Lucian himself admired. In his writings, Lucian highlights the contrast between Alexander’s deceptive practices and the genuine philosophical pursuits of Epicurus, culminating in a eulogy that underscores the value of Epicurean thought. While Lucian’s portrayal casts Alexander as a master of fraud and deceit, it is essential to recognize that he may not have been entirely unique among the oracles of his time.
The ancient world was rife with dishonest exploitation, and many shrines and religious figures engaged in similar practices, capitalizing on the vulnerabilities of their followers. This context raises questions about the nature of belief and the fine line between genuine spirituality and manipulation, further complicating Alexander’s legacy as both a mystic and a controversial figure.

The Fall from Grace
However, the very traits that propelled Alexander to prominence would ultimately lead to his downfall. As his following expanded, so did the scrutiny of his claims. Skeptics emerged, questioning the authenticity of his prophecies and the motives behind his charismatic facade. The Roman authorities, wary of his growing influence, began to take notice. They viewed him as a potential threat to the stability of the Republic.
In a dramatic turn of events, a series of failed prophecies began to erode Alexander’s credibility. As famine and unrest continued to plague the region, his once-loyal followers grew disillusioned. The promises of salvation turned to ashes, and the fervor that had once surrounded him began to dissipate. The authorities seized the opportunity to discredit him, branding him a fraud and a charlatan.
Alexander lived a long life, reaching the age of seventy, but ultimately succumbed to gangrene of the leg, complicated by myiasis. His death, occurring not at the hands of Roman authorities but due to health complications, underscores the irony of a mystic who navigated the treacherous waters of his time, only to be brought down by the frailties of the human body.
Lucian of Samosata. (n.d.). Alexander the False Prophet. (Trans. by A. M. Harmon). In The Works of Lucian of Samosata (Vol. 1). Harvard University Press.
Kelly, C. (2006). The Roman Empire: A Very Short Introduction. Oxford University Press.
Migliorati, G. (2020). Building the supernatural: The cult of Glykon of Abonuteichos from Lucian of Samosata to cognitive science. Cultural and Religious Studies, 8(6), 357-365. https://doi.org/10.17265/2328-2177/2020.06.004
Cover Image Credit: The bronze coin of Antoninus Pius minted in Abonoteichos and showing the snake god Glycon with the legend “ΓΛVΚΩΝ ΑΒΩΝΟΤΕΙΧΕΙΤΩΝ” (29 mm, 16.89 g) Credit: CC BY-SA 3.0