A Polish-Russian team of archaeologists, excavating in the “Siberian Valley of the Kings” have announced the discovery of a burial mound containing ornate treasures from 2,500 years ago.
Excavations in the Chinge-Tey area were conducted by a Polish-Russian team from the Jagiellonian University in Krakow and the State Hermitage Museum in St. Petersburg.
The Chinge-Tey site is in the Turano-Ujukska Valley which has been ycleped the “Siberian Valley of the Kings” because of the proliferation of large burial mounds packed with rich grave goods that have been discovered there.
The site is associated with the Scythian culture, a nomadic people known from as early as the 9th century BC, who migrated westward from Central Asia into southern Russia during the 8th and 7th century BC.
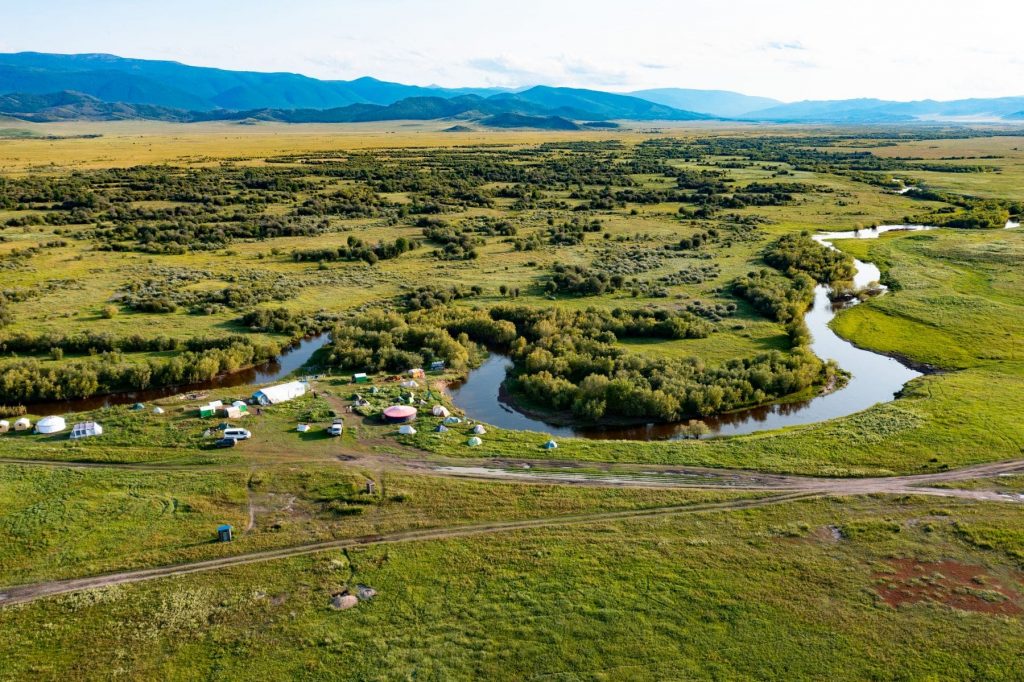

Archaeologists have discovered two new mounds in the new research. The first mound was damaged to the point of being almost leveled and was only detected thanks to aerial laser scanning that spotted the circular structure more than 80 feet in diameter.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
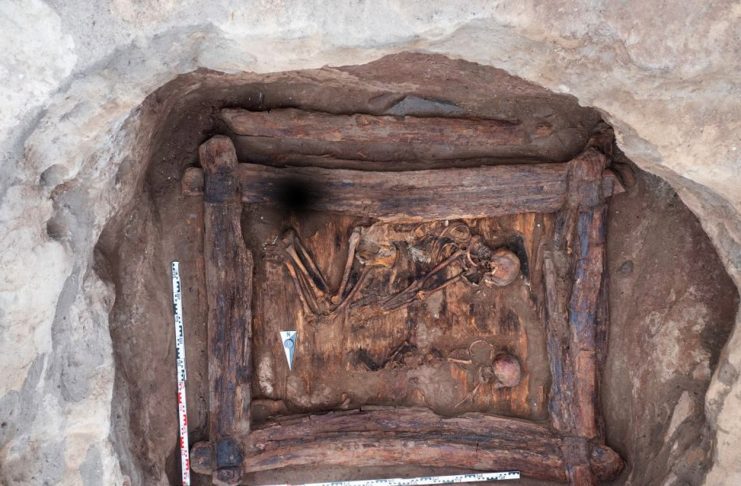
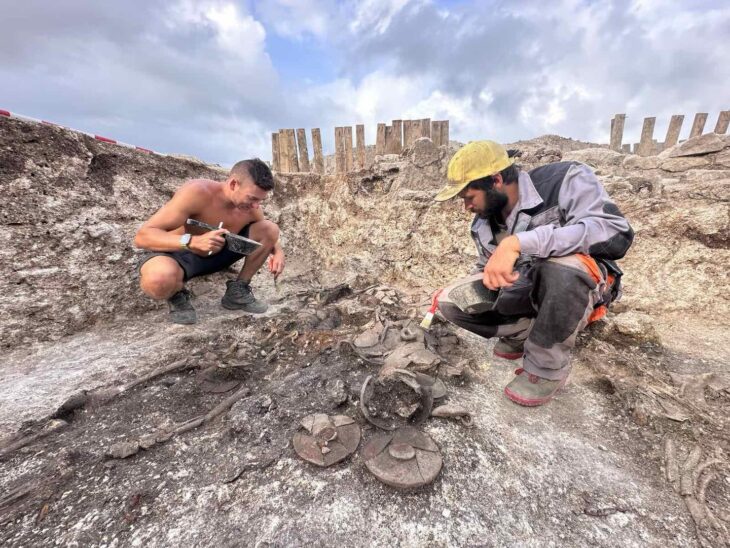
Archaeologists excavated the former mound and discovered a wooden burial chamber in the center. The heavy, elaborate chamber was built on a framework of interlocking beams with wooden floorboards and topped with three layers of beams to form a roof.
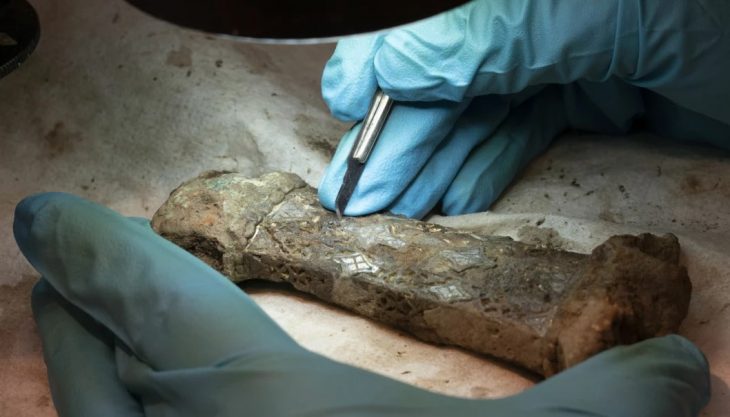
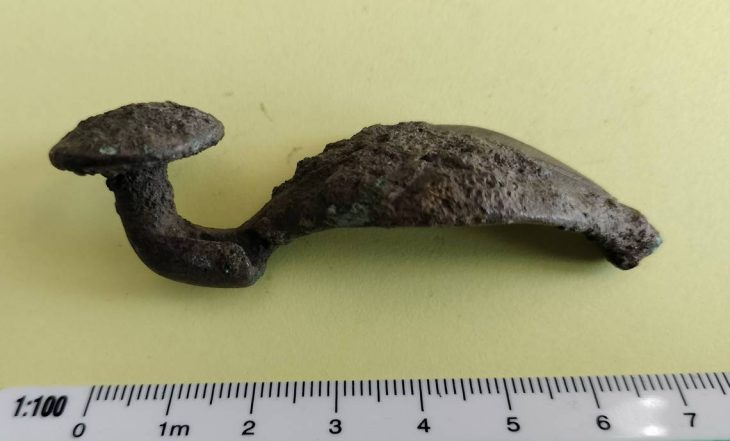
The first mound held a wooden burial chamber constructed on a framework of solid beams, containing a 50-year-old woman and a very young child. Placed alongside the burial were various golden ornaments, an iron knife, a comb, a bronze mirror, and an ornate crescent or moon-shaped piece of jewelry.
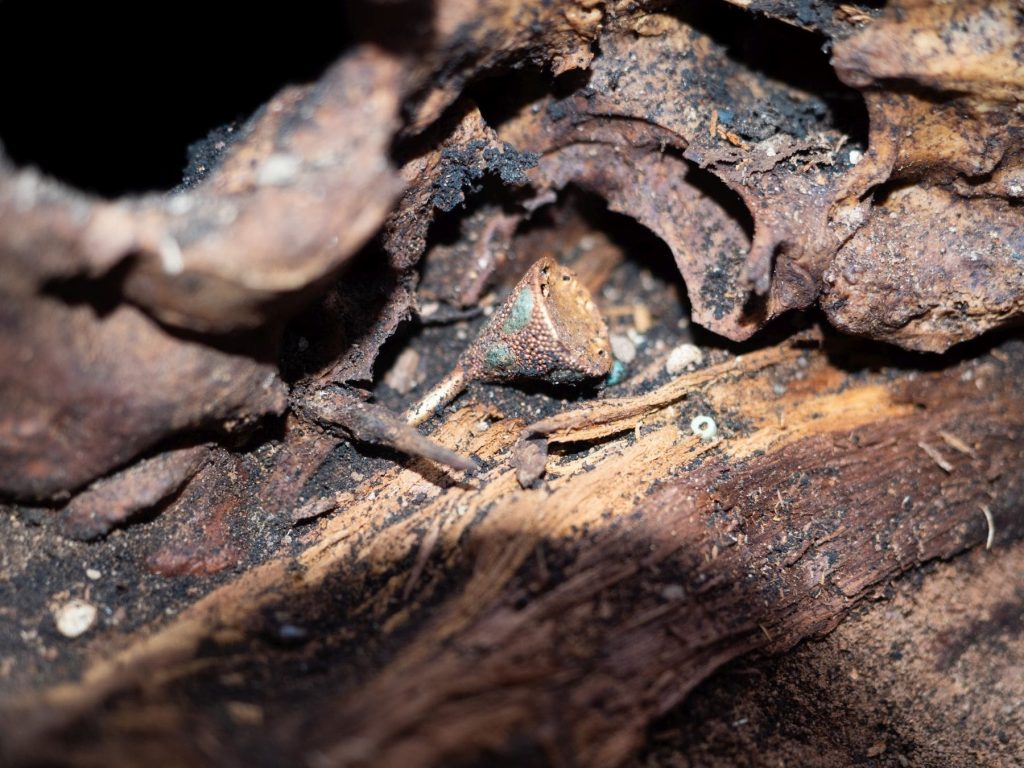

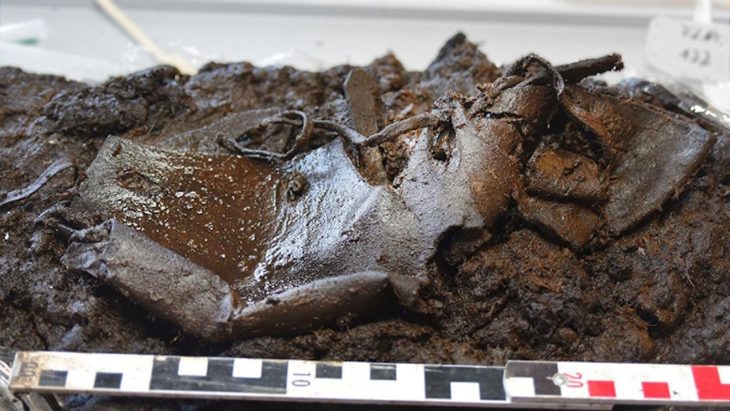
Several organic objects, including an arrow shaft, an ice ax handle, a quiver fragment, and a wooden comb attached to the bronze mirror by a leather loop, have also been recovered.
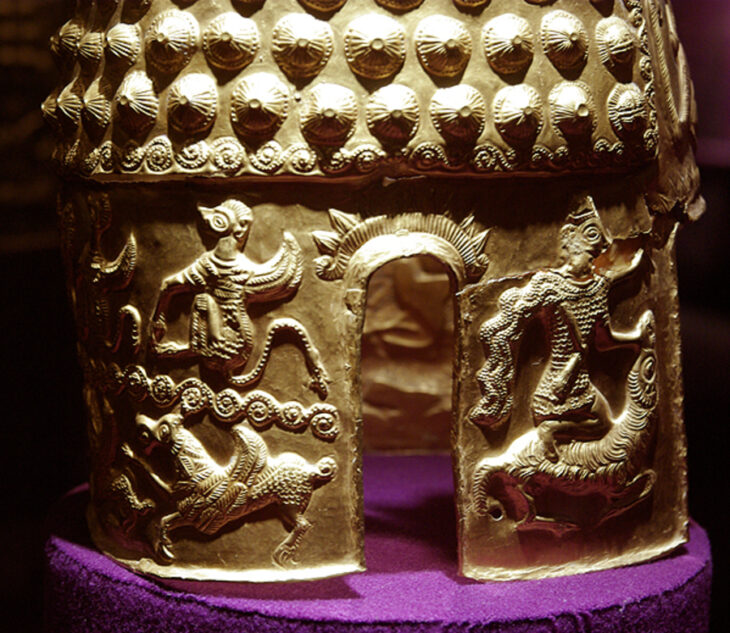
“A particularly interesting monument was the golden pectoral, a crescent or moon-shaped ornament hanging at the neck” – noted in an interview with PAP the head of the Polish part of the expedition, Dr. Łukasz Oleszczak from the Jagiellonian University in Krakow. He emphasized that such objects, known from burial mounds in southern Siberia, have so far been found almost exclusively in men’s graves.
Project leader Dr. Łukasz Oleszczak, “They were considered a symbol of belonging to some social group, caste, perhaps warriors – men at least. Placing him in a woman’s grave is a very interesting departure from this custom. It certainly proves the unique role of the deceased in the community of inhabitants of the Valley of the Kings” — said.
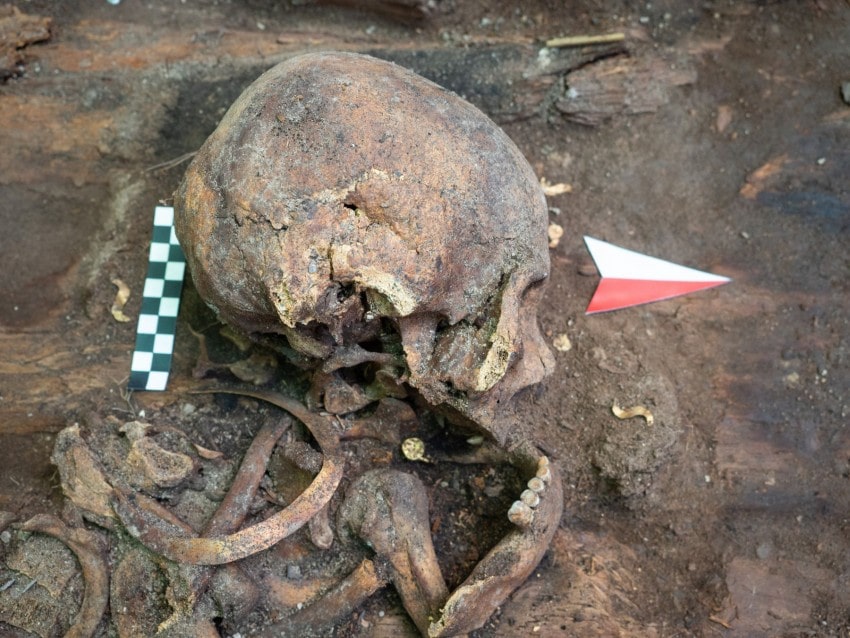

It is worth noting that there is a large mound of nomadic princes nearby. According to archaeologists, the woman probably belonged to his environment, as did other people buried in the mound under study.
According to researchers, the burials date from the 6th century BC and were likely the deceased retinue of a Scythian noble, for which during this period the Urano-Ujukska Valley was one of the most important ritual centers of the entire Scythian-Siberian world.
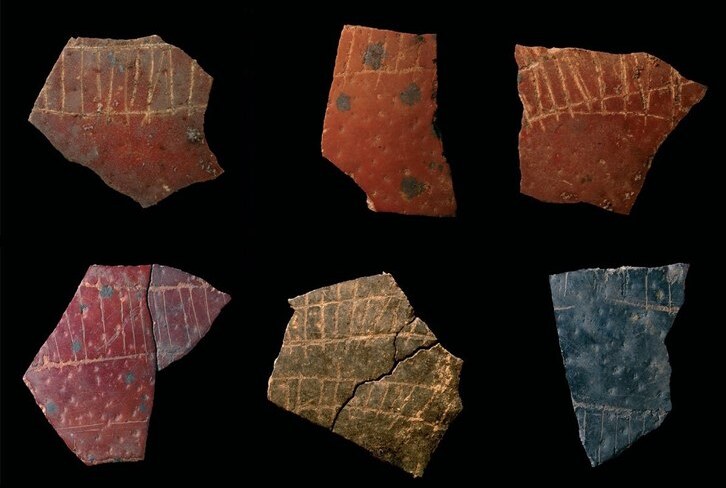
There are traces of even more grave goods, bronze objects buried around the mound. A few pieces have been found — a bronze ice ax, animal-shaped figurines — using a metal detector, but archaeologists believe there were many more than were scattered during agricultural work at the site in the 20th century.