Leonardo da Vinci’s centuries-old sketches show that he may have understood key aspects of gravity long before Galileo, Newton, and Einstein.
Engineers from Caltech have discovered that Leonardo da Vinci’s understanding of gravity—though not wholly accurate—was centuries ahead of his time.
Recent research from the California Institute of Technology looked at long-forgotten diagrams in Leonardo da Vinci’s notebooks. According to a statement from the university these notebooks, which have now been digitized, show experiments from the early 1500s of particles falling from a pitcher, demonstrating gravity is a form of acceleration.
Da Vinci, who lived from 1452 to 1519, was well ahead of the curve in exploring these concepts. It wasn’t until 1604 that Galileo Galilei would theorize that the distance covered by a falling object was proportional to the square of time elapsed and not until the late 17th century that Sir Isaac Newton would expand on that to develop a law of universal gravitation, describing how objects are attracted to one another. Da Vinci’s primary hurdle was being limited by the tools at his disposal. For example, he lacked a means of precisely measuring time as objects fell.
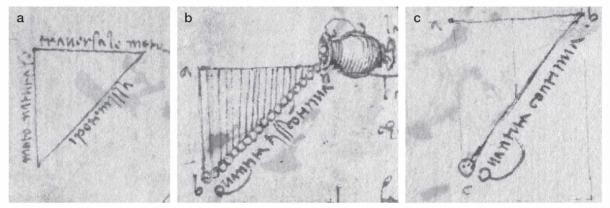
Da Vinci’s experiments were first spotted by Mory Gharib, the Hans W. Liepmann Professor of Aeronautics and Medical Engineering, in the Codex Arundel, a collection of papers written by da Vinci that cover science, art, and personal topics. In early 2017, Gharib was exploring da Vinci’s techniques of flow visualization to discuss with students he was teaching in a graduate course when he noticed a series of sketches showing triangles generated by sand-like particles pouring out from a jar in the newly released Codex Arundel, which can be viewed online courtesy of the British Library.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“What caught my eye was when he wrote ‘Equatione di Moti‘ on the hypotenuse of one of his sketched triangles—the one that was an isosceles right triangle,” says Gharib, lead author of the Leonardo paper. “I became interested to see what Leonardo meant by that phrase.”
The researchers had to translate da Vinci’s notes into Italian, which were written in his renowned left-handed mirror writing that reads from right to left, in order to analyze the sketches. The researchers then carried out da Vinci’s experiments using computer simulations.
According to Da Vinci’s notes, the velocity of the falling material accelerates downwards, and as the particles fall, they are no longer influenced by the pitcher but are instead accelerated by gravity pulling them downward. However, at the time, he was unable to translate his observations into an equation.

“What we saw is that Leonardo wrestled with this, but he modeled it as the falling object’s distance was proportional to 2 to the t power [with t representing time] instead proportional to t squared,” Chris Roh, co-author of the study and assistant professor at Cornell University, said in the statement. “It’s wrong, but we later found out that he used this sort of wrong equation in the correct way.”
When modeling the water vase experiments, the team yielded the same error da Vinci did centuries ago.
“We don’t know if da Vinci did further experiments or probed this question more deeply,” Gharib said in the statement. “But the fact that he was grappling with this problem in this way — in the early 1500s — demonstrates just how far ahead his thinking was.”
Their findings were published in the journal Leonardo. The paper is titled “Leonardo da Vinci’s Visualization of Gravity as a Form of Acceleration.”