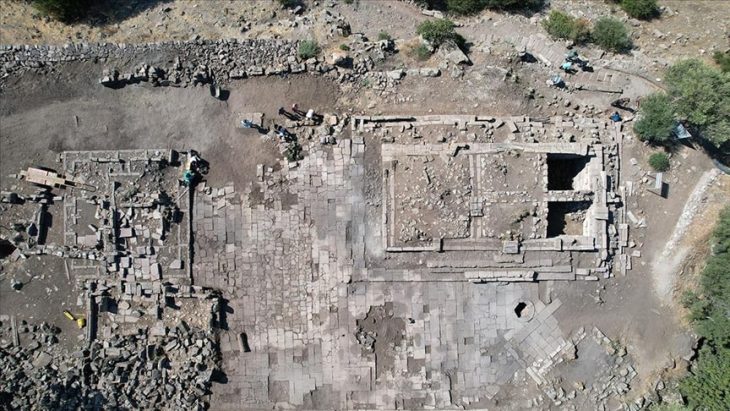
A genetic analysis of DNA taken from ancient skeletons appears to have answered a conundrum that has captivated researchers for more than 2,000 years: the origin of the Etruscans.
The study, published in the journal Science Advances on Friday, finds that the Etruscans, a sophisticated pre-Roman civilization in central Italy, were of local origin rather than migrants from the Near East, as previously thought.
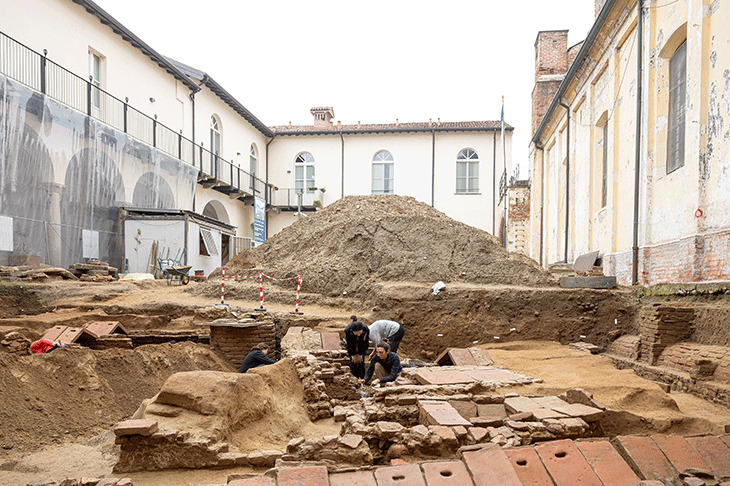
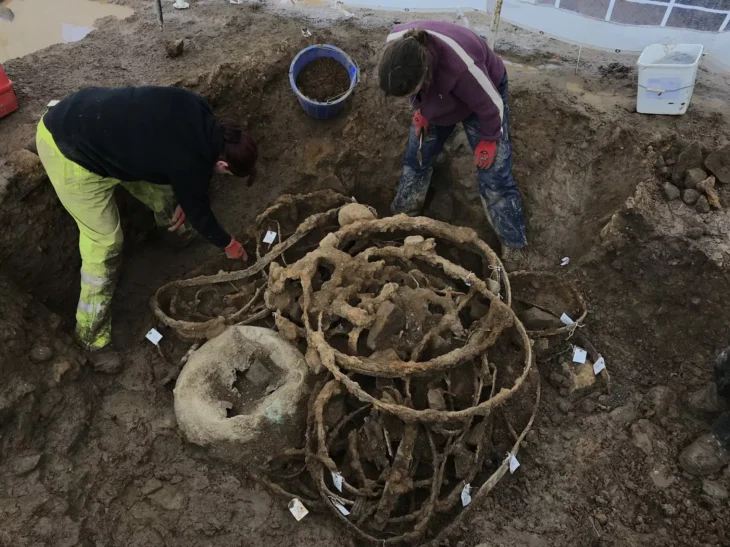
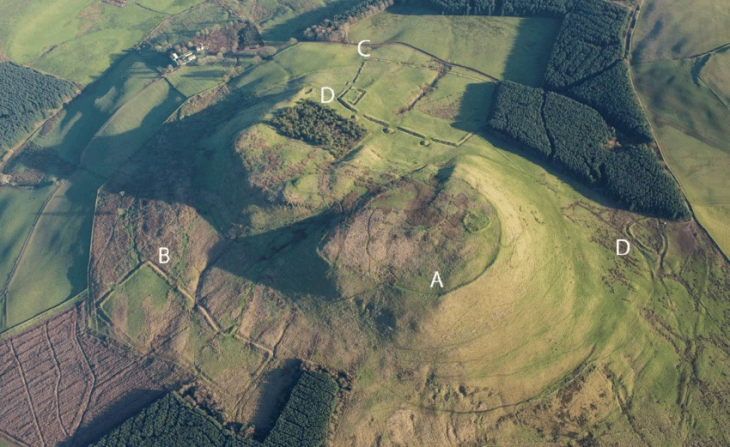
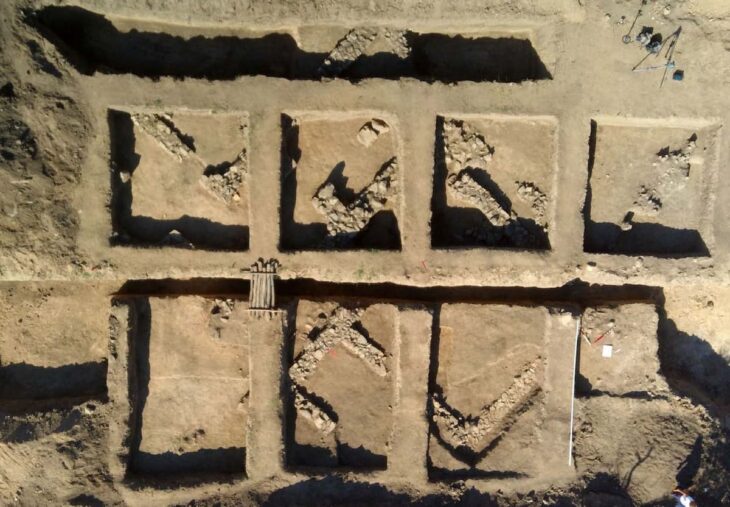
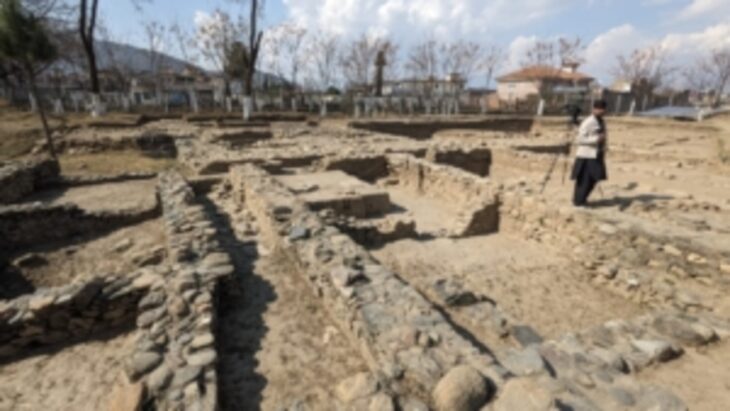
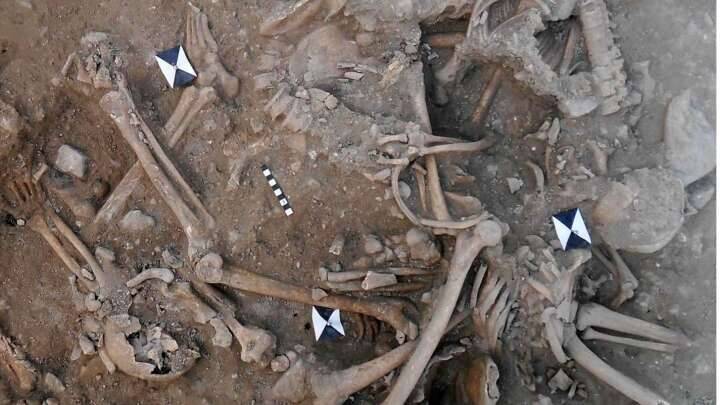
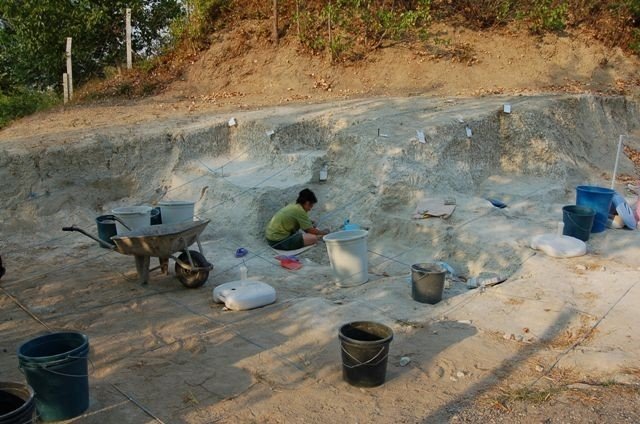
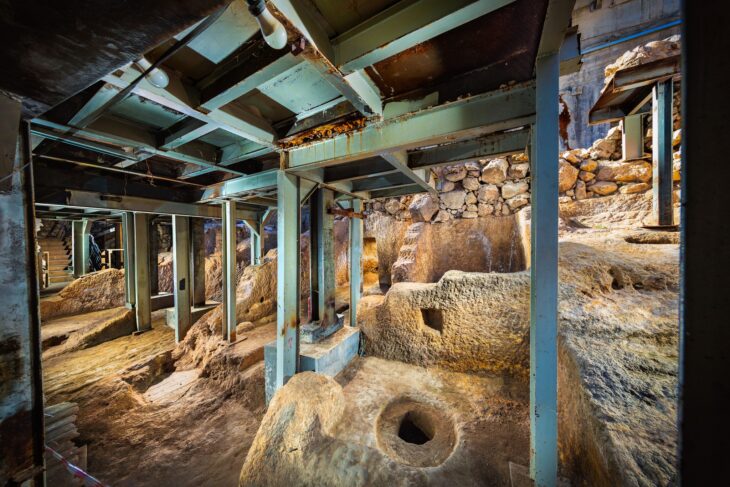
Geneticists from the Max Planck Institute, Tubingen University, and the University of Florence sequenced the DNA of 82 individuals who lived in central and southern Italy between 800 B.C.E. and 1000 C.E.Their results show that the Etruscans, despite their unique cultural expressions, were closely related to their italic neighbors, and reveal major genetic transformations associated with historical events.
According to Professor Cosimo Posth, an archaeogeneticist at Tubingen, the DNA of the ancient Etruscans – who made up almost half of the sample – was found to be closely connected to that of other neighboring Italic communities, including their Roman adversaries. This contradicts a long-held notion, originally offered by Herodotus, the 5th-century B.C.E. Greek historian known as the “Father of History,” that the Etruscans were Greeks who moved to Italy from western Anatolia.
Although the current consensus among archaeologists supports a local origin for the Etruscans, genetic studies have been inconclusive due to a paucity of ancient DNA from the region. The latest study, which used a time transect of ancient genetic information obtained from 12 archaeological sites spanning almost 2000 years, answers lingering doubts regarding Etruscan origins by revealing no indication for a recent population migration from Anatolia. In reality, the Etruscans shared the genetic profile of adjacent Latins, with a substantial part of their genetic profiles derived from steppe-related ancestry that arrived in the region during the Bronze Age.
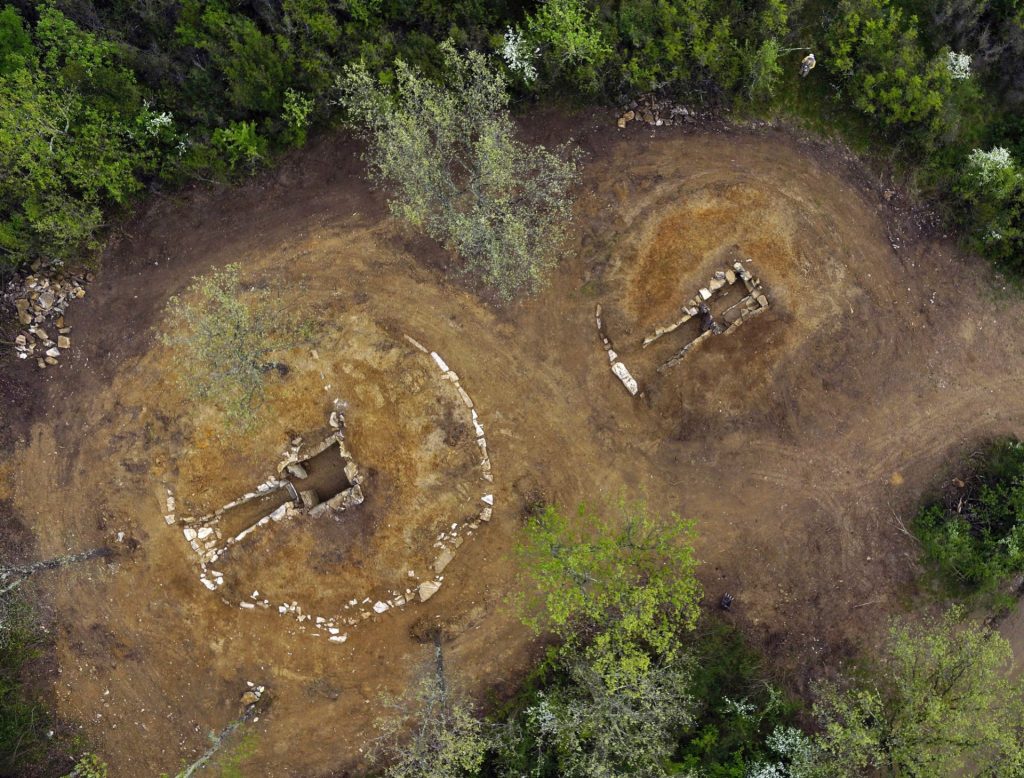

Given that steppe-related groups were most likely responsible for the spread of Indo-European languages, which are now spoken by billions of people around the world, the persistence of a non-Indo-European Etruscan language is an intriguing and still unexplained phenomenon that will necessitate further archaeological, historical, linguistic, and genetic research.
Despite the presence of a few people from the eastern Mediterranean, northern Africa, and central Europe, the Etruscan-related gene pool remained constant for at least 800 years, spanning the Iron Age and the Roman Republic. However, the study revealf that during the succeeding Roman Imperial period, central Italy witnessed a large-scale genetic change as a result of mixing with eastern Mediterranean populations, which most likely included slaves and soldiers moved around the Roman Empire.

Looking at the more recent Early Middle Ages, the researchers identified northern European ancestries spreading across the Italian peninsula following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire. These results suggest that Germanic migrants, including individuals associated with the newly established Longobard Kingdom, might have left a traceable impact on the genetic landscape of central Italy.
In the regions of Tuscany, Lazio, and Basilicata the population’s ancestry remained largely continuous between the Early Medieval times and today, suggesting that the main gene pool of present-day people from central and southern Italy was largely formed at least 1000 years ago.
Although more ancient DNA from across Italy is needed to support the above conclusions, ancestry shifts in Tuscany and northern Lazio similar to those reported for the city of Rome and its surroundings suggests that historical events during the first millennium CE had a major impact on the genetic transformations over much of the Italian peninsula.
“The Roman Empire appears to have left a long-lasting contribution to the genetic profile of southern Europeans, bridging the gap between European and eastern Mediterranean populations on the genetic map of western Eurasia,” says Cosimo Posth, Professor at the University of Tübingen and Senckenberg Centre for Human Evolution and Palaeoenvironment.