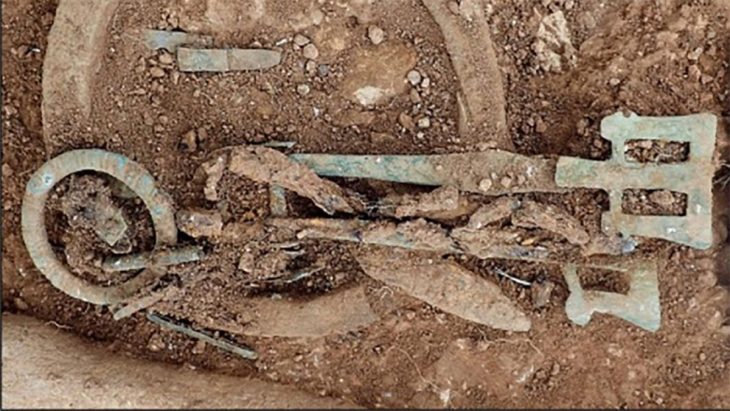
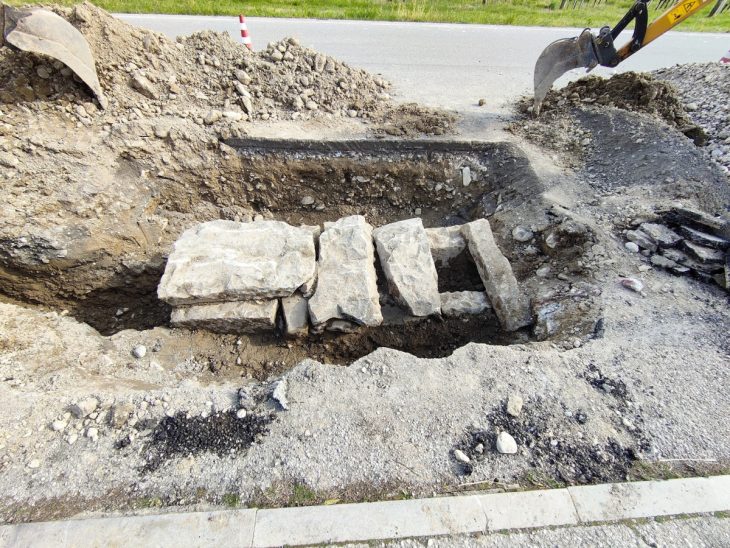
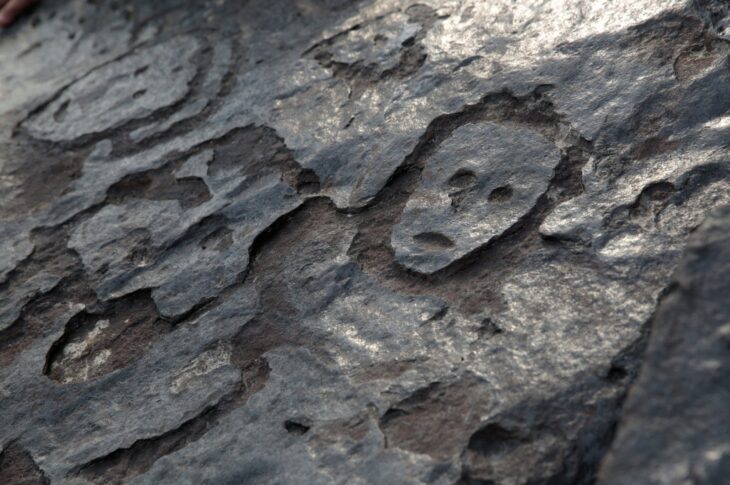
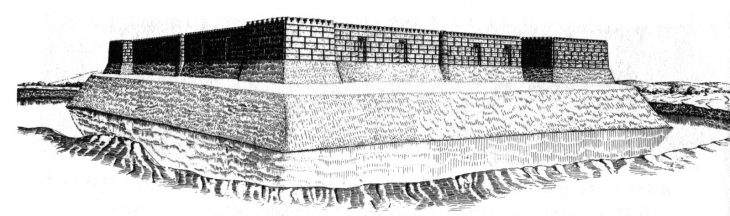
New findings demonstrate the resilience and inventiveness of local Bronze Age societies (Umm an-Nar Bronze Age culture), as well as the emirate’s role in regional and international trade, nearly 65 years after the first archaeological excavations in Abu Dhabi.
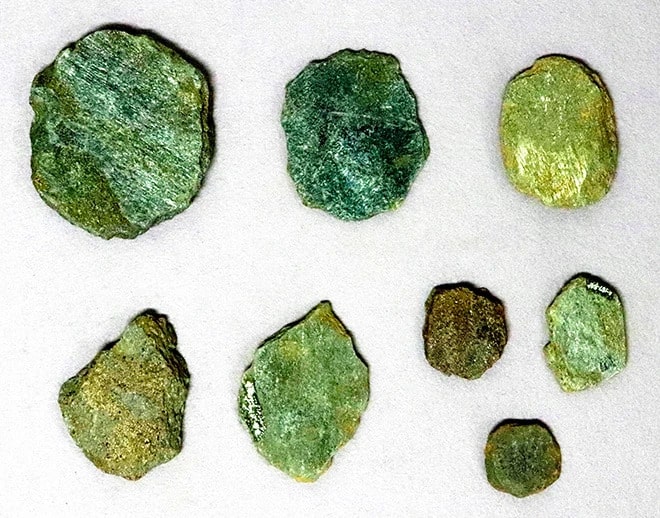
A recurring theme at Abu Dhabi excavation sites has been the use of natural resources, such as copper, pearls, plaster, and freshwater, to facilitate international trade, sustain communities, and establish prosperity.
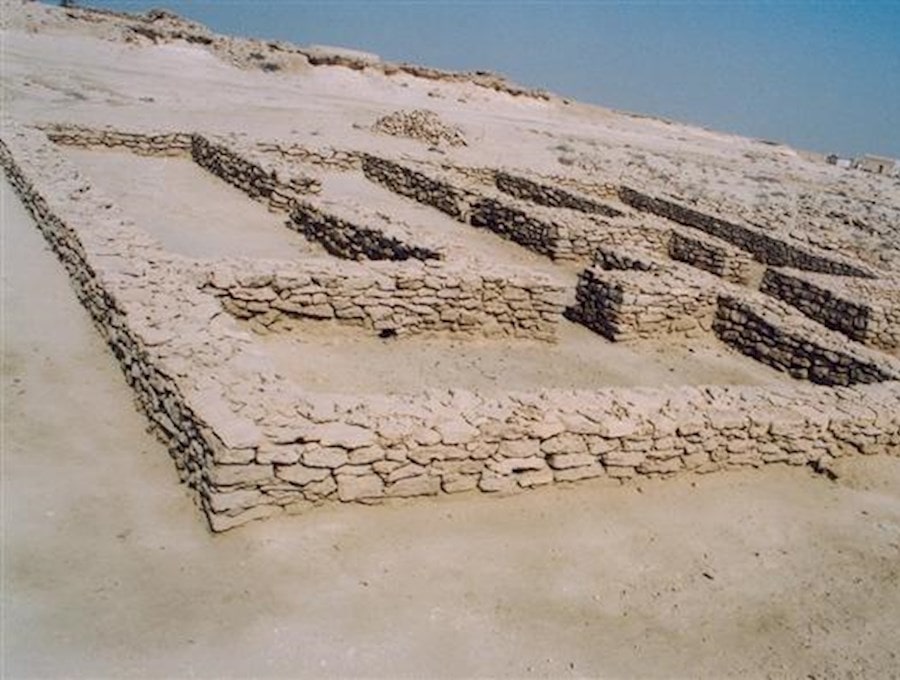
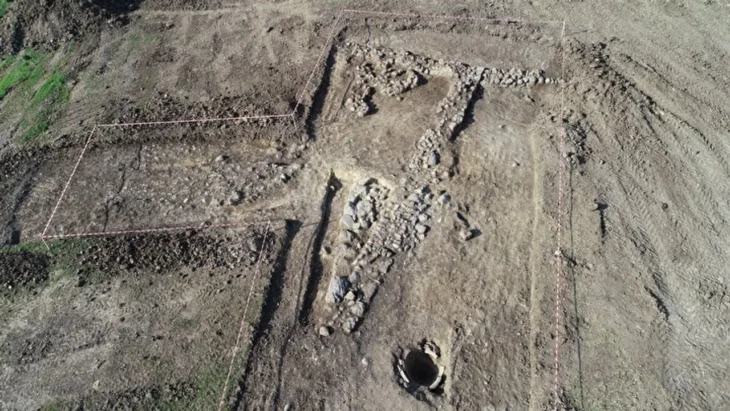
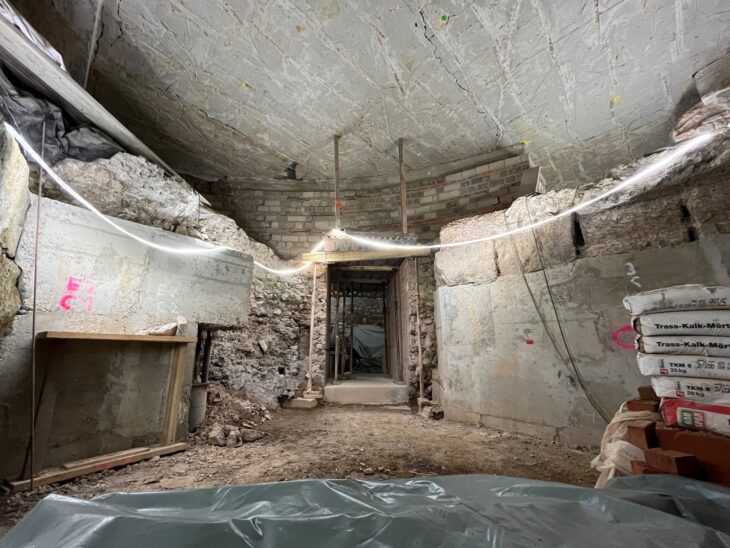
Archaeologists from the Abu Dhabi Department of Culture and Tourism (DCT Abu Dhabi) kicked off the new archaeological season by announcing discoveries from the Umm Nar Bronze Age culture (2700-2000 BCE) on Sas Al Nakhl Island.
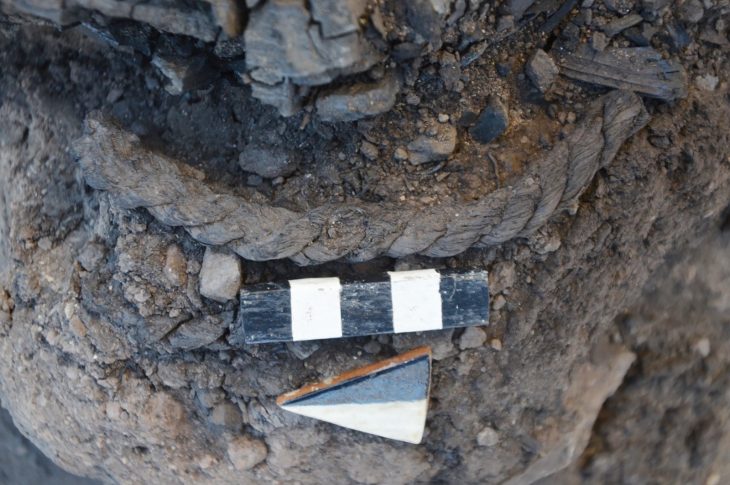
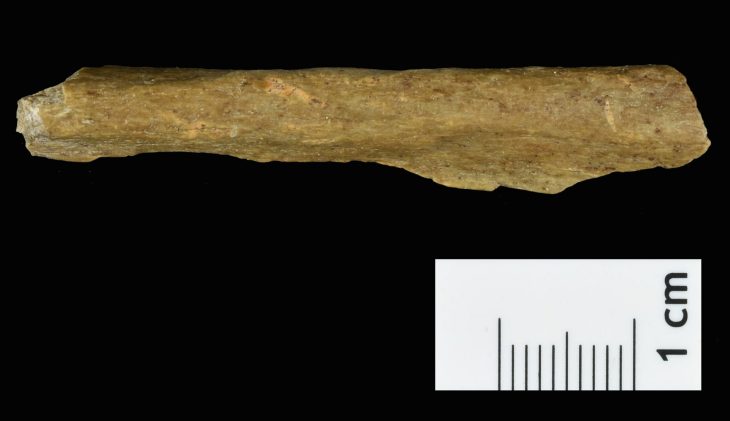
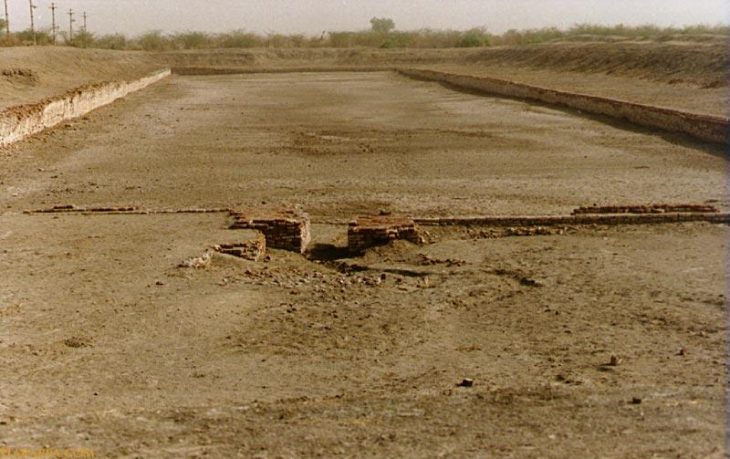
Recent excavations on Sas Al Nakhl Island, also known as Umm an-Nar, have revealed bitumen from ancient Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq) that was used to waterproof pottery, as well as a clay-lined storage pit. One fragment, which bears the impression of wood and two pieces of rope, was most likely part of a Bronze Age boat.
Sas Al Nakhl also referred to locally as Umm an-Nar, which means “mother of fire” or “the place of fire,” is situated close to the contemporary city center. Ashes and dark soil, which result from fires, cover large areas of the site, which may be the reason for this name. The island has given the Bronze Age Umm an-Nar culture its name because it was the first site of this era to be excavated in the area.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
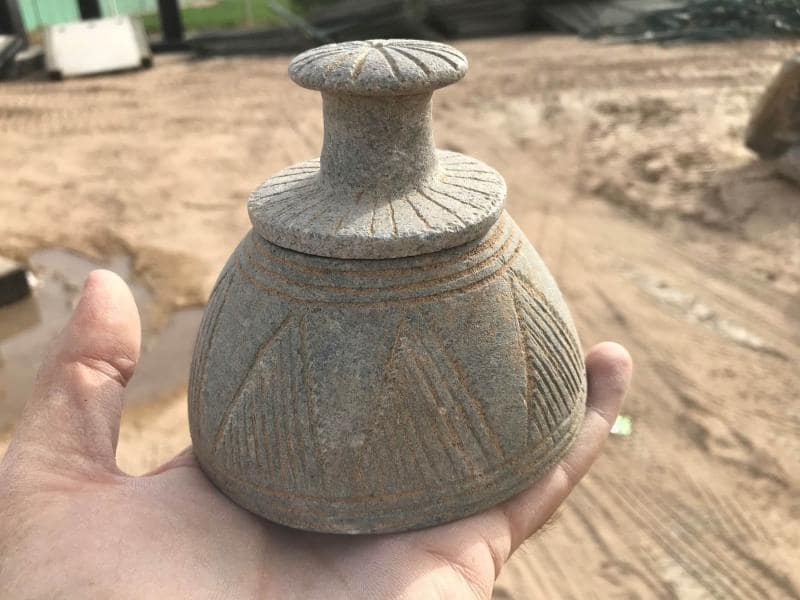

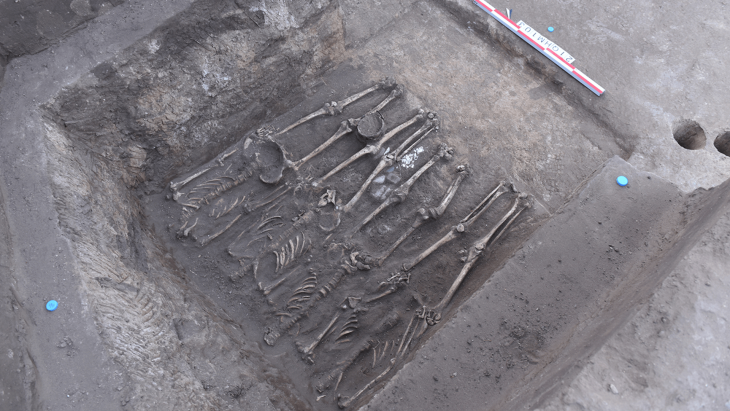
Finds from the recent excavations include a well-preserved assemblage of over 30,000 bones revealing new insights into the Bronze Age diet. This diet consisted mostly of fish and seabirds. Large animal bones discovered gathered around a large, circular fireplace point to ritualistic or group activities. A few of the bones have been fashioned into spindles and spatulas, among other things.
These new findings indicate that it was also a thriving port of significant international importance between 2800 and 2200 BCE, trading with Mesopotamia and the Indus Valley (modern-day Pakistan and India).
Bitumen from the site has been traced back to sources in ancient Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq), where it was used to waterproof pottery and a clay-lined storage pit. One large fragment bears the impression of wood and two pieces of rope, indicating that this was likely once part of the waterproofing on the hull of a Bronze Age boat, providing evidence of the long history of seafaring.
H.E. Mohamed Khalifa Al Mubarak, Chairman of Department of Culture & Tourism Abu Dhabi, said: “Our Founding Father Sheikh Zayed was instrumental in driving understanding of Abu Dhabi’s history through his passion for the land and people of the United Arab Emirates. DCT Abu Dhabi’s ambitious archaeology programme is a commitment to perpetuate that legacy to discover, preserve, and educate about our country’s past.”
Abu Dhabi currently has seven active excavation sites. Excavations are scheduled for the 2023–24 season in Al Ain, Sas Al Nakhl, Ghagha Island, the westernmost island of the United Arab Emirates, where DCT Abu Dhabi archaeologists have discovered 8,500-year-old structures, and Delma Island, where they are uncovering a 7,000-year-old settlement.
Cover Photo: Abu Dhabi Culture