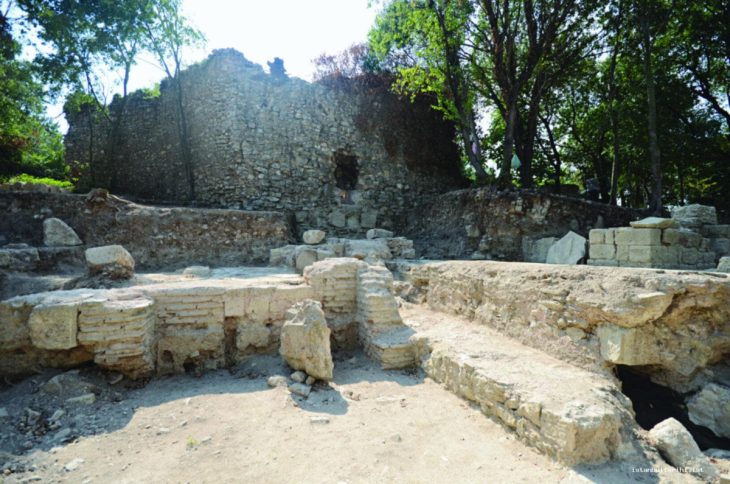
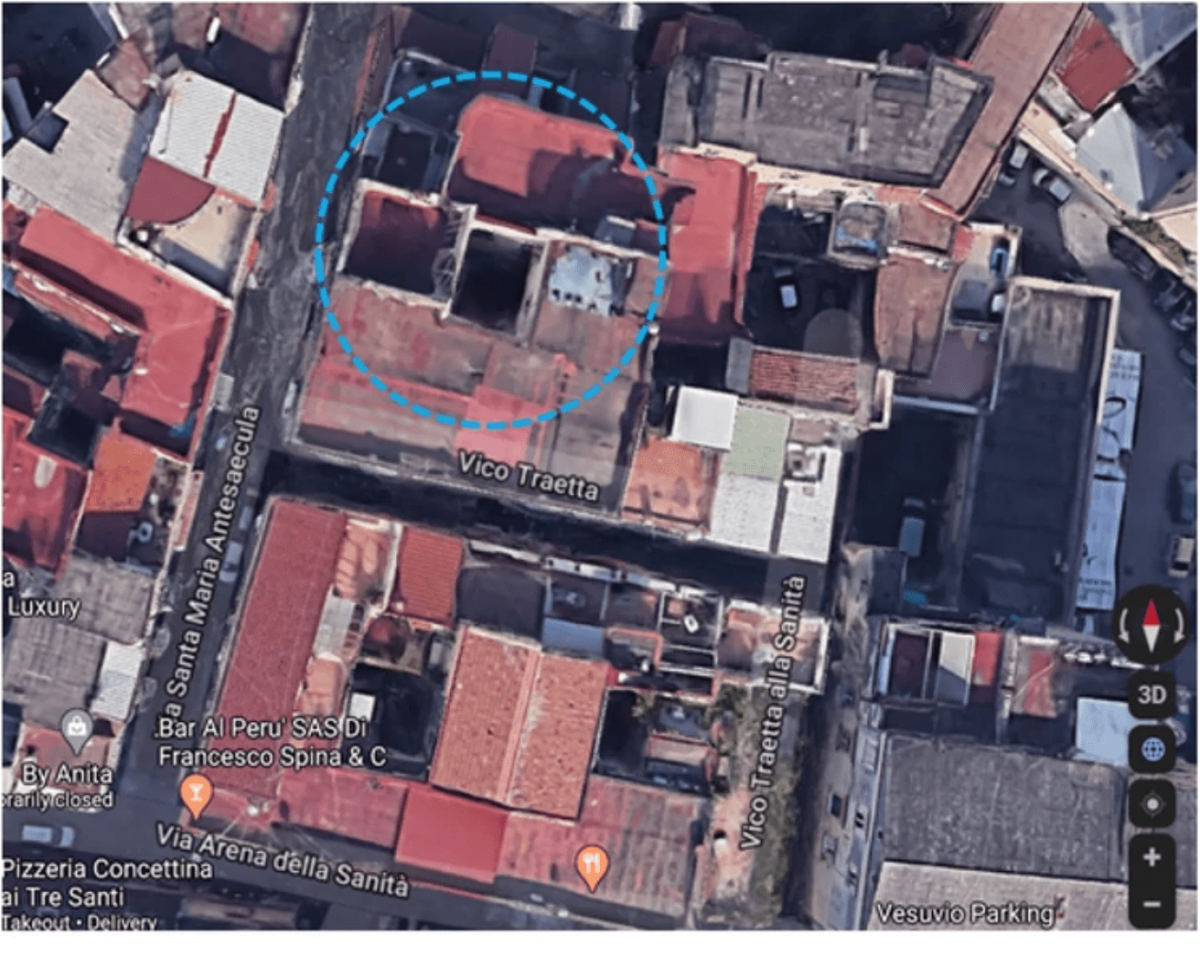
The ruins of the ancient necropolis of Neapolis, built by the Greeks between the end of the fourth and the beginning of the third century BC, are located about 10 meters beneath modern-day Naples.
Unfortunately, the Sanità district has a high population density and urban characteristics, making systematic excavations extremely difficult. Nonetheless, the archaeological research that led to the discovery of the Ipogei dei Togati and the Ipogei dei Melograni led researchers to make assumptions about the presence of other unknown monuments.
The use of cosmic rays and lasers allowed researchers to examine the underground without the need for any physical excavation.
The collaboration between particle physics and archaeology, two seemingly unrelated fields, produced a technique known as muography, which is particularly useful in urban settings where it is impractical to use active study techniques due to its non-invasive nature.
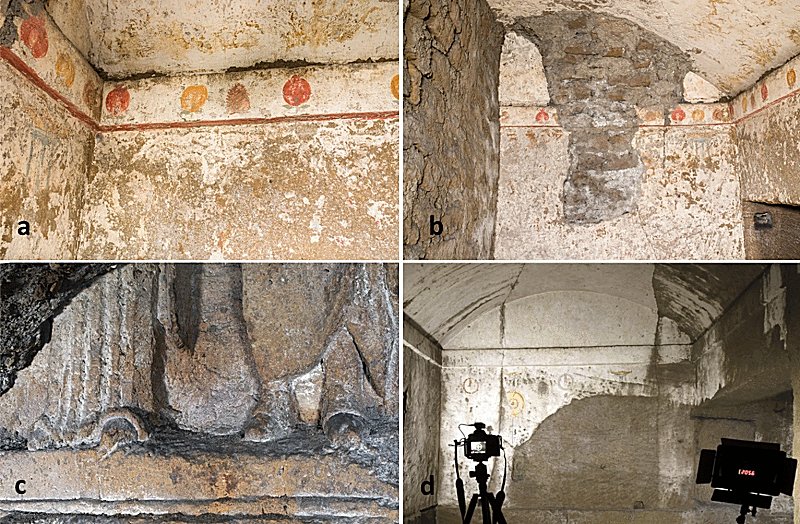

In collaboration with the University of Nagoya (Japan), a group of researchers from the University of Naples Federico II and the National Institute of Nuclear Physics (INFN) used muography to detect the presence of possible cavities in the underground of Naples‘ Sanità district. One of the most significant structures discovered is a hidden Hellenistic chamber that most likely houses a burial.
Muography is a technique that makes use of muons, which are high-energy charged particles produced by cosmic rays in the upper layers of the atmosphere. These muons were installed 18 meters below the Sanità district’s current street level to measure muon flux for about a month.
Researchers used a special technology called “nuclear emulsion” to record the tracks of these muons. This technology uses highly sensitive photographic film to capture and visualize the paths of these particles. As a result, the researchers were able to generate a radiographic image of the upper layers and observe both known and unknown structures.
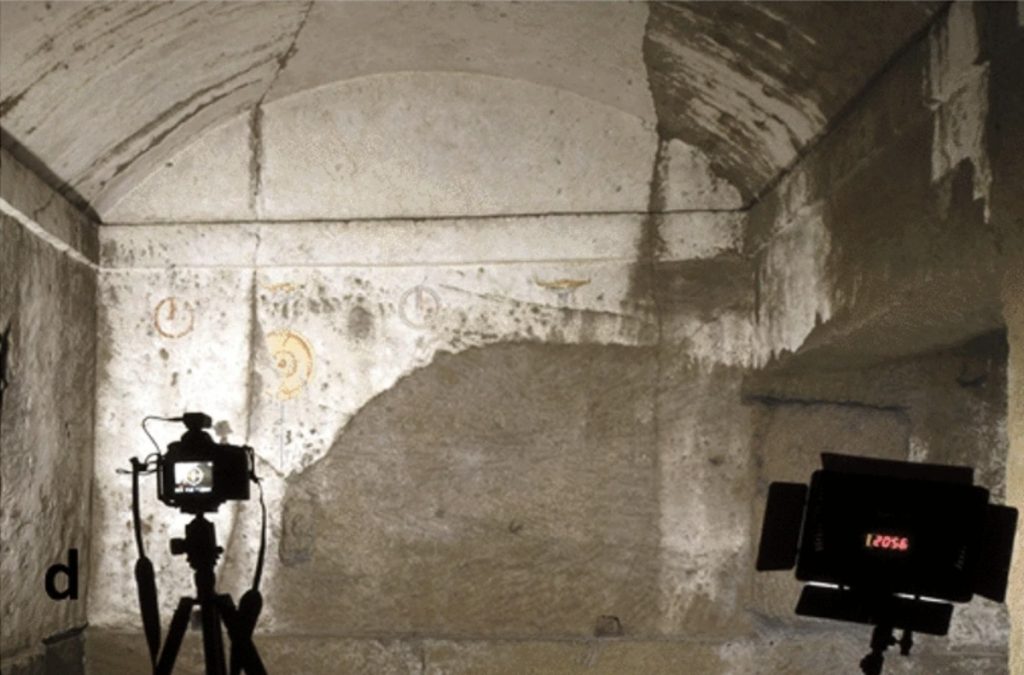

The muography revealed an excess of muons in the data, which could only be explained by the presence of a new burial chamber. The study explained that the chamber’s area measures roughly 6.5 by 11.5 feet and has a rectangular shape, indicating that it is human-made rather than natural.
Based on the depth of the chamber, the researchers believe it was part of an ancient Greek necropolis dating from the sixth to third centuries B.C. This hypogeum was most likely the tomb of a wealthy individual.
The researchers suspect this chamber is similar to others discovered in the late 1800s, such as the Hypogeum of the Toga-Wearers and the Hypogeum of the Pomegranates.
Cover Photo: Foreground top view of the studied site as seen with Google Maps. Nature / CC BY 4.0