Two anthropology professors from the University of Wyoming have discovered a prehistoric plaza high in the Andes, known as Callacpuma stone plaza, which was built nearly 5,000 years ago by ancient nomadic groups.
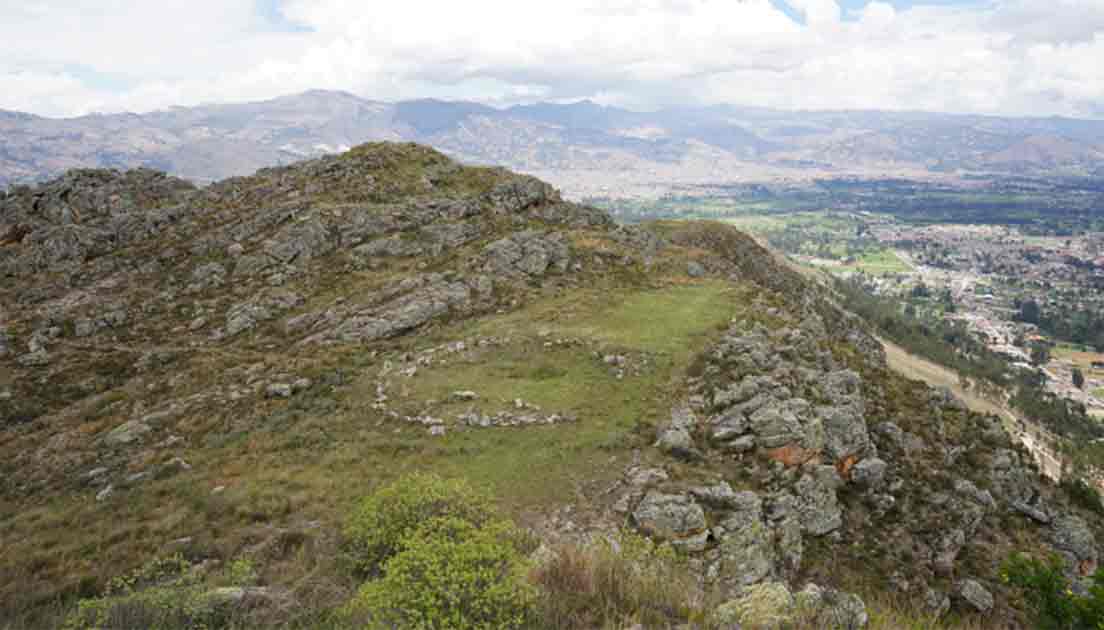
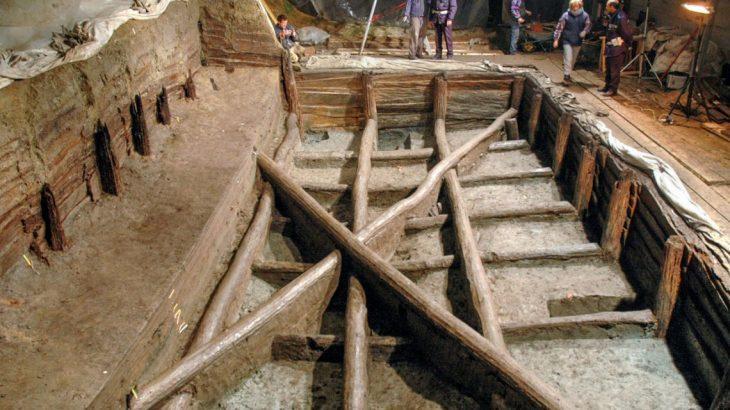
The plaza, which is situated at the Callacpuma archaeological site in the Cajamarca Basin of northern Peru, was constructed using large megalithic stones that were arranged vertically, a technique not previously used in the Andes.
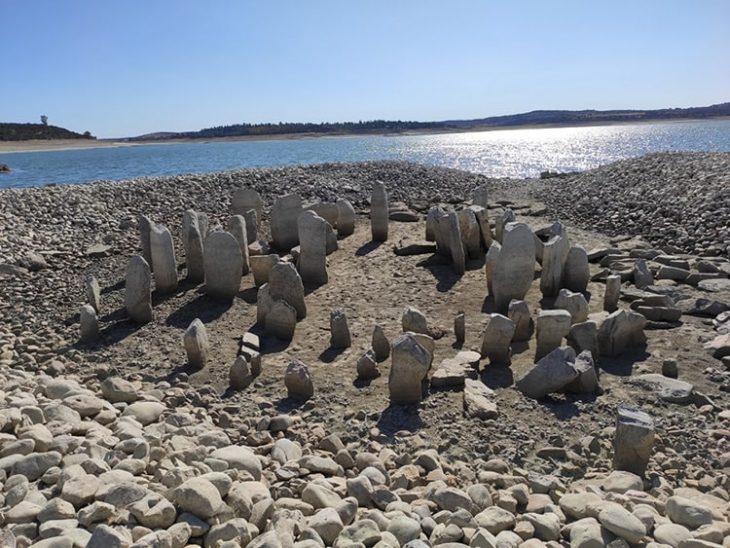
This significant finding is a unique structure of a stone circle, where offerings were made to long-forgotten gods over several millennia at an elevation of more than 3,000 meters (9850 feet) above sea level.
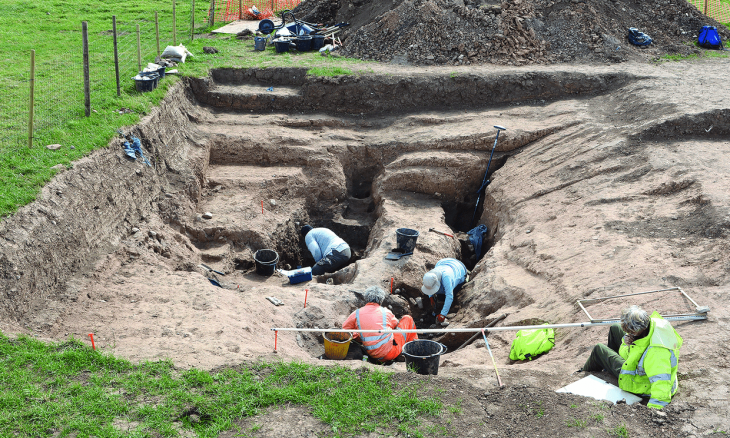
The project’s leaders, Associate Professor Jason Toohey, and Professor Melissa Murphy, have been researching this topic since the project began in 2015. Excavations for the plaza began in 2018.
Their article, published in the journal Science Advances, provides new information about the northern Andes’ oldest known circular megalithic plaza. Radiocarbon dating indicates that it was built around 4,750 years ago, during the Late Preceramic Period, making it one of the Americas’ earliest examples of this type of architecture.
Large megalithic stones are set in two concentric circles, each measuring 18 meters (60 feet) in diameter. This arrangement creates a ceremonial area that is full of unknown information from the time when hunter-gatherers in what is now Peru began to build more sophisticated societies.

A prominent feature of the late preceramic era, the plaza represents a critical period of transition in South America when coastal fishing communities started to trade with emerging mountain agricultural societies. It is a prime example of monumental architecture built prior to the widespread adoption of agriculture and long-term settlements.
“This structure was built approximately 100 years before the Great Pyramids of Egypt and around the same time as Stonehenge,” Jason L. Toohey says.
These dates signify that the circular plaza at Callacpuma is the earliest known example of monumental and megalithic architecture in the Cajamarca Valley—and one of the earliest examples in ancient Peru.
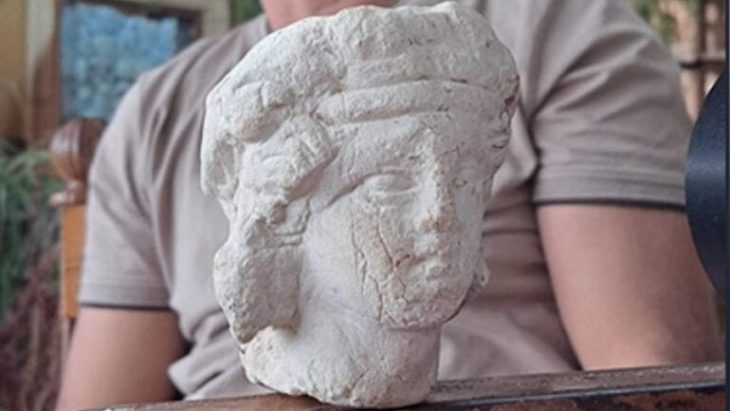
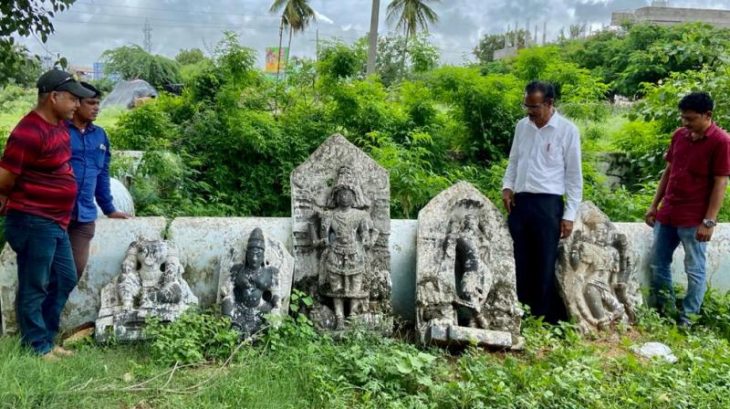
Further discoveries at the site include unworked lapis lazuli gems, quartz crystals, and pieces of ceramic cups and bowls, all of which demonstrate the site’s significance and continued use even after the local populations had mastered pottery.
Dated to the Layzón period (500–200 BC), recent artifacts made of soft kaolin clay indicate that the stone circle was visited on a regular basis until it was ceremoniously sealed during that same period for unidentified reasons. Semi-nomadic peoples’ building of these ritual sites reflects a change in their belief systems, which place more emphasis on group efforts and interregional cooperation.
The project is led by Toohey and Patricia Chirinos Ogata from the University of California-Santa Barbara. The team also includes Murphy, as well as undergraduate and graduate students from Peru and the U.S.
They work with locals close to the Callacpuma site on research findings and the significance of cultural heritage as part of their outreach to the community. Working together, further scientific investigations and site preservation can continue.
Cover Photo: Jason L. Toohey et al. / Science Advances